Nosebleeds, also known as Epistaxis, are a common medical condition that can affect individuals of all ages. While they are typically not serious, frequent or severe nosebleeds may indicate an underlying health issue. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to treat and prevent nosebleeds is essential for maintaining good health. This article explores everything you need to know about this condition.
What Are Nosebleeds?
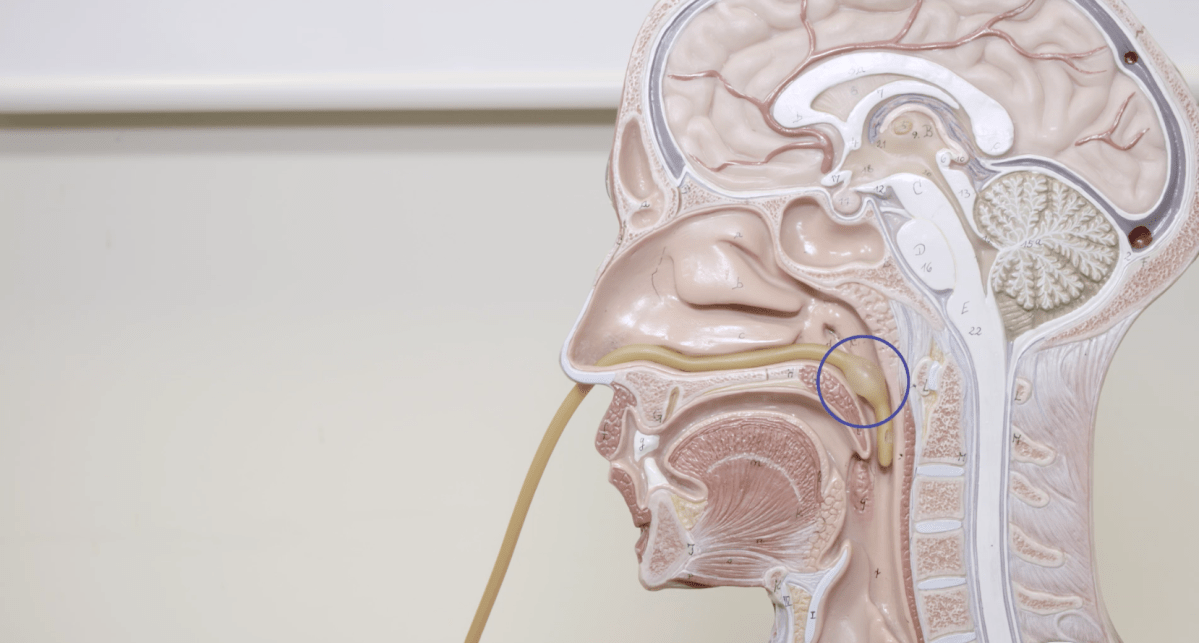
Nosebleeds occur when blood vessels in the nasal passages rupture, leading to bleeding from the nose. They can originate from either the front or the back of the nasal cavity. Most nosebleeds are anterior, meaning they come from the front part of the nose and are generally easier to manage. Posterior nosebleeds, which originate from deeper within the nasal cavity, are less common but can be more serious.
Common Causes of Nosebleeds
There are numerous factors that can lead to nosebleeds. Some of the most common causes include:
- Dry Air: Exposure to dry air, especially during winter months or in arid climates, can cause the nasal membranes to become dry and cracked, increasing the likelihood of bleeding.
- Allergies and Sinus Infections: Conditions such as allergies and sinus infections can irritate the nasal lining, making it more prone to bleeding.
- Nasal Trauma: Accidental injuries, such as a blow to the nose or excessive nose picking, can damage blood vessels and trigger nosebleeds.
- Mechanical Irritation: The use of nasal sprays, inhalers, or other devices inserted into the nose can irritate the nasal lining and cause bleeding.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can increase the risk of nosebleeds, as elevated pressure in the blood vessels makes them more likely to burst.
- Blood Disorders: Certain medical conditions, such as hemophilia or thrombocytopenia, can impair the blood’s ability to clot, leading to frequent or severe nosebleeds.
- Medications: Blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or anticoagulants, can interfere with the body’s natural clotting process, making nosebleeds more likely.
- Chemical Exposure: Inhalation of certain chemicals or irritants can damage the nasal lining and result in bleeding.
Symptoms of Nosebleeds
The primary symptom of a nosebleed is the presence of blood coming from one or both nostrils. However, there are additional signs and symptoms that may accompany nosebleeds, depending on their severity and underlying cause:
- Mild Bleeding: In most cases, nosebleeds involve only a small amount of blood and stop on their own within a few minutes.
- Prolonged Bleeding: If the bleeding persists for more than 20 minutes, it may indicate a more serious issue, such as a posterior nosebleed or an underlying medical condition.
- Dizziness or Fainting: Excessive blood loss can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, or even fainting, particularly in individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
- Nasal Congestion: Some people may experience difficulty breathing through the nose due to swelling or blockage caused by the bleeding.
- Fatigue: Frequent nosebleeds can lead to feelings of tiredness or weakness, especially if they result in significant blood loss over time.
