Sheehan’s Syndrome, also known as postpartum pituitary necrosis, is a rare but serious condition that occurs when the pituitary gland is damaged due to severe blood loss or extremely low blood pressure during or after childbirth. This condition can lead to a variety of hormonal imbalances and health complications. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Sheehan’s Syndrome.
What is Sheehan’s Syndrome?
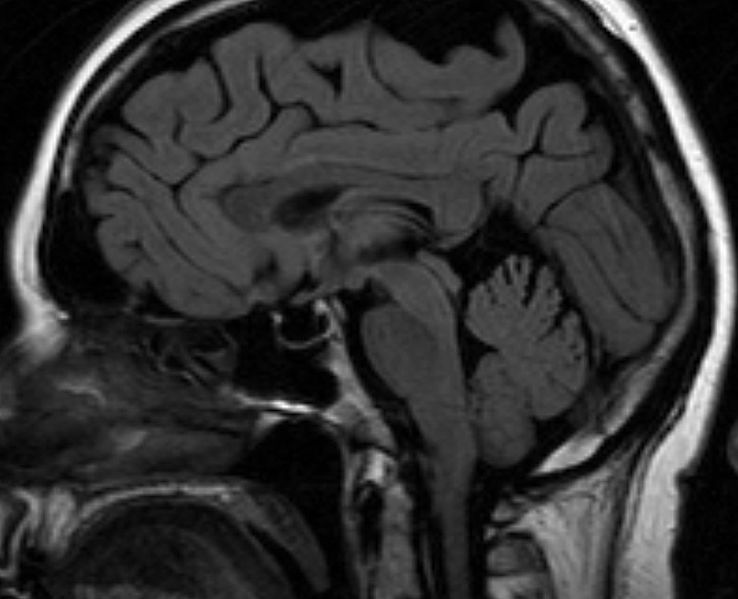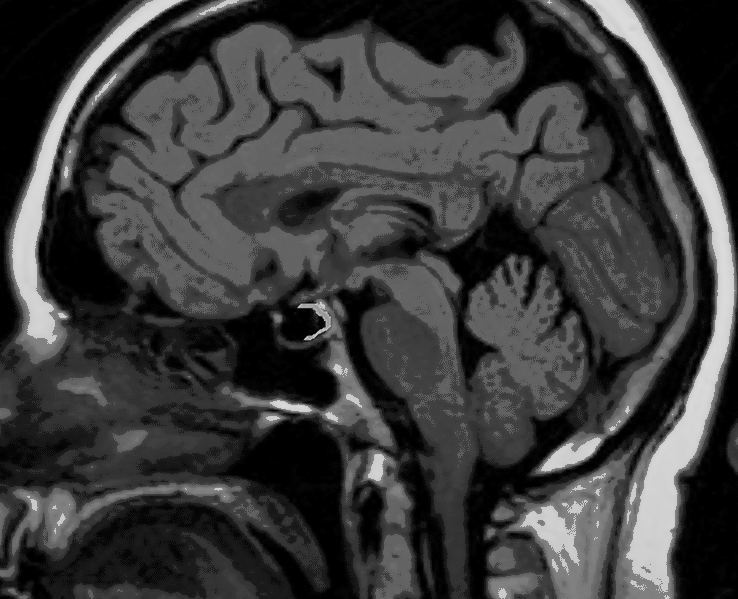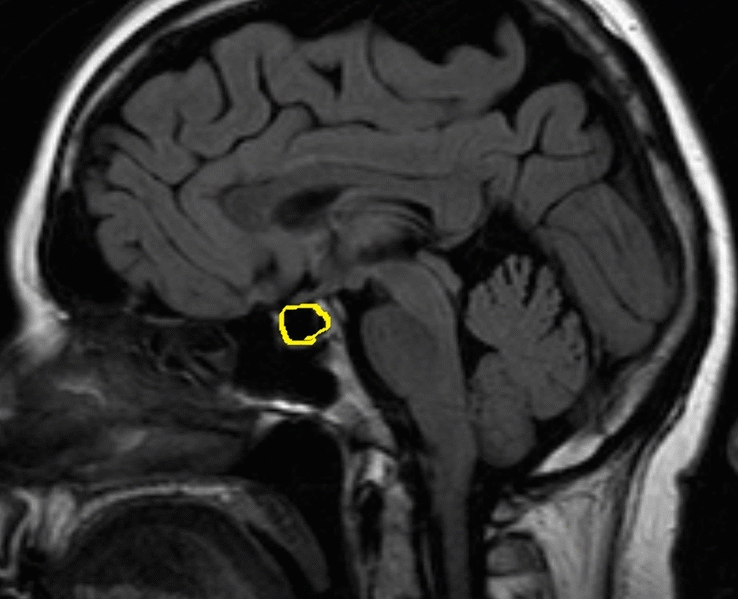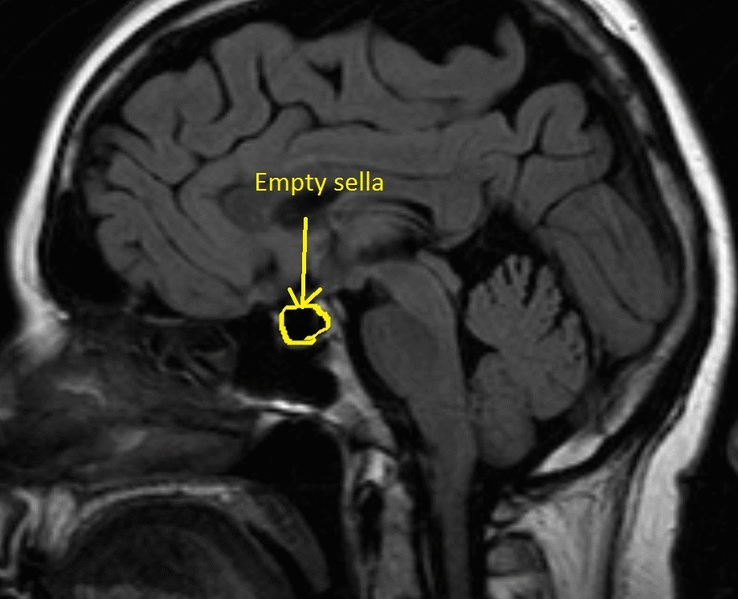
Sheehan’s Syndrome occurs when the pituitary gland, a small organ located at the base of the brain, is damaged. The pituitary gland plays a crucial role in regulating various hormones in the body. When it is damaged, it can no longer produce adequate amounts of these hormones, leading to a range of health issues.
Causes of Sheehan’s Syndrome
The primary cause of Sheehan’s Syndrome is severe blood loss or shock during or after childbirth. This can result in insufficient blood supply to the pituitary gland, causing tissue death or necrosis. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
- Excessive bleeding during delivery
- Placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterus prematurely
- Uterine rupture, which can cause significant internal bleeding
- Inadequate medical care during childbirth
Risk Factors
While Sheehan’s Syndrome is rare, certain factors can increase the risk of developing this condition:
- Multiple pregnancies, which can increase the likelihood of complications during delivery
- Prolonged labor, which may lead to excessive blood loss
- Pre-existing conditions such as anemia or clotting disorders
Symptoms of Sheehan’s Syndrome
The symptoms of Sheehan’s Syndrome can vary depending on the extent of the damage to the pituitary gland. Some women may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe manifestations. Common symptoms include:
- Inability to produce breast milk after childbirth
- Irregular or absent menstrual periods
- Fatigue and weakness
- Low blood pressure
- Weight loss or difficulty gaining weight
- Decreased libido
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
Delayed Symptoms
In some cases, symptoms may not appear immediately after childbirth. Women may experience a gradual onset of symptoms over months or even years. This delayed presentation can make diagnosis challenging.
