Savant Syndrome, often abbreviated as SS, is a rare but fascinating condition where individuals with developmental disorders or brain injuries exhibit extraordinary skills that stand in stark contrast to their overall limitations. These skills can range from prodigious memory to exceptional artistic or mathematical abilities. While the phenomenon has intrigued scientists, psychologists, and the general public for decades, much about Savant Syndrome remains a mystery. This article delves into the intricacies of this condition, exploring its characteristics, the remarkable skills associated with it, and the challenges faced by those who live with it.

What is Savant Syndrome?
Savant Syndrome is a condition in which individuals with significant cognitive impairments, such as autism spectrum disorder or other neurological conditions, display extraordinary talents or abilities. These talents are often referred to as “islands of genius” because they shine brightly amidst a sea of limitations. The condition was first described in the late 19th century by Dr. J. Langdon Down, who coined the term “idiot savant.” Over time, the terminology evolved to become more respectful and accurate, leading to the current name, Savant Syndrome.
The prevalence of Savant Syndrome is estimated to be around one in ten individuals with autism spectrum disorder, though it can also occur in people with other developmental disabilities or brain injuries. Despite its rarity, the condition has captured the imagination of many due to the seemingly paradoxical nature of its manifestations.
Characteristics of Savant Syndrome
Individuals with Savant Syndrome typically exhibit skills that fall into one of five categories:
- Music: Many savants demonstrate an uncanny ability to play musical instruments, compose music, or memorize complex pieces after hearing them only once.
- Art: Some individuals possess extraordinary artistic talent, creating detailed and intricate works of art despite having little to no formal training.
- Mathematics: A subset of savants excel in mathematical calculations, solving complex problems with speed and accuracy far beyond the capabilities of most people.
- Memory: Exceptional memory is a hallmark of Savant Syndrome, with some individuals able to recall vast amounts of information, such as historical dates, maps, or even entire books.
- Calendar Calculation: This skill involves determining the day of the week for any given date, past or future, with remarkable precision.
These skills are not learned in the traditional sense but rather seem to emerge spontaneously. For example, a person might suddenly begin playing the piano flawlessly without ever having taken a lesson. This spontaneous emergence of abilities is one of the most intriguing aspects of Savant Syndrome.
The Science Behind Savant Syndrome
Despite decades of research, the exact cause of Savant Syndrome remains unknown. However, several theories attempt to explain its origins:
Neurological Explanations
One prevailing theory suggests that Savant Syndrome arises from changes in brain structure or function. Brain imaging studies have shown that individuals with Savant Syndrome often exhibit unusual patterns of neural activity. For instance, certain areas of the brain may be overactive, while others are underactive. This imbalance could lead to heightened abilities in specific domains while impairing general cognitive functioning.
Another hypothesis posits that Savant Syndrome results from the brain’s compensatory mechanisms. When one part of the brain is damaged or underdeveloped, other regions may compensate by becoming hyperactive or specialized. This could explain why individuals with developmental disorders or brain injuries sometimes develop extraordinary skills.
Genetic Factors
Some researchers believe that genetic factors may play a role in Savant Syndrome. Certain genetic mutations or variations could predispose individuals to both developmental disorders and exceptional abilities. However, more research is needed to identify specific genes associated with the condition.
Environmental Influences
While genetics and neurology are critical factors, environmental influences may also contribute to the development of Savant Syndrome. For example, early exposure to music, art, or numbers might trigger latent abilities in susceptible individuals. Additionally, supportive environments that encourage exploration and creativity could help nurture these talents.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Savant Syndrome
While the extraordinary abilities associated with Savant Syndrome are undoubtedly impressive, they often come at a cost. Individuals with this condition face numerous challenges that can impact their quality of life and social integration.
Cognitive and Social Limitations
Most individuals with Savant Syndrome have significant cognitive impairments that affect their daily lives. They may struggle with communication, social interaction, and independent living. For example, a person with autism spectrum disorder who possesses exceptional artistic talent might still find it difficult to engage in conversations or navigate social situations.
Emotional and Psychological Struggles
The disparity between an individual’s exceptional skills and their overall limitations can lead to emotional and psychological challenges. Feelings of frustration, isolation, and low self-esteem are common among people with Savant Syndrome. They may feel misunderstood or alienated by society, particularly if their talents are viewed as mere curiosities rather than integral parts of their identity.
Exploitation and Misunderstanding
Unfortunately, individuals with Savant Syndrome are sometimes exploited for their talents. Their abilities may be showcased in ways that prioritize entertainment over dignity, reducing them to spectacles rather than recognizing their humanity. Moreover, misconceptions about the condition can perpetuate stereotypes and hinder efforts to provide appropriate support and resources.
Famous Cases of Savant Syndrome
Throughout history, there have been several well-documented cases of individuals with Savant Syndrome whose talents have left a lasting impact on society.
Kim Peek
Kim Peek, the inspiration for the character Raymond Babbitt in the movie “Rain Man,” was a renowned savant with an extraordinary memory. He could read two pages of a book simultaneously, one with each eye, and retain nearly all the information he encountered. His knowledge spanned a wide range of topics, including literature, history, geography, and sports statistics.
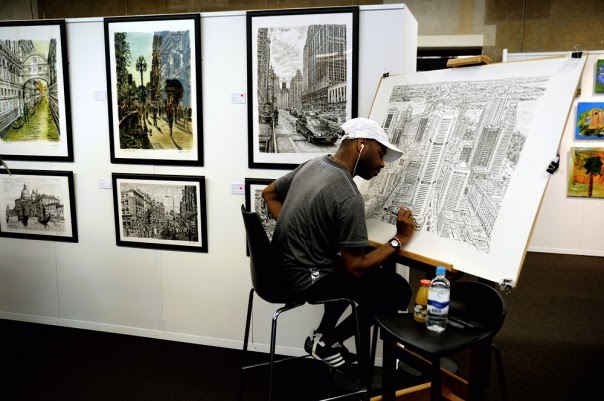
Stephen Wiltshire
Stephen Wiltshire is a British artist known for his incredible ability to draw detailed cityscapes from memory. After taking a brief helicopter ride over a city, he can recreate its skyline with astonishing accuracy, down to the number of windows on each building. His work has earned him international acclaim and demonstrated the potential of artistic savants.
Derek Paravicini
Derek Paravicini is a blind musician with severe learning disabilities who possesses an unparalleled gift for playing the piano. Despite being unable to read sheet music, he can play thousands of songs from memory and improvise complex compositions. His performances have captivated audiences worldwide and highlighted the transformative power of music.
Support and Resources for Individuals with Savant Syndrome
Providing adequate support and resources for individuals with Savant Syndrome requires a multifaceted approach that addresses their unique needs and challenges.
Education and Therapy
Specialized educational programs and therapies can help individuals with Savant Syndrome develop their talents while improving their overall functioning. For example, music therapy has proven effective in enhancing communication and social skills among autistic savants. Similarly, occupational therapy can assist with daily living tasks and promote independence.
Community and Advocacy
Building inclusive communities that celebrate diversity and foster acceptance is crucial for supporting individuals with Savant Syndrome. Advocacy organizations play a vital role in raising awareness, combating stigma, and advocating for policies that ensure equal opportunities for all.
Research and Innovation
Ongoing research into the causes and mechanisms of Savant Syndrome holds promise for unlocking new insights into human cognition and potential treatments for related conditions. Advances in neuroscience, genetics, and artificial intelligence could pave the way for innovative interventions that enhance the lives of individuals with Savant Syndrome.





