Vaginal yeast infection, also known as vaginal candidiasis, is a common condition that affects many women at some point in their lives. Often referred to by its abbreviation, VYI, this condition can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the available treatments are essential steps toward managing and preventing this issue effectively.
What Is Vaginal Yeast Infection?
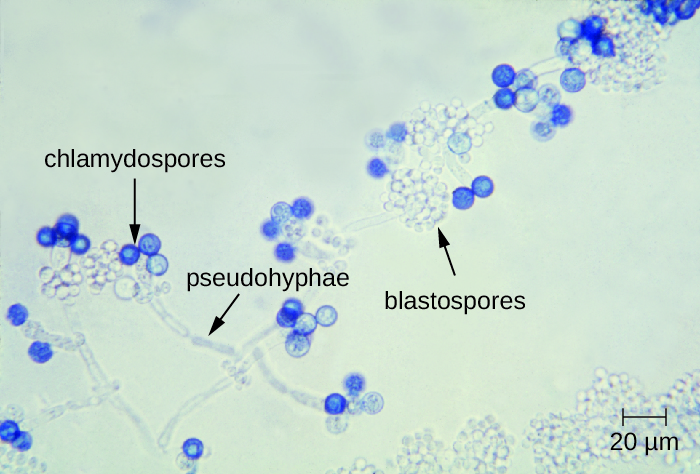
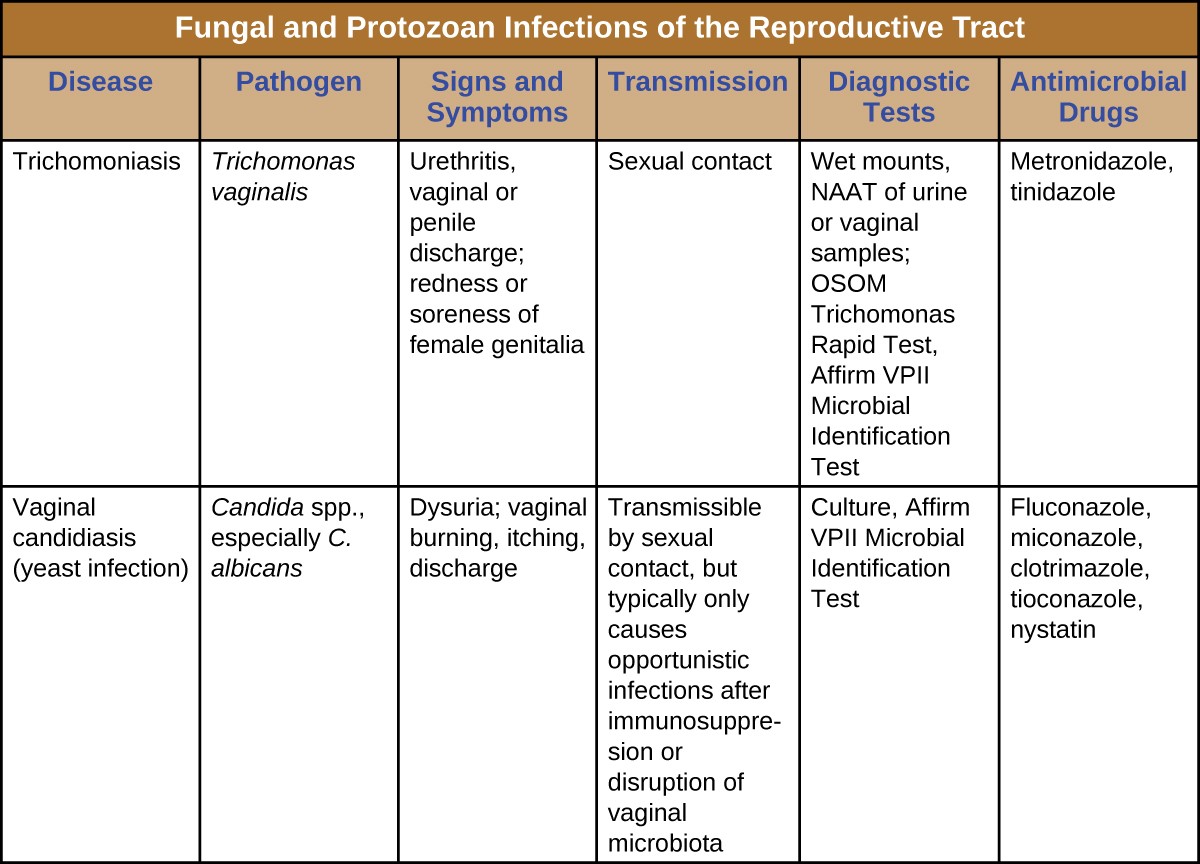
A vaginal yeast infection occurs when there is an overgrowth of a type of fungus called Candida. This fungus naturally exists in small amounts in the vagina, digestive tract, and on the skin without causing any harm. However, under certain conditions, the balance of microorganisms in the body can be disrupted, leading to an overgrowth of Candida and resulting in an infection.
