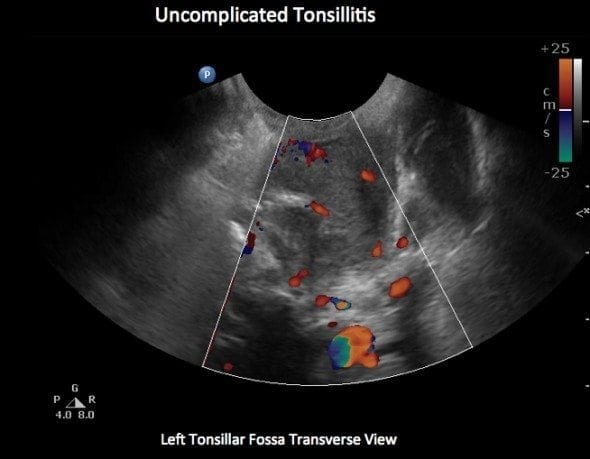
Tonsillitis, often abbreviated as “tonsil inflammation,” is a common condition that affects people of all ages but is most prevalent in children and young adults. The inflammation of the tonsils can lead to discomfort, pain, and other complications if not addressed properly. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and exploring treatment options are essential steps in managing this condition effectively.
What Are the Tonsils?
The tonsils are two small, oval-shaped masses of tissue located at the back of the throat, one on each side. They are part of the immune system and act as the body’s first line of defense against infections entering through the mouth or nose. Despite their protective role, the tonsils themselves can become infected or inflamed, leading to a condition known as tonsillitis.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis occurs when the tonsils become infected or inflamed. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
Viral Infections
- Common Cold Viruses: Many cases of tonsillitis are caused by viruses responsible for the common cold.
- Influenza: The flu virus can also lead to inflammation of the tonsils.
- Epstein-Barr Virus: This virus is responsible for infectious mononucleosis, which often causes severe tonsillitis.
- Adenovirus: Known for causing respiratory infections, adenovirus can also affect the tonsils.
Bacterial Infections
- Streptococcus Pyogenes: This bacterium is the most common cause of bacterial tonsillitis, often referred to as strep throat.
- Other Bacteria: While less common, other types of bacteria can also infect the tonsils.
Risk Factors
- Frequent exposure to germs, especially in schools or crowded environments.
- Young age, as children and teenagers have more active tonsils.
- Weakened immune system due to illness or poor nutrition.
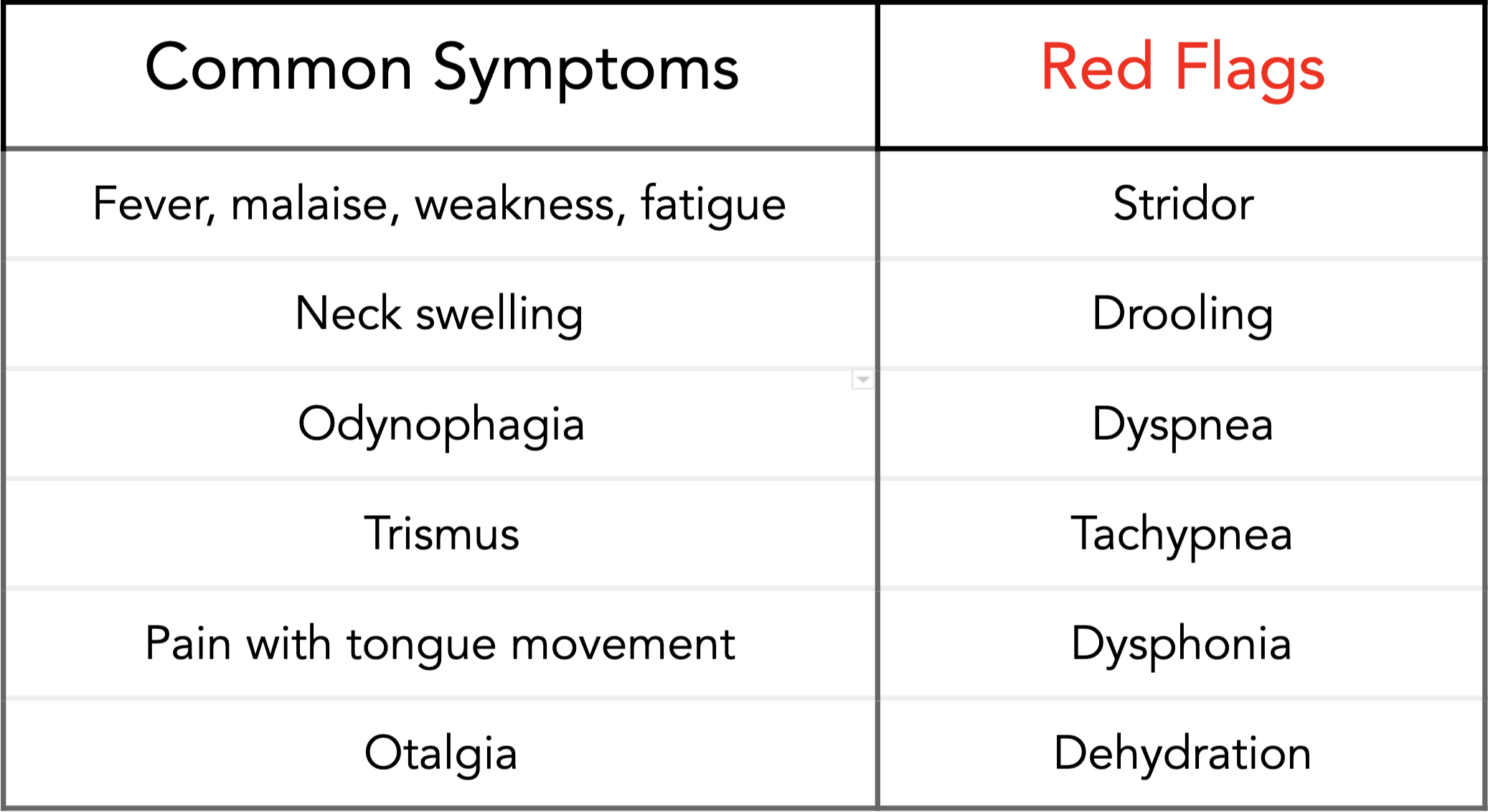
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can present with a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking timely medical attention.
