Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, commonly abbreviated as SJS, is a rare but serious medical condition that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is considered a medical emergency due to its potential to cause severe complications and even death if not treated promptly. This article provides a comprehensive overview of this condition, including its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.

What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is a severe disorder that causes the skin and mucous membranes to react adversely. The condition often begins with flu-like symptoms and progresses to a painful rash that spreads and blisters. Eventually, the top layer of the affected skin dies, sheds, and begins to heal. This condition is closely related to another more severe form called toxic epidermal necrolysis, which involves more extensive skin damage.
How Common is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Although it is classified as a rare disease, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome can occur in individuals of all ages and backgrounds. Certain populations, such as those with weakened immune systems or specific genetic predispositions, are at a higher risk of developing this condition. Early recognition and intervention are critical to improving outcomes for affected individuals.
Causes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
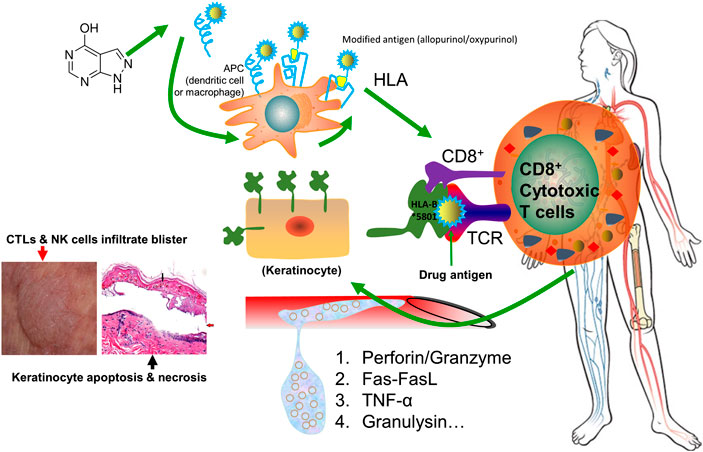
The exact cause of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is often linked to an abnormal immune system reaction triggered by certain medications, infections, or other factors. Understanding these triggers is essential for prevention and early diagnosis.
Medications That May Trigger Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Several medications have been identified as potential triggers for this condition. Some of the most common include:
- Antibiotics, particularly sulfonamides and penicillins
- Anticonvulsants, such as phenytoin and carbamazepine
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Allopurinol, used to treat gout
It is important to note that not everyone who takes these medications will develop the condition. However, individuals with a history of adverse drug reactions should exercise caution and consult their healthcare provider before starting new medications.
Infections Associated With Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Certain infections have also been linked to the development of this condition. These include:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Pneumonia
- HIV/AIDS
- Herpes simplex virus
Infections may weaken the immune system or trigger an abnormal response, leading to the onset of symptoms associated with this condition.
Other Potential Triggers
Besides medications and infections, other factors may contribute to the development of this condition. These include:
- Vaccinations
- Radiation therapy
- Exposure to certain chemicals
While these triggers are less common, they highlight the importance of understanding individual risk factors and seeking medical advice when unusual symptoms arise.
Symptoms of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
The symptoms of this condition typically appear in stages, beginning with nonspecific signs that may resemble a common viral illness. As the condition progresses, more severe symptoms emerge, requiring immediate medical attention.
Early Symptoms
In the initial phase, individuals may experience:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Burning eyes
These early symptoms can easily be mistaken for a mild infection or flu, making early diagnosis challenging. However, recognizing these signs and seeking prompt medical evaluation is crucial.
Progression of Symptoms
As the condition advances, more severe symptoms develop, including:
- A red or purple rash that spreads across the body
- Blisters on the skin and mucous membranes
- Painful peeling of the skin
- Swelling of the face and tongue
The rash often starts on the face and chest before spreading to other areas. Blisters may form on the lips, mouth, eyes, and genital regions, causing significant discomfort and increasing the risk of infection.
Complications of Severe Symptoms
If left untreated, the condition can lead to life-threatening complications, such as:
- Secondary infections due to exposed skin
- Dehydration from fluid loss
- Respiratory failure
- Permanent damage to the eyes and vision
These complications underscore the importance of seeking immediate medical care if any of the above symptoms are observed.
Treatment Options for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Timely and appropriate treatment is essential for managing this condition and minimizing the risk of complications. The treatment approach typically involves hospitalization and a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
Immediate Medical Care
Individuals suspected of having this condition should be admitted to a hospital, preferably one with a burn unit or specialized dermatology department. Immediate steps include:
- Discontinuation of any suspected triggering medications
- Fluid replacement to prevent dehydration
- Pain management to alleviate discomfort
Stopping the offending medication is a critical first step, as continued exposure can worsen the condition.
Wound Care and Skin Management
Proper wound care is essential to prevent infections and promote healing. This may involve:
- Gentle removal of dead skin
- Dressing wounds with non-adhesive bandages
- Application of topical medications to reduce inflammation
Healthcare providers may use specialized techniques to protect the skin and minimize scarring during the healing process.
Medications Used in Treatment
Depending on the severity of the condition, medications may be prescribed to address specific symptoms and complications. These include:
- Antibiotics to treat or prevent infections
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy to modulate the immune response
Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s needs and may require adjustments based on their response to therapy.
Supportive Therapies
In addition to medical interventions, supportive therapies play a vital role in recovery. These may include:
- Nutritional support to ensure adequate nourishment
- Eye care to prevent long-term vision problems
- Psychological support to address emotional challenges
A holistic approach to treatment helps address both the physical and emotional aspects of recovery.
Prevention of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
While it may not always be possible to prevent this condition, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing it. These include:
- Informing healthcare providers about any history of adverse drug reactions
- Avoiding medications known to trigger the condition
- Monitoring for early symptoms when starting new treatments
Education and awareness are key to preventing this condition and ensuring timely intervention when necessary.