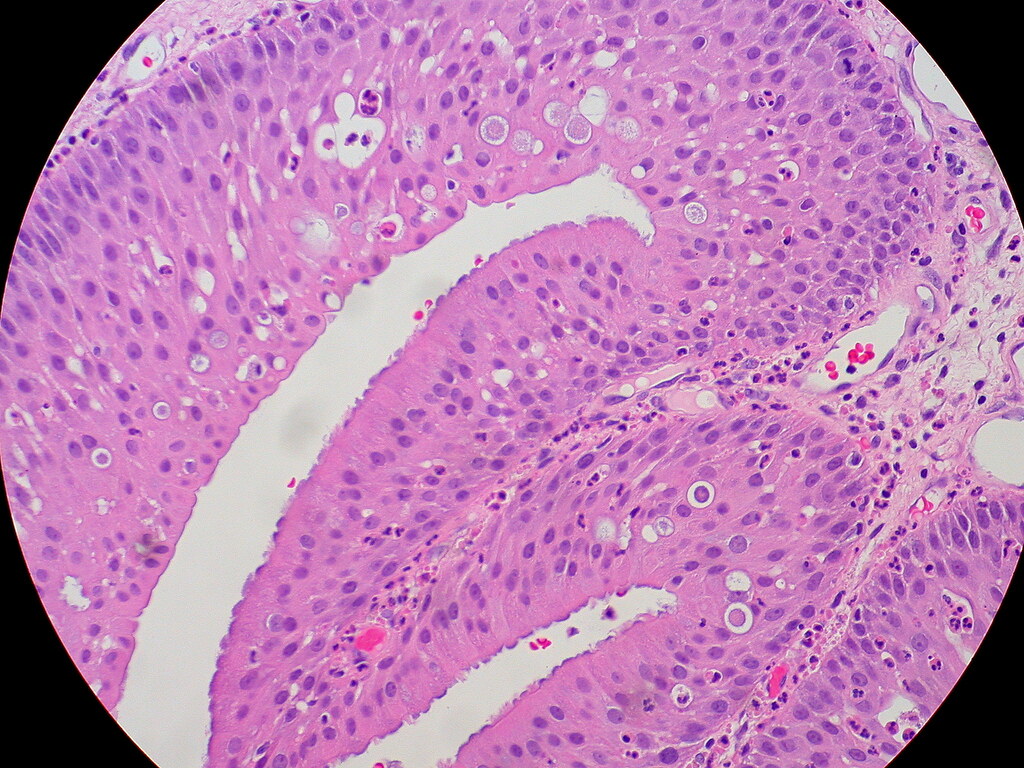
Papillomas, often abbreviated as PAs, are benign growths that can occur in various parts of the body. These growths are typically caused by a viral infection and can manifest in different forms depending on their location and underlying cause. In this article, we will explore the types of papillomas, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
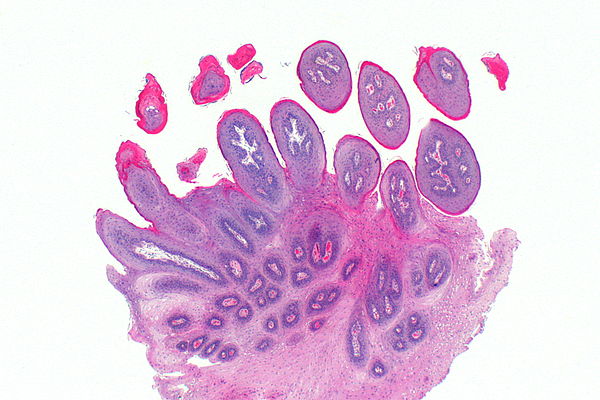
What Are Papillomas?
Papillomas are non-cancerous tumors that arise from epithelial tissue, which is the thin layer of cells covering the surfaces of organs and structures throughout the body. These growths can appear in areas such as the skin, respiratory tract, breast, and genital regions. While they are generally harmless, some types of papillomas may cause discomfort or complications if left untreated.
Common Characteristics of Papillomas
- They are usually small and flesh-colored or slightly darker.
- They may have a cauliflower-like appearance due to their uneven surface.
- They can grow individually or in clusters.
- In some cases, they may cause itching, irritation, or bleeding.
Types of Papillomas
Papillomas can be classified based on their location and specific characteristics. Below are some of the most common types:
Skin Papillomas
Skin papillomas are the most frequently observed type and are often referred to as warts. These growths can appear anywhere on the skin and are caused by the human papillomavirus. They are highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces.
