Serotonin syndrome, also known as serotonin toxicity, is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when there is an excessive accumulation of serotonin in the body. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, digestion, and other bodily functions. While serotonin is essential for normal brain and body function, too much of it can lead to serious complications. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of this condition.

What is Serotonin?
Serotonin is a chemical produced by nerve cells in the brain and the gastrointestinal tract. It helps transmit signals between nerve cells and contributes to various physiological processes. Serotonin influences mood regulation, appetite, sleep cycles, and even muscle function. The balance of serotonin in the body is tightly regulated, and disruptions to this balance can lead to adverse effects.
Causes of Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome typically occurs when there is an overactivation of serotonin receptors due to an excess of serotonin in the central nervous system. This can happen for several reasons:
Medications That Increase Serotonin Levels
- Antidepressants: Certain types of antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, are commonly associated with serotonin syndrome. These medications work by increasing the availability of serotonin in the brain.
- Migraine Medications: Triptans, which are used to treat migraines, can also increase serotonin levels and may contribute to the development of serotonin syndrome when combined with other serotonergic drugs.
- Opioid Pain Relievers: Some opioid medications, such as fentanyl and tramadol, have serotonergic properties and can elevate serotonin levels.
- Herbal Supplements: Herbal supplements like St. John’s Wort and certain weight-loss supplements containing serotonin-boosting ingredients can also pose a risk.
Drug Interactions
One of the most common causes of serotonin syndrome is the interaction between multiple medications that affect serotonin levels. For example, combining antidepressants with migraine medications or opioids can significantly increase the risk of developing this condition.
Overdose of Serotonergic Substances
Taking excessive doses of medications or supplements that increase serotonin levels can overwhelm the body’s ability to regulate serotonin, leading to serotonin syndrome.
Symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome
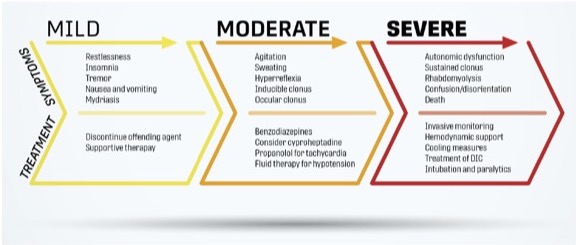
The symptoms of serotonin syndrome can range from mild to severe and often develop rapidly after starting a new medication, increasing the dosage of an existing medication, or combining serotonergic substances. Symptoms are typically categorized into three groups: cognitive, autonomic, and neuromuscular.
Cognitive Symptoms
- Confusion
- Agitation
- Restlessness
- Disorientation
Autonomic Symptoms
- Rapid heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Fever
- Excessive sweating
- Flushing of the skin
Neuromuscular Symptoms
- Muscle rigidity
- Tremors
- Clonus (involuntary muscle spasms)
- Poor coordination
In severe cases, serotonin syndrome can lead to life-threatening complications such as seizures, kidney failure, respiratory distress, and even death if left untreated.
Diagnosis of Serotonin Syndrome
Diagnosing serotonin syndrome can be challenging because its symptoms overlap with those of other medical conditions. There is no specific laboratory test to confirm serotonin syndrome, so healthcare providers rely on clinical evaluation and patient history to make a diagnosis.
Key Diagnostic Criteria
Healthcare providers often use a set of criteria known as the Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria to diagnose serotonin syndrome. These criteria include:
- Recent use of serotonergic medications
- Presence of specific symptoms such as clonus, agitation, and fever
- Exclusion of other conditions that could mimic serotonin syndrome, such as infections or neurological disorders
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is essential for diagnosing serotonin syndrome. During the exam, healthcare providers look for signs such as hyperreflexia (overactive reflexes), muscle rigidity, and changes in mental status.
Laboratory Tests
While there is no specific test for serotonin syndrome, certain laboratory tests may be performed to rule out other conditions and assess the severity of the syndrome. These tests may include:
- Blood tests to check electrolyte levels and kidney function
- Urinalysis to detect any underlying infections
- Electrocardiogram to monitor heart function
Treatment of Serotonin Syndrome
The treatment of serotonin syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases, discontinuing the offending medication may be sufficient. However, more severe cases require immediate medical intervention to prevent complications.
Discontinuation of Serotonergic Medications
The first step in treating serotonin syndrome is to stop taking any medications or supplements that increase serotonin levels. This should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider to avoid withdrawal symptoms or other complications.
Supportive Care
For mild cases, supportive care is often sufficient. This may include:
- Hydration through intravenous fluids
- Monitoring vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature
- Use of benzodiazepines to reduce agitation and muscle rigidity
Medications to Block Serotonin
In moderate to severe cases, medications may be administered to block the effects of serotonin. One such medication is cyproheptadine, an antihistamine that also has serotonin-blocking properties. This medication can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Hospitalization for Severe Cases
Severe cases of serotonin syndrome require hospitalization for close monitoring and intensive treatment. In the hospital, patients may receive:
- Oxygen therapy to support breathing
- Medications to control high blood pressure and heart rate
- Cooling measures to manage fever
- Paralysis and mechanical ventilation in extreme cases of muscle rigidity and respiratory distress
Prevention of Future Episodes
Once a patient has recovered from serotonin syndrome, it is important to take steps to prevent future episodes. This may involve:
- Avoiding medications and supplements that increase serotonin levels
- Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new medications
- Educating oneself about the risks of drug interactions
When to Seek Medical Attention
Serotonin syndrome can progress rapidly, and early intervention is critical to preventing severe complications. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms such as confusion, rapid heart rate, muscle rigidity, or fever after starting a new medication or increasing the dosage of an existing medication, seek medical attention immediately.
Final Thoughts
Serotonin syndrome is a serious condition that requires prompt recognition and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk and ensure their safety. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen, and report any unusual symptoms promptly.