Common Symptoms
- Sore throat that may worsen when swallowing.
- Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white or yellow patches.
- Hoarse or muffled voice.
- Fever and chills.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
- Bad breath.
- Difficulty swallowing or opening the mouth wide.
- Headache and fatigue.
Symptoms in Children
In younger children, tonsillitis may present slightly differently:
- Drooling due to difficulty swallowing.
- Refusal to eat or drink.
- Irritability and fussiness.
- Unusual sleep patterns or snoring.
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
A proper diagnosis is crucial to determine whether tonsillitis is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, as this will influence the treatment approach.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will typically begin with a physical examination. This involves:
- Inspecting the throat for redness, swelling, or patches on the tonsils.
- Checking for swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
- Assessing the patient’s overall condition, including fever and other symptoms.
Throat Swab Test
To confirm a bacterial infection, a throat swab test may be performed. During this test:
- A cotton swab is used to collect a sample from the back of the throat.
- The sample is then tested for the presence of specific bacteria, such as Streptococcus Pyogenes.
Blood Tests
In some cases, blood tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions or to confirm the presence of a viral infection like infectious mononucleosis.
Treatment Options for Tonsillitis
The treatment for tonsillitis depends on its underlying cause and severity. Both home remedies and medical interventions can be effective in managing the condition.
Treatment for Viral Tonsillitis
Since viral tonsillitis cannot be treated with antibiotics, the focus is on alleviating symptoms:
- Rest: Adequate rest helps the body fight off the infection.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids prevents dehydration and soothes the throat.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can reduce pain and fever.
- Warm Saltwater Gargle: Gargling with warm salt water can reduce throat irritation.
- Humidifier: Using a humidifier adds moisture to the air, easing throat discomfort.
Treatment for Bacterial Tonsillitis
If tonsillitis is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are usually prescribed:
- Antibiotics: A course of antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, is typically prescribed to treat bacterial infections.
- Completing the Course: It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to prevent recurrence or complications.
Surgical Intervention
In cases of recurrent tonsillitis or complications, surgery may be recommended:
- Tonsillectomy: This surgical procedure involves the removal of the tonsils and is considered when tonsillitis occurs frequently or does not respond to other treatments.
- Adenoidectomy: If the adenoids are also affected, they may be removed during the same procedure.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals explore alternative therapies to complement traditional treatments:
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, such as echinacea or licorice root, are believed to boost the immune system.
- Honey and Lemon: A mixture of honey and lemon in warm water can provide soothing relief for a sore throat.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam can help reduce nasal congestion and throat irritation.
Preventing Tonsillitis
While it may not always be possible to prevent tonsillitis, certain measures can reduce the risk of infection:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing.
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick.
- Boosting the immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep.
- Keeping shared items, such as utensils and towels, clean and separate.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of tonsillitis resolve on their own or with simple treatments, certain signs indicate the need for immediate medical attention:
- Severe difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- High fever that does not respond to medication.
- Signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth or reduced urination.
- Persistent symptoms lasting more than a few days without improvement.
Complications of Untreated Tonsillitis
If left untreated, tonsillitis can lead to complications, including:
- Spread of infection to surrounding areas, such as the ears or sinuses.
- Formation of abscesses around the tonsils.
- Chronic or recurrent tonsillitis.
- Rarely, rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation in cases of untreated strep throat.
Living with Recurrent Tonsillitis
For individuals who experience frequent episodes of tonsillitis, lifestyle adjustments and medical management are key:
- Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor the condition.
- Considering long-term preventive measures, such as immunizations or dietary changes.
- Exploring surgical options if the condition significantly impacts quality of life.