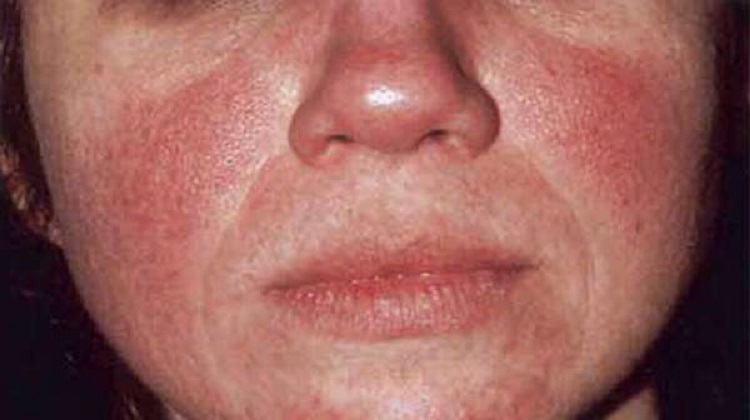
Rosacea, often abbreviated as ROS, is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. It is characterized by persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small bumps or pimples. This condition can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life if left untreated. In this article, we will explore what rosacea is, its potential causes, common symptoms, and available treatments to help those affected better understand and manage this condition.
What Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a long-term inflammatory skin disorder that typically manifests on the central part of the face. While it most commonly occurs in adults aged thirty to fifty, it can affect individuals of all ages. The exact cause of rosacea remains unknown, but researchers believe it involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. People with fair skin are more prone to developing this condition, although it can occur in individuals of any skin type.
This skin condition is often mistaken for acne due to its similar appearance, but the two are distinct. Unlike acne, rosacea does not involve blackheads or whiteheads. Instead, it presents as persistent redness, swelling, and sometimes thickening of the skin. Understanding the differences between these conditions is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Potential Causes of Rosacea
Although the precise cause of rosacea has yet to be identified, several contributing factors have been identified through research. Below are some of the most widely recognized potential causes:
Genetic Predisposition
Family history plays a significant role in the development of rosacea. Individuals with close relatives who have the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. This suggests that genetics may influence susceptibility to rosacea.
Abnormal Blood Vessel Function
One theory is that rosacea is linked to abnormalities in the blood vessels of the face. These abnormalities may cause the persistent redness and flushing associated with the condition. Over time, the blood vessels may become more visible, leading to the characteristic appearance of rosacea.
Immune System Response
Some studies suggest that an overactive immune system may contribute to rosacea. Certain proteins released by the immune system may trigger inflammation in the skin, resulting in redness and swelling.
Demodex Mites
Demodex mites are microscopic organisms that naturally live on human skin. However, individuals with rosacea often have higher levels of these mites on their faces. Researchers believe that an overpopulation of demodex mites may irritate the skin and exacerbate symptoms.
Environmental Triggers
Various environmental factors can worsen rosacea symptoms. Common triggers include exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, spicy foods, alcohol consumption, and stress. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage the condition effectively.
Symptoms of Rosacea
The symptoms of rosacea can vary from person to person, and they often develop gradually over time. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe manifestations. Below are the most common signs and symptoms associated with rosacea:
Facial Redness
Persistent redness in the central part of the face is one of the hallmark symptoms of rosacea. This redness often resembles a blush or sunburn and may come and go initially before becoming more permanent.
Visible Blood Vessels
Small blood vessels on the nose and cheeks may become visible as the condition progresses. These enlarged blood vessels can contribute to the overall redness of the skin.
Bumps and Pimples
Some individuals with rosacea develop small, red, pus-filled bumps on their faces. These bumps can resemble acne but do not contain blackheads or whiteheads.
Swelling
Facial swelling, particularly around the eyes, nose, and cheeks, is another common symptom. This swelling can make the skin feel tender or sensitive to touch.
Burning or Stinging Sensation
Many people with rosacea report experiencing a burning or stinging sensation on their skin. This discomfort is often accompanied by increased sensitivity to skincare products or environmental factors.
Thickened Skin
In advanced cases, the skin on the nose may thicken and become bumpy. This condition, known as rhinophyma, is more common in men and can lead to significant cosmetic concerns.
Ocular Symptoms
Rosacea can also affect the eyes, leading to dryness, irritation, redness, and a gritty sensation. In severe cases, it may result in vision problems if left untreated.
Treatments for Rosacea
While there is no cure for rosacea, various treatments can help manage its symptoms and improve the appearance of the skin. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and severity of the condition. Below are some of the most common treatment options:
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of rosacea flare-ups. These modifications include:
- Avoiding known triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, and extreme temperatures.
- Using gentle skincare products that do not irritate the skin.
- Wearing sunscreen daily to protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
Topical Medications
Topical treatments are often prescribed to reduce redness and inflammation. These medications are applied directly to the skin and may include:
- Metronidazole cream or gel, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Azelaic acid, which helps reduce redness and kill bacteria on the skin.
- Ivermectin cream, which targets demodex mites and reduces inflammation.
Oral Medications
In more severe cases, oral medications may be prescribed to control symptoms. These include:
- Antibiotics such as doxycycline, which help reduce inflammation and bacterial growth.
- Isotretinoin, a powerful medication used for severe cases that do not respond to other treatments.
Laser and Light Therapies
Laser and light-based therapies are effective in reducing visible blood vessels and improving overall skin texture. These treatments work by targeting the blood vessels beneath the skin’s surface, causing them to shrink and fade. Common procedures include:
- Pulsed dye laser therapy, which reduces redness and visible blood vessels.
- Intense pulsed light therapy, which addresses multiple skin concerns simultaneously.
Surgical Options
For individuals with rhinophyma, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove excess tissue and restore the natural shape of the nose. Procedures such as dermabrasion or electrocautery can achieve these results.
Eyecare Treatments
If rosacea affects the eyes, specific treatments may be required to alleviate symptoms. These treatments include:
- Artificial tears to relieve dryness and irritation.
- Antibiotic eye drops or ointments to treat infections.
- Regular eyelid hygiene practices to prevent further complications.
Managing Rosacea Long-Term
Living with rosacea requires ongoing care and attention. Even after successful treatment, symptoms can return if preventive measures are not maintained. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed. Additionally, staying informed about new developments in rosacea research can provide valuable insights into emerging therapies and management strategies.
Education and awareness are key components of managing rosacea effectively. By understanding the triggers, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the impact of this condition on their daily lives.