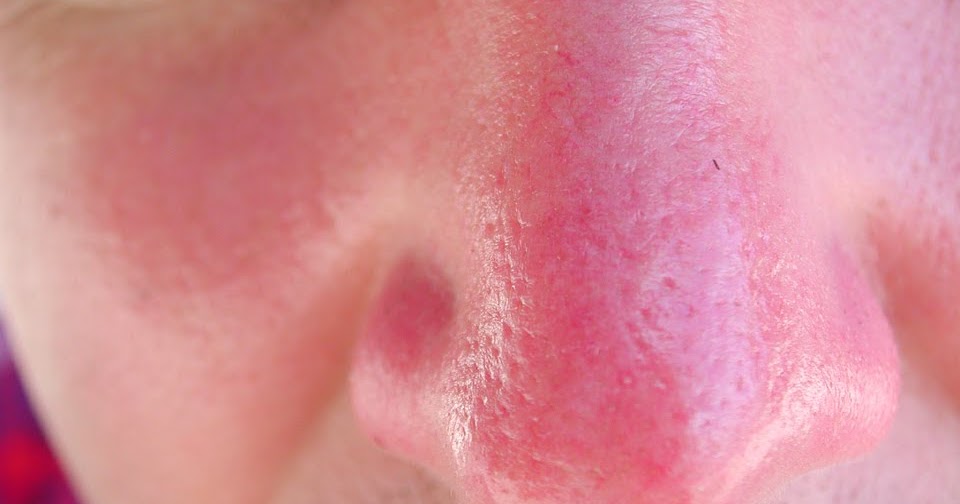
Sunburn is a common condition caused by overexposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. It can affect people of all ages and skin types, leading to discomfort and potential long-term health risks. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and learning how to prevent and treat sunburn are essential for maintaining healthy skin. This article will explore these aspects in detail to help you stay informed and protected.
What Causes Sunburn?
Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive amounts of ultraviolet radiation, primarily from the sun but also from artificial sources like tanning beds. The ultraviolet rays penetrate the outer layers of the skin, causing damage to the cells and blood vessels. This triggers an inflammatory response, which results in the characteristic redness, warmth, and pain associated with sunburn.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Sunburn
- Fair Skin: People with lighter skin tones have less melanin, the pigment that provides some natural protection against ultraviolet radiation.
- High Altitude: At higher altitudes, the atmosphere is thinner, allowing more ultraviolet rays to reach the skin.
- Proximity to the Equator: Regions closer to the equator receive stronger and more direct sunlight throughout the year.
- Time of Day: Ultraviolet radiation is strongest between ten in the morning and four in the afternoon.
- Reflective Surfaces: Water, sand, snow, and concrete can reflect ultraviolet rays, increasing exposure.
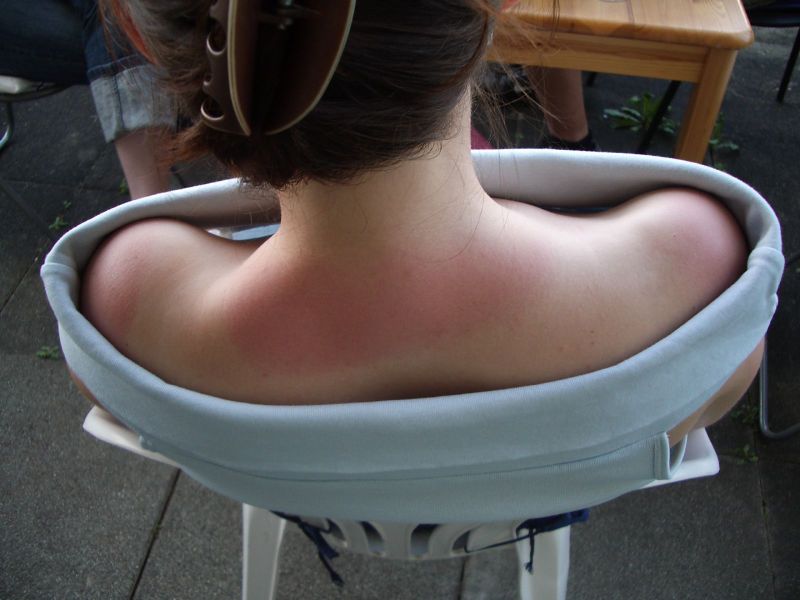
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sunburn
The symptoms of sunburn can vary depending on the severity of the exposure. Mild cases may only cause temporary discomfort, while severe cases can lead to blistering and systemic effects.
