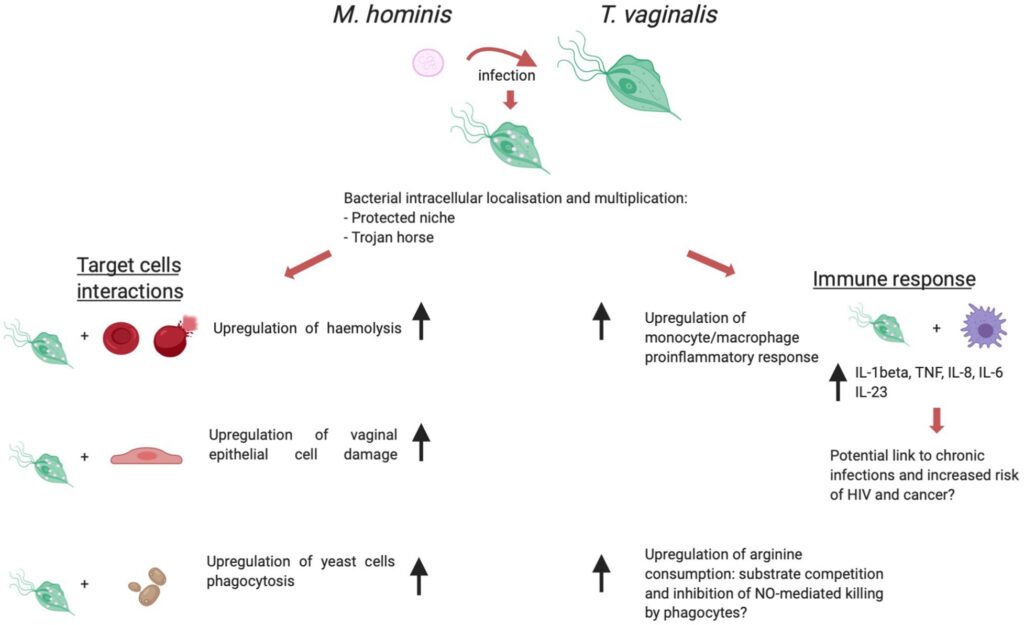
Trichomoniasis, often abbreviated as TV, is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people remain unaware of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Trichomoniasis, covering everything from its origins to its management.
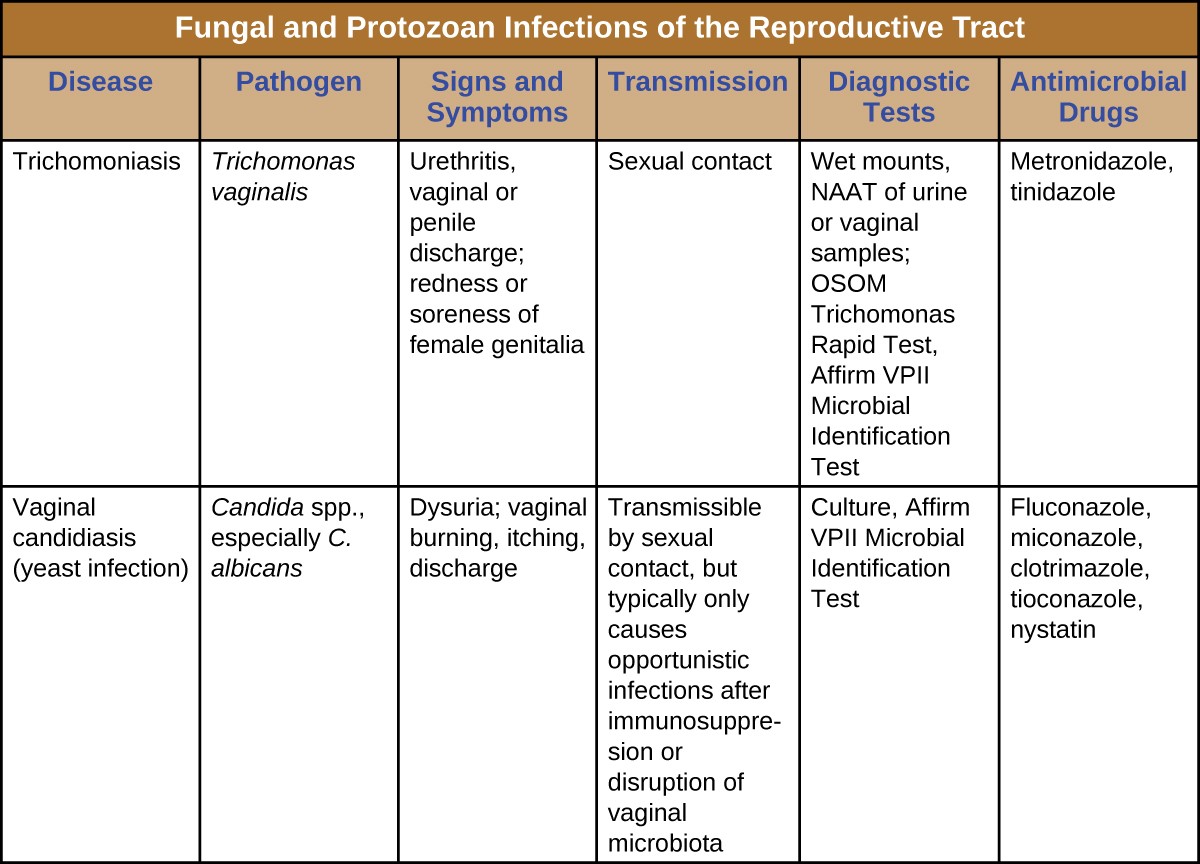
What is Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is an infection caused by a microscopic parasite known as Trichomonas vaginalis. This parasite primarily affects the genital area and is transmitted through sexual contact. It can infect both men and women, though women are more frequently diagnosed with the condition. The infection is highly treatable, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications.