Treatment Options for Nosebleeds
The treatment for nosebleeds depends on their severity and underlying cause. In most cases, simple home remedies are sufficient to stop the bleeding. However, persistent or severe nosebleeds may require medical intervention.
Home Remedies for Managing Nosebleeds
If you experience a nosebleed, follow these steps to stop the bleeding and prevent further complications:
- Stay Calm: Panic can increase your heart rate and worsen the bleeding. Try to remain calm and breathe deeply.
- Sit Upright: Sit in an upright position with your head slightly tilted forward. This helps prevent blood from flowing down the throat, which can cause choking or nausea.
- Pinch the Nose: Use your thumb and index finger to pinch the soft part of your nose just below the bridge. Maintain this pressure for at least 10 to 15 minutes without releasing.
- Apply Cold Compress: Place a cold compress or ice pack on the bridge of your nose to constrict blood vessels and reduce bleeding.
- Avoid Blowing Your Nose: Refrain from blowing your nose or inserting anything into it for several hours after the bleeding has stopped to allow the blood vessels to heal.
Medical Treatments for Severe Nosebleeds
In cases where home remedies are ineffective or the nosebleed is severe, medical treatment may be necessary. Some of the common medical interventions include:
- Cauterization: A healthcare provider may use a chemical agent or electrical device to seal off the bleeding blood vessel.
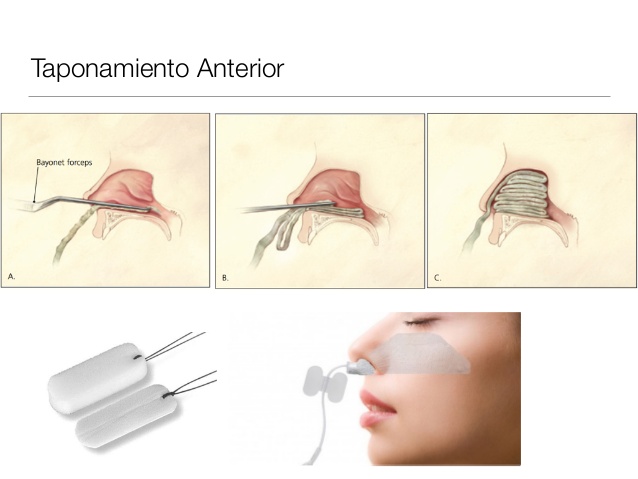
- Nasal Packing: For posterior nosebleeds, a doctor may insert a special type of gauze or balloon into the nasal cavity to apply pressure and stop the bleeding.
- Medication Adjustment: If the nosebleeds are caused by blood-thinning medications, your doctor may adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative treatment.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, surgery may be required to address structural issues within the nasal cavity, such as a deviated septum or abnormal blood vessels.
Preventing Nosebleeds
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of nosebleeds. Here are some tips to help you avoid this uncomfortable condition:
Humidify Your Environment
Using a humidifier in your home, especially during dry seasons, can keep the air moist and prevent the nasal membranes from drying out. This is particularly important if you live in a region with low humidity levels.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps maintain moisture in the nasal passages and reduces the risk of cracking or irritation. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water per day.
Avoid Nasal Irritants
Minimize exposure to allergens, smoke, and other irritants that can inflame the nasal lining. If you have allergies, consider using over-the-counter antihistamines or consulting a healthcare provider for long-term management.
Practice Gentle Nasal Care
Avoid excessive nose blowing or picking, as these actions can damage the delicate blood vessels in the nose. If you need to clear your nasal passages, do so gently and with care.
Use Saline Sprays
Saline nasal sprays can help keep the nasal membranes hydrated and reduce the risk of dryness and cracking. These sprays are available over the counter and are safe for regular use.
Monitor Blood Pressure
If you have high blood pressure, work with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively. Keeping your blood pressure within a healthy range can lower the risk of nosebleeds.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most nosebleeds are harmless and resolve on their own, certain situations warrant immediate medical attention. Seek professional help if you experience any of the following:
- The bleeding lasts longer than 20 minutes despite applying pressure.
- The nosebleed occurs after a head injury or trauma.
- You feel dizzy, weak, or faint due to blood loss.
- You notice frequent nosebleeds accompanied by other unusual symptoms, such as bruising or bleeding gums.
- You are taking blood-thinning medications and cannot stop the bleeding.
In these cases, prompt evaluation by a healthcare provider is crucial to identify and address any underlying issues.
Understanding the Role of Underlying Health Conditions
Occasionally, nosebleeds may be a symptom of a more serious health condition. Some of the potential underlying causes include:
- Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can weaken blood vessels, making them more susceptible to rupture.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like leukemia, hemophilia, or von Willebrand disease can interfere with the blood’s ability to clot properly.
- Liver Disease: Impaired liver function can affect the production of clotting factors, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Tumors: Although rare, tumors in the nasal cavity or sinuses can cause recurrent nosebleeds.
If you suspect that your nosebleeds are related to an underlying health issue, consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate testing.
Conclusion
Nosebleeds are a common and usually harmless occurrence, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatments is essential for effective management. By adopting preventive measures and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can minimize the impact of nosebleeds on your daily life.