Common Types of Candida
- Candida albicans: This is the most common type of fungus responsible for yeast infections.
- Candida glabrata: A less common but still significant cause of infections.
- Candida tropicalis: Another type that may lead to yeast infections, though it is rarer.
Causes of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Several factors can contribute to the development of a vaginal yeast infection. These include hormonal changes, lifestyle habits, and underlying health conditions.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can create an environment that encourages the growth of Candida. Some common scenarios include:
- Pregnancy: Increased estrogen levels during pregnancy can alter the vaginal environment, making it more susceptible to infection.
- Menstruation: The hormonal shifts that occur during the menstrual cycle can also affect the balance of microorganisms.
- Use of Birth Control Pills: Hormonal contraceptives can sometimes increase the risk of developing a yeast infection.
Weakened Immune System
A compromised immune system can make it harder for the body to control the growth of Candida. Conditions such as diabetes, HIV, or cancer treatments like chemotherapy can weaken immunity and increase susceptibility to yeast infections.
Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics are designed to kill harmful bacteria, but they can also eliminate beneficial bacteria that help keep Candida in check. When these good bacteria are reduced, Candida can multiply unchecked, leading to an infection.
Poor Hygiene Practices
Improper hygiene habits can also contribute to the development of yeast infections. For example:
- Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing can trap moisture and heat, creating an ideal environment for fungal growth.
- Using scented soaps, douches, or feminine hygiene products can irritate the vaginal area and disrupt its natural balance.
Symptoms of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection is crucial for seeking timely treatment. While the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person, there are several common signs to look out for.
Itching and Irritation
One of the hallmark symptoms of a yeast infection is intense itching and irritation in and around the vaginal area. This discomfort can make it difficult to focus on daily activities and may worsen at night.
Abnormal Discharge
A yeast infection often causes a thick, white discharge that resembles cottage cheese. Unlike other types of vaginal infections, this discharge typically does not have a strong odor.
Burning Sensation
Women with a yeast infection may experience a burning sensation, particularly during urination or sexual intercourse. This symptom can add to the overall discomfort caused by the infection.
Redness and Swelling
The vaginal area may appear red and swollen due to inflammation caused by the overgrowth of Candida. In severe cases, small cuts or cracks may develop on the skin.
Treatments for Vaginal Yeast Infection
Fortunately, vaginal yeast infections are treatable, and several options are available depending on the severity of the condition and individual preferences.
Over-the-Counter Antifungal Medications
Mild to moderate yeast infections can often be treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications. These treatments come in various forms, including:
- Creams: Applied directly to the affected area to relieve itching and irritation.
- Suppositories: Inserted into the vagina to target the source of the infection.
- Vaginal Tablets: Similar to suppositories, these dissolve inside the vagina to combat the overgrowth of Candida.
Prescription Medications
For more severe or recurrent infections, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger antifungal medications. These can include oral tablets or extended-duration topical treatments. Common prescription options include:
- Fluconazole: An oral medication taken as a single dose or in multiple doses over several days.
- Itraconazole: Another oral option that may be prescribed for persistent infections.
Natural Remedies
Some women prefer to explore natural remedies to alleviate symptoms and support healing. While these methods may provide relief, they should not replace medical treatment for severe infections. Popular natural remedies include:
- Probiotics: Consuming foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, or taking probiotic supplements can help restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the body.
- Coconut Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, coconut oil can be applied topically to soothe irritation.
- Garlic: Incorporating garlic into the diet or using it as a topical remedy may help combat fungal growth.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent future yeast infections and promote overall vaginal health. Consider the following tips:
- Wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting clothing.
- Avoid using scented products in the vaginal area, including soaps, bubble baths, and sprays.
- Practice good hygiene by washing the genital area with water and mild, unscented soap.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to support immune function.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
While many yeast infections can be managed at home, there are situations where it is important to seek medical advice. Contact a healthcare provider if:
- This is your first yeast infection, as it is important to confirm the diagnosis.
- Symptoms do not improve after using over-the-counter treatments.
- You experience frequent or recurring infections, which may indicate an underlying health issue.
- You have severe symptoms, such as extensive redness, swelling, or open sores.
Preventing Vaginal Yeast Infections
Taking proactive steps to maintain vaginal health can reduce the risk of developing yeast infections. Here are some prevention strategies:
Maintain Proper Hygiene
Good hygiene practices play a key role in preventing infections. Wash the genital area regularly with water and mild soap, and always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to avoid introducing bacteria into the vagina.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals with diabetes, keeping blood sugar levels under control is essential. High blood sugar can encourage the growth of Candida, increasing the likelihood of infection.
Limit Antibiotic Use
Only use antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare provider, and discuss alternative treatments if possible. If antibiotics are necessary, consider taking probiotics to help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria.
Choose Breathable Fabrics
Opt for loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics like cotton. Avoid synthetic materials that trap heat and moisture, creating an environment conducive to fungal growth.