Rib fractures, often abbreviated as RF, are a common injury that can result from trauma or underlying medical conditions. These injuries can range from mild to severe, depending on the number of ribs affected and whether other structures in the chest cavity are involved. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and recovery process is essential for managing this condition effectively. In this article, we will explore these aspects in detail to provide a comprehensive guide to rib fractures.
What Are Rib Fractures?
Rib fractures occur when one or more of the bones in the rib cage break or crack. The rib cage consists of twelve pairs of ribs that protect vital organs such as the heart and lungs. When these bones are fractured, it can lead to pain, difficulty breathing, and other complications. Rib fractures are most commonly caused by trauma but can also occur due to repetitive stress or weakened bones.
Causes of Rib Fractures
There are several potential causes of rib fractures, with trauma being the most prevalent. Below are some of the leading causes:
1. Trauma
- Car Accidents: High-impact collisions can cause significant force to be applied to the chest, leading to rib fractures.
- Falls: Falling from a height or slipping and landing on the chest can result in broken ribs.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports like football or hockey can cause rib fractures due to direct blows to the chest.
- Physical Assault: Blunt force trauma from punches or kicks can fracture the ribs.
2. Repetitive Stress
In some cases, repeated stress on the ribs, such as from chronic coughing or intense physical activity, can lead to fractures. This type of injury is more common in athletes or individuals with prolonged respiratory conditions.
3. Weakened Bones
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened and brittle bones, increases the risk of rib fractures. Even minor impacts or movements can cause fractures in individuals with this condition.
4. Medical Conditions
Certain diseases, such as bone cancer or infections, can weaken the ribs and make them more susceptible to fractures. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy may also contribute to bone fragility.
Symptoms of Rib Fractures
The symptoms of rib fractures can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others may have severe pain and difficulty performing daily activities. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the chest area that worsens with movement, deep breathing, or coughing
- Tenderness or swelling around the injured area
- Bruising on the skin over the fractured rib
- Difficulty taking deep breaths
- A grinding or crunching sensation when pressing on the ribs
- Shortness of breath, especially if multiple ribs are fractured
In severe cases, rib fractures can lead to complications such as punctured lungs or damage to blood vessels. If you experience symptoms like rapid breathing, dizziness, or coughing up blood, seek immediate medical attention.
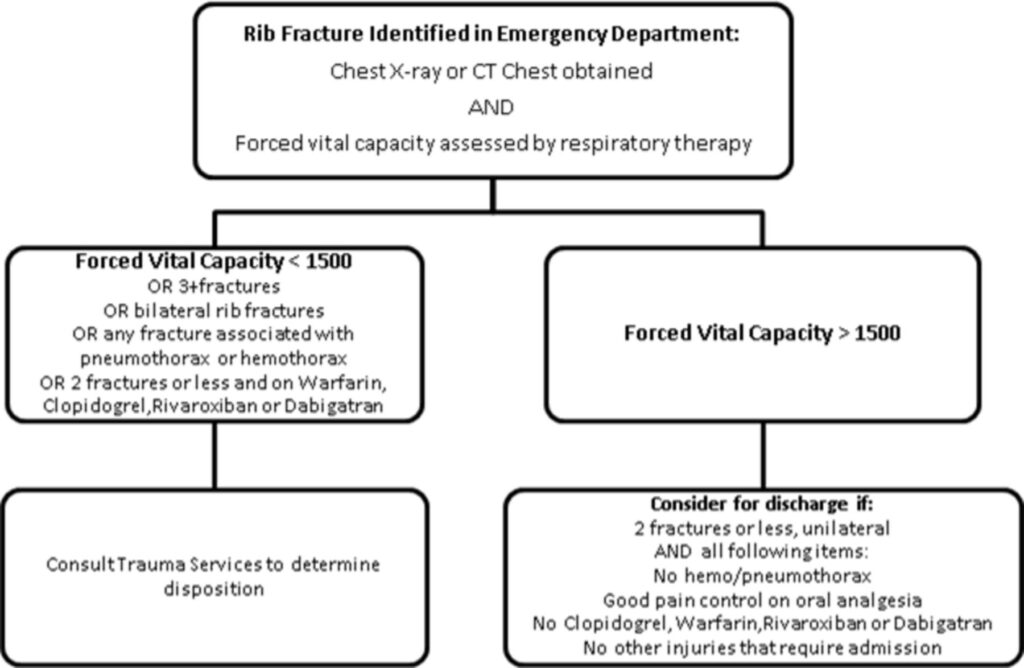
Diagnosis of Rib Fractures
Diagnosing rib fractures typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. Healthcare providers use these methods to determine the location and severity of the injury.
1. Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a doctor will assess the chest area for signs of tenderness, swelling, or deformities. They may also ask about the circumstances surrounding the injury and any symptoms you are experiencing.
2. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are crucial for confirming the presence of rib fractures and ruling out other potential injuries. Common imaging techniques include:
- X-rays: X-rays are often the first step in diagnosing rib fractures. While they may not always detect hairline fractures, they are effective at identifying more severe breaks.