How Does Trichomoniasis Spread?
The parasite responsible for Trichomoniasis thrives in warm, moist environments. It is typically passed between individuals during unprotected sexual activity, including vaginal intercourse. Unlike some other sexually transmitted infections, Trichomoniasis cannot be transmitted through casual contact such as hugging, kissing, or sharing utensils. However, it can spread through shared sex toys if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
- Vaginal intercourse
- Shared sex toys without cleaning
- Unprotected sexual activity
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
One of the challenges of diagnosing Trichomoniasis is that many infected individuals do not experience noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may vary depending on the gender of the individual.
Symptoms in Women
In women, Trichomoniasis often affects the lower genital tract, including the vagina, vulva, and urethra. Common symptoms include:
- Frothy, yellow-green vaginal discharge with a strong odor
- Vaginal itching or irritation
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Swelling or redness around the genital area
It is important to note that these symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions, such as yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis. Therefore, professional medical evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms in Men
Men who contract Trichomoniasis often experience milder symptoms compared to women. In some cases, they may not exhibit any signs of infection. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
- Irritation or itching inside the penis
- Burning sensation after urination or ejaculation
- Thin, white discharge from the penis
Due to the subtlety of symptoms in men, many cases go undiagnosed, increasing the risk of transmission to sexual partners.
Diagnosis of Trichomoniasis
Accurate diagnosis of Trichomoniasis requires specific medical tests. If you suspect you have been exposed to the infection or are experiencing symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Physical Examination
A healthcare professional will begin by conducting a physical examination. For women, this may involve a pelvic exam to check for signs of infection, such as unusual discharge or inflammation. In men, a visual inspection of the genital area may be performed.
Laboratory Tests
To confirm the presence of the parasite, laboratory tests are necessary. These may include:
- Microscopic Examination: A sample of vaginal or penile discharge is examined under a microscope to identify the parasite.
- Culture Test: A culture test involves growing the parasite in a lab setting to confirm its presence. This method is highly accurate but may take several days to yield results.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT): This advanced test detects the genetic material of the parasite and is considered one of the most reliable diagnostic tools available.
Early diagnosis is critical to prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Treatment Options for Trichomoniasis
Fortunately, Trichomoniasis is a curable condition. With appropriate treatment, most individuals can eliminate the infection and avoid long-term health issues.
Medications
The primary treatment for Trichomoniasis involves the use of prescription medications. The most commonly prescribed drug is metronidazole, which is available in oral form. In some cases, tinidazole may also be used as an alternative. Both medications work by targeting and killing the parasite responsible for the infection.
- Metronidazole: Typically taken as a single dose or divided into smaller doses over several days.
- Tinidazole: Similar to metronidazole but may be preferred in certain situations.
It is important to complete the full course of medication, even if symptoms improve before the treatment is finished. Failure to do so can result in the persistence of the infection.
Precautions During Treatment
While undergoing treatment, individuals should abstain from alcohol consumption. Both metronidazole and tinidazole can cause severe reactions when combined with alcohol, including nausea, vomiting, and headaches. Additionally, sexual activity should be avoided until both partners have completed treatment and are confirmed to be free of the infection.
Treating Sexual Partners
To prevent reinfection, it is essential for sexual partners to be treated simultaneously. Even if a partner does not exhibit symptoms, they may still carry the parasite and contribute to the spread of the infection. Open communication and mutual cooperation are key to successful treatment outcomes.
Complications of Untreated Trichomoniasis
If left untreated, Trichomoniasis can lead to a range of complications, particularly in women. These complications may include:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: An infection of the reproductive organs that can cause chronic pain and infertility.
- Pregnancy Complications: Pregnant women with Trichomoniasis are at higher risk of preterm delivery and low birth weight in newborns.
- Increased Risk of Other Infections: Trichomoniasis can make individuals more susceptible to other sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
For men, untreated Trichomoniasis is less likely to cause severe complications but can still lead to discomfort and potential transmission to partners.
Preventing Trichomoniasis
Prevention is always better than cure. By adopting safe sexual practices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting Trichomoniasis.
Safe Sexual Practices
Practicing safe sex is one of the most effective ways to prevent Trichomoniasis. This includes:
- Using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual activity
- Limiting the number of sexual partners
- Getting regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about Trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted infections is crucial for prevention. Educational programs and open discussions can help dispel myths and encourage individuals to seek medical advice when needed.
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good personal hygiene is another important aspect of prevention. This includes cleaning sex toys thoroughly before and after use and avoiding sharing items that come into contact with genital areas.
Final Thoughts
Trichomoniasis is a common yet often overlooked sexually transmitted infection. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking timely medical care are essential steps in managing the condition effectively. By prioritizing safe sexual practices and staying informed, individuals can protect themselves and their partners from the risks associated with Trichomoniasis.