Common Symptoms of Sunburn
- Redness: The skin turns red due to increased blood flow as the body attempts to repair the damaged tissue.
- Pain and Tenderness: Affected areas often feel warm to the touch and may be painful or tender.
- Swelling: Inflammation can cause the skin to swell, especially in more severe cases.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled blisters may form on the skin, indicating a second-degree burn.
- Peeling: As the skin heals, the damaged outer layer may peel away to reveal new skin underneath.
Systemic Symptoms in Severe Cases
In extreme cases, sunburn can lead to symptoms that affect the entire body. These include fever, chills, headache, nausea, and dehydration. If these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
How to Prevent Sunburn
Preventing sunburn is far easier and more effective than treating it after it occurs. By adopting simple protective measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of sunburn and its associated complications.
Use Sunscreen Properly
Sunscreen is one of the most effective tools for preventing sunburn. When choosing a sunscreen, look for products that offer broad-spectrum protection, meaning they shield against both UVA and UVB rays. The sunscreen should have a sun protection factor of at least thirty. Apply it generously to all exposed skin at least fifteen minutes before going outside, and reapply every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing provides a physical barrier between your skin and the sun’s rays. Opt for tightly woven fabrics that cover as much skin as possible. Wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses with UV protection can also help shield sensitive areas like the face, neck, and eyes.
Seek Shade During Peak Hours
One of the simplest ways to avoid sunburn is to limit direct exposure during peak sunlight hours. Stay indoors or seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or other structures when the sun is at its strongest.
Be Mindful of Reflective Surfaces
Reflective surfaces can intensify ultraviolet exposure, so take extra precautions when near water, sand, or snow. Wearing sunscreen and protective clothing is especially important in these environments.
Avoid Tanning Beds
Tanning beds emit ultraviolet radiation similar to that of the sun and can cause sunburn and long-term skin damage. Avoid using tanning beds altogether to protect your skin.
Treating Sunburn Effectively
If you do get sunburned, prompt treatment can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing. While mild cases can usually be managed at home, severe sunburn may require medical attention.
Immediate Steps to Take
As soon as you notice signs of sunburn, take the following steps to minimize damage and relieve symptoms:
- Get Out of the Sun: Move to a shaded or indoor area to prevent further exposure.
- Cool the Skin: Take a cool bath or shower to soothe the skin. Avoid using harsh soaps, as they can irritate the skin further.
- Apply Moisturizer: After bathing, apply a gentle moisturizer to help hydrate the skin. Products containing aloe vera or soy can provide additional relief.
- Stay Hydrated: Sunburn can cause fluid loss, so drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
To manage pain and discomfort, consider the following options:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or aspirin can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Cold Compresses: Apply a cold, damp cloth to the affected areas to ease burning sensations.
- Avoid Popping Blisters: If blisters form, resist the urge to pop them, as this can increase the risk of infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of sunburn can be treated at home, certain situations warrant professional medical care. Seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Severe blistering over a large area of the body
- Fever, chills, or confusion
- Signs of infection, such as pus or red streaks around blisters
- Dizziness or fainting
Long-Term Effects of Sunburn
Repeated or severe sunburns can have lasting consequences for your skin and overall health. Understanding these risks can motivate you to take sun protection more seriously.
Premature Aging
Chronic exposure to ultraviolet radiation accelerates the aging process of the skin. This can lead to wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, and a leathery texture. Protecting your skin from the sun is one of the best ways to maintain a youthful appearance.
Increase in Skin Cancer Risk
Sunburn damages the DNA in skin cells, increasing the risk of developing skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma are all linked to excessive sun exposure. Early detection and prevention are key to reducing this risk.
Weakened Immune System
Ultraviolet radiation can suppress the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and diseases. This is another reason why protecting your skin from the sun is crucial for overall health.
Special Considerations for Children and Infants
Children and infants are particularly vulnerable to sunburn due to their delicate skin and lower levels of melanin. Extra care should be taken to protect them from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Sun Protection for Young Children
For children over six months, use sunscreen specifically formulated for kids and ensure they wear protective clothing and hats. Encourage them to play in shaded areas during peak sunlight hours.
Infant Sun Safety
Infants under six months should be kept out of direct sunlight as much as possible. Dress them in lightweight, long-sleeved clothing and use a stroller with a canopy or umbrella for shade.