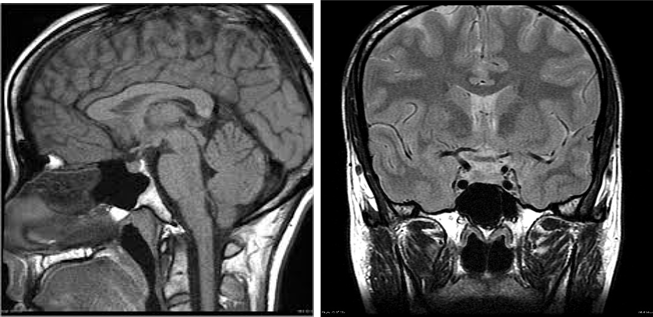
Diagnosing Sheehan’s Syndrome
Diagnosing Sheehan’s Syndrome requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. Since the symptoms can mimic other conditions, a detailed medical history and physical examination are essential. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone, cortisol, and prolactin
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI to assess the size and structure of the pituitary gland
- Stimulation tests to evaluate the pituitary gland’s ability to produce hormones in response to specific stimuli
Challenges in Diagnosis
One of the challenges in diagnosing Sheehan’s Syndrome is that the symptoms often develop gradually and can be attributed to other causes, such as stress or fatigue. Additionally, many women may not connect their symptoms to childbirth, especially if they occur months or years later.
Treatment Options for Sheehan’s Syndrome
Treatment for Sheehan’s Syndrome focuses on hormone replacement therapy to compensate for the hormones that the pituitary gland can no longer produce. The specific treatment plan will depend on the hormones that are deficient. Common treatments include:
- Corticosteroids to replace cortisol, which helps regulate metabolism and immune response
- Thyroid hormone replacement to address low levels of thyroid hormones
- Estrogen and progesterone therapy for women who are not producing adequate levels of these hormones
- Growth hormone therapy in some cases to address growth-related issues
Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to hormone replacement therapy, individuals with Sheehan’s Syndrome may need to make lifestyle adjustments to manage their condition effectively. These adjustments can include:
- Regular follow-up appointments with an endocrinologist to monitor hormone levels
- A balanced diet to support overall health and well-being
- Exercise to maintain muscle mass and bone density
- Stress management techniques to reduce the impact of stress on the body
Living with Sheehan’s Syndrome
Living with Sheehan’s Syndrome requires ongoing management and attention to one’s health. While the condition cannot be cured, proper treatment can help individuals lead fulfilling lives. It is important for those affected to stay informed about their condition and work closely with healthcare providers to optimize their treatment plan.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Dealing with a chronic condition like Sheehan’s Syndrome can take an emotional toll. Many women may feel frustrated or overwhelmed by the changes in their bodies and the need for lifelong treatment. Seeking support from mental health professionals, support groups, or loved ones can be beneficial in coping with these challenges.
Pregnancy and Sheehan’s Syndrome
Women with Sheehan’s Syndrome who wish to become pregnant again should consult with their healthcare provider. Pregnancy can pose additional risks for individuals with this condition, and careful planning and monitoring are essential to ensure a safe pregnancy and delivery.
Preventing Sheehan’s Syndrome
While not all cases of Sheehan’s Syndrome can be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Access to quality prenatal care to identify and manage potential complications early
- Proper management of labor and delivery to minimize blood loss
- Timely medical intervention in cases of excessive bleeding or shock
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about Sheehan’s Syndrome among healthcare providers and the general public is crucial. Early recognition of symptoms and prompt medical intervention can improve outcomes for women affected by this condition.
Research and Advances in Treatment
Ongoing research into Sheehan’s Syndrome and related conditions continues to advance our understanding of the pituitary gland and its functions. Scientists are exploring new treatment options and therapies to improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Emerging Therapies
Recent advancements in hormone replacement therapy and regenerative medicine hold promise for more effective treatments in the future. Researchers are also investigating the potential of stem cell therapy to repair or regenerate damaged pituitary tissue.