Nearsightedness, commonly referred to as myopia, is a prevalent vision condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Individuals with this condition can see nearby objects clearly, but distant objects appear blurry. The prevalence of myopia has been increasing over the years, raising concerns about its impact on public health. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and potential solutions for nearsightedness.
What Is Nearsightedness?