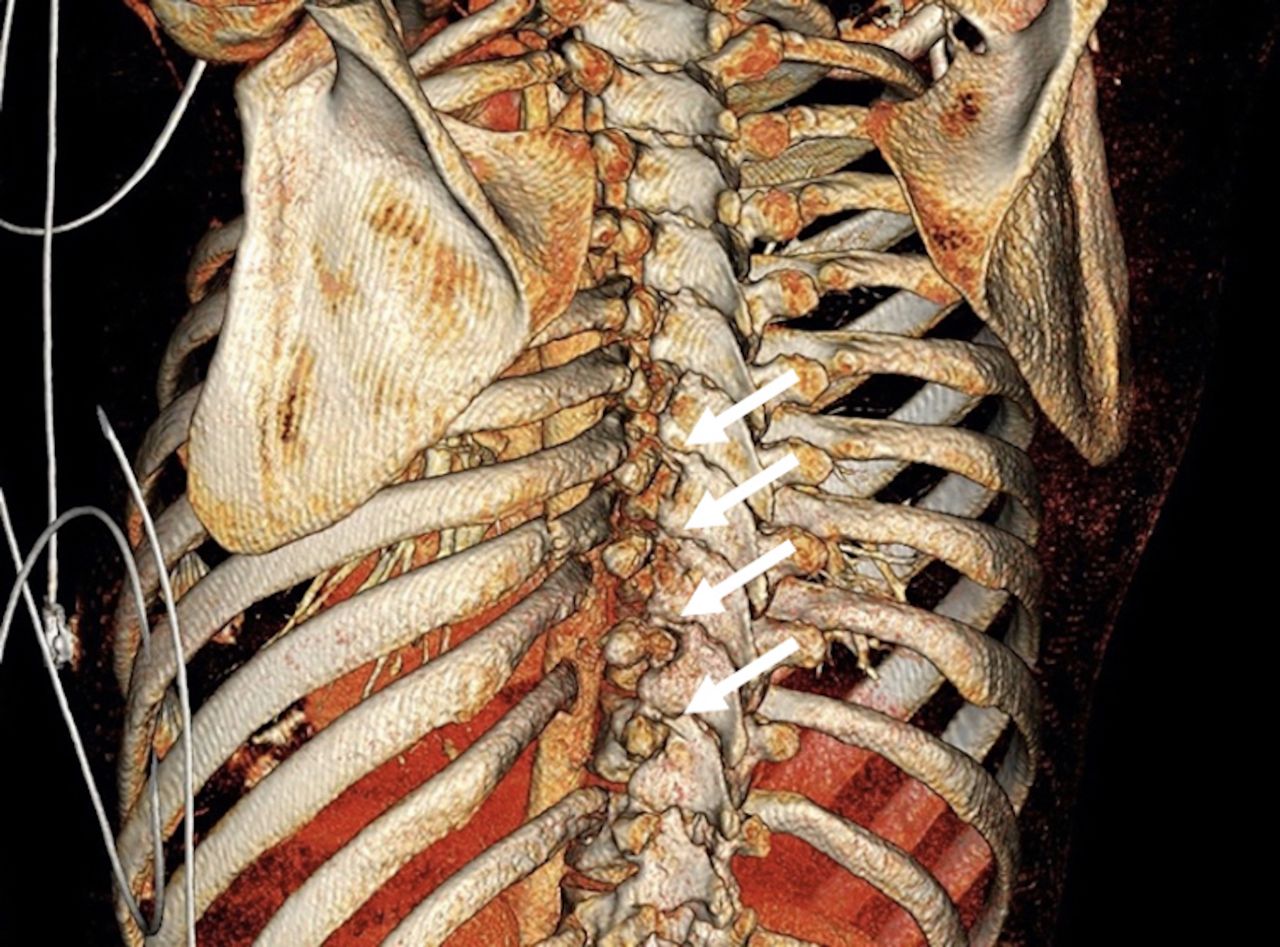
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans provide detailed images of the chest and can help identify fractures that are not visible on X-rays.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans are less commonly used but may be recommended in cases where soft tissue damage is suspected.
3. Additional Tests
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to evaluate the extent of the injury. For example, a pulmonary function test may be conducted to assess how well the lungs are working after a rib fracture.
Recovery Process for Rib Fractures
The recovery process for rib fractures depends on the severity of the injury and the overall health of the individual. While minor fractures may heal on their own, more severe cases may require medical intervention and extended recovery time.
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is a critical component of recovery from rib fractures. Avoiding strenuous activities and movements that strain the chest can help prevent further injury and promote healing. It is important to listen to your body and avoid pushing through pain during the recovery period.
2. Pain Management
Pain management is essential for ensuring comfort and facilitating recovery. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce discomfort. In more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications or recommend nerve blocks to alleviate pain.
3. Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises are often recommended to prevent complications such as pneumonia. These exercises help expand the lungs and improve oxygenation, which is particularly important if the injury affects breathing. A healthcare provider may teach specific techniques to perform safely.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy may be beneficial for individuals recovering from rib fractures, especially if the injury has led to muscle weakness or limited mobility. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to restore strength and flexibility gradually.
5. Surgical Intervention
In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to stabilize the ribs or repair damage to surrounding structures. Surgery is typically reserved for severe fractures that involve multiple ribs or compromise organ function.
6. Nutritional Support
Adequate nutrition plays a vital role in the healing process. Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein can support bone repair and overall recovery. Individuals with osteoporosis or other conditions affecting bone health may benefit from dietary supplements under medical supervision.
Preventing Rib Fractures
While not all rib fractures can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of injury:
- Wear appropriate protective gear during high-risk activities, such as contact sports or construction work.
- Practice safe driving habits and ensure that vehicles are equipped with functioning airbags and seat belts.
- Use caution when engaging in activities that involve heights or uneven surfaces to prevent falls.
- Maintain strong and healthy bones through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sun exposure for vitamin D synthesis.
- Address underlying medical conditions that may weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, with the help of a healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many rib fractures heal without complications, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe or worsening pain that does not improve with rest or medication
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood or noticing blood in saliva
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
- Signs of infection, such as fever or increased redness and swelling around the injury site
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact a healthcare provider or visit the emergency room promptly.