Subtypes of Skin Papillomas
- Common Warts: These are rough, raised bumps that typically appear on the hands or fingers.
- Plantar Warts: Found on the soles of the feet, these warts can cause pain when walking.
- Flat Warts: Small, smooth, and flat-topped, these warts often appear on the face, thighs, or arms.
- Genital Warts: These occur in the genital area and are considered a sexually transmitted infection.
Respiratory Papillomas
Respiratory papillomas develop in the airways, including the throat, vocal cords, and lungs. These growths can obstruct breathing and affect speech. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is a rare condition where multiple papillomas form in the respiratory tract, requiring ongoing medical management.
Breast Papillomas
Breast papillomas are benign tumors that grow within the milk ducts of the breast. They are more common in women over the age of forty. Although they are not cancerous, breast papillomas can sometimes lead to complications such as nipple discharge or discomfort.
Inverted Papillomas
Inverted papillomas are rare and occur in the nasal cavity or sinuses. Unlike other types of papillomas, these growths have a higher risk of becoming malignant. Surgical removal is often recommended to prevent potential complications.
Causes of Papillomas
The primary cause of papillomas is infection with the human papillomavirus. This virus has over one hundred strains, each affecting different parts of the body. The mode of transmission and risk factors vary depending on the type of papilloma.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a group of viruses that infect the skin and mucous membranes. It spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact, sexual activity, or exposure to contaminated objects. Certain strains of HPV are associated with specific types of papillomas, such as genital warts and respiratory papillomas.
Risk Factors for Developing Papillomas
- Weakened immune system due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive medications.
- Frequent skin injuries or abrasions that create entry points for the virus.
- Close contact with individuals who have active papillomas.
- Engaging in unprotected sexual activity.
- Poor hygiene practices that increase the likelihood of viral exposure.
Symptoms of Papillomas
The symptoms of papillomas depend on their type and location. Some papillomas may not cause noticeable symptoms, while others can lead to discomfort or functional issues.
Symptoms of Skin Papillomas
- Visible bumps or growths on the skin.
- Itching or irritation around the affected area.
- Bleeding if the growth is scratched or injured.
Symptoms of Respiratory Papillomas
- Hoarseness or changes in voice quality.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- Chronic cough or throat irritation.
Symptoms of Breast Papillomas
- Nipple discharge, which may be clear, bloody, or milky.
- A lump or swelling near the nipple.
- Tenderness or discomfort in the breast.
Symptoms of Inverted Papillomas
- Nasal congestion or blockage.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Loss of sense of smell.
Treatments for Papillomas
Treatment options for papillomas vary depending on the type, size, and location of the growths. In some cases, no treatment is necessary if the papillomas do not cause symptoms or complications. However, medical intervention may be required for persistent or problematic papillomas.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical approaches are often used for smaller or less severe papillomas. These treatments aim to reduce the size of the growths or eliminate them entirely.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the papilloma using liquid nitrogen. This method is commonly used for skin papillomas and is effective in destroying the abnormal tissue. The treated area may blister and peel off as it heals.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy uses concentrated beams of light to remove papillomas. This technique is particularly useful for delicate areas, such as the vocal cords or nasal passages. Laser therapy minimizes scarring and promotes faster healing compared to traditional surgery.
Topical Medications
Certain topical medications, such as salicylic acid or imiquimod cream, can be applied directly to the affected area. These treatments work by gradually breaking down the papilloma or stimulating the immune system to fight the virus.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical removal is often necessary for larger or more complex papillomas. This approach ensures complete elimination of the growth and reduces the risk of recurrence.
Excision
Excision involves cutting out the papilloma using a scalpel or surgical scissors. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is suitable for accessible growths, such as those on the skin or breast.
Electrocautery
Electrocautery uses an electric current to burn away the papilloma. This method is effective for removing multiple growths and helps control bleeding during the procedure.
Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery is used for papillomas located in hard-to-reach areas, such as the respiratory tract or sinuses. A thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera is inserted to guide the removal process, ensuring precision and minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Preventive Measures
While not all papillomas can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing these growths:
- Vaccination against high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus.
- Practicing good hygiene and avoiding direct contact with infected individuals.
- Using protection during sexual activity to minimize the risk of genital warts.
- Maintaining a strong immune system through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any unusual growths or experience symptoms associated with papillomas. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes. Additionally, individuals with a history of recurrent papillomas should undergo regular check-ups to monitor their condition.