Peyronie’s Disease, often abbreviated as PD, is a condition that affects the penis, leading to abnormal curvature and potential discomfort during sexual activity. While it may not be life-threatening, it can significantly impact a man’s quality of life, self-esteem, and intimate relationships. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for this condition in detail.
Understanding Peyronie’s Disease
Peyronie’s Disease occurs when fibrous scar tissue, also known as plaques, forms inside the penis. This buildup causes the penis to bend or curve, especially during an erection. The degree of curvature varies from person to person, ranging from mild to severe. In some cases, the condition resolves on its own, while in others, it may require medical intervention.
How Common Is It?
- Studies suggest that approximately 3 to 9 percent of men are affected by this condition.
- It is more commonly observed in men between the ages of 40 and 70.
- However, younger men can also develop the condition, particularly after trauma to the genital area.
Causes of Peyronie’s Disease
The exact cause of Peyronie’s Disease remains unclear, but researchers have identified several contributing factors. These include injury, genetic predisposition, and underlying health conditions.
Injury or Trauma
One of the most common causes of Peyronie’s Disease is physical trauma to the penis. This can occur due to:
- Accidents during sexual intercourse
- Sports injuries
- Vigorous masturbation
When the penis is injured, the body attempts to heal itself by forming scar tissue. However, in some cases, this healing process goes awry, leading to the development of fibrous plaques.
Genetic Factors
Some men may have a genetic predisposition to developing Peyronie’s Disease. If a close family member has been diagnosed with the condition, there is an increased likelihood of experiencing it yourself. Additionally, certain connective tissue disorders, such as Dupuytren’s contracture, are associated with a higher risk.
Underlying Health Conditions
Several health conditions can increase the risk of developing Peyronie’s Disease, including:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Tobacco use
- Autoimmune disorders
These conditions can affect blood flow and tissue elasticity, making the penis more susceptible to scarring.
Symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease
The symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition. Some men may experience only mild symptoms, while others may face significant challenges. Below are the most common signs to look out for:
Penile Curvature
The hallmark symptom of Peyronie’s Disease is a noticeable curvature of the penis. This curvature typically becomes apparent during an erection and can range from slight bending to severe angulation. The direction of the bend—upward, downward, or sideways—depends on the location of the scar tissue.
Pain During Erection
Many men with Peyronie’s Disease report experiencing pain during erections. This discomfort is often caused by the tension created by the fibrous plaques pulling on the surrounding tissues. The pain may diminish over time as the condition stabilizes, but it can persist in some cases.
Plaque Formation
Fibrous plaques can sometimes be felt as hard lumps or bands beneath the skin of the penis. These plaques are usually located on the upper or lower side of the shaft and can vary in size. In some cases, they may even be visible through the skin.
Erectile Dysfunction
Peyronie’s Disease can contribute to difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection. This is often due to a combination of psychological stress and physical limitations caused by the curvature. Erectile dysfunction can further exacerbate feelings of anxiety and frustration.
Diagnosing Peyronie’s Disease
If you suspect you may have Peyronie’s Disease, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnostic process typically involves:
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your doctor will begin by taking a detailed medical history, asking about any past injuries, symptoms, and their duration. A physical examination will follow, during which the doctor will assess the curvature of the penis and check for the presence of plaques.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended. These tests help visualize the internal structures of the penis, providing valuable information about the extent and location of scar tissue.
Treatment Options for Peyronie’s Disease
Treatment for Peyronie’s Disease depends on the severity of symptoms and how much the condition impacts your daily life. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, several approaches are available to manage the condition effectively.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For mild cases, non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense. These options aim to reduce pain, improve flexibility, and prevent further progression of the disease.
Oral Medications
Certain medications may help reduce inflammation and break down scar tissue. Examples include:
- Potassium para-aminobenzoate
- Tamoxifen
- Colchicine
While these medications can be effective for some men, results vary, and they may take several months to show improvement.
Injections
Injections directly into the plaques can help soften and reduce scar tissue. Commonly used substances include:
- Collagenase clostridium histolyticum
- Verapamil
- Interferon
These injections are typically administered by a healthcare professional and may require multiple sessions.
Traction Devices
Penile traction devices apply gentle, consistent pressure to the penis, aiming to stretch the tissue and reduce curvature. These devices are most effective when used consistently over an extended period.
Surgical Treatments
For severe cases that do not respond to non-surgical methods, surgery may be considered. Surgical options include:
Plication Procedures
This involves folding or suturing the unaffected side of the penis to straighten it. Plication is minimally invasive and generally safe but may result in slight shortening of the penis.
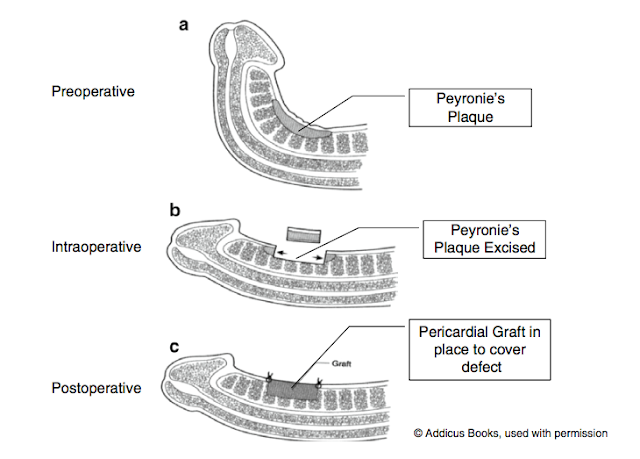
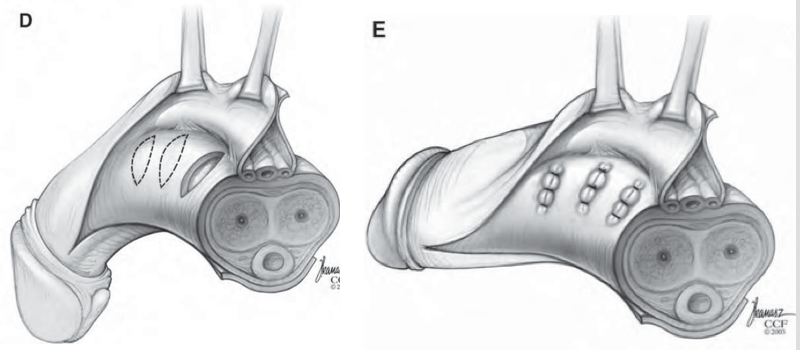
Grafting Procedures
In this procedure, the scar tissue is removed and replaced with a graft. Grafting can correct significant curvature but carries a higher risk of complications, such as erectile dysfunction.
Penile Implants
For men with both Peyronie’s Disease and erectile dysfunction, penile implants may be an option. These devices provide structural support and restore erectile function.
Lifestyle Changes and Support
Beyond medical treatments, adopting healthy lifestyle changes can complement your recovery. Quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet can improve overall penile health. Additionally, seeking emotional support from partners, friends, or support groups can help address the psychological impact of the condition.
Living with Peyronie’s Disease
While Peyronie’s Disease can be challenging, it is important to remember that effective treatments are available. Open communication with your healthcare provider and loved ones is key to managing the condition successfully. By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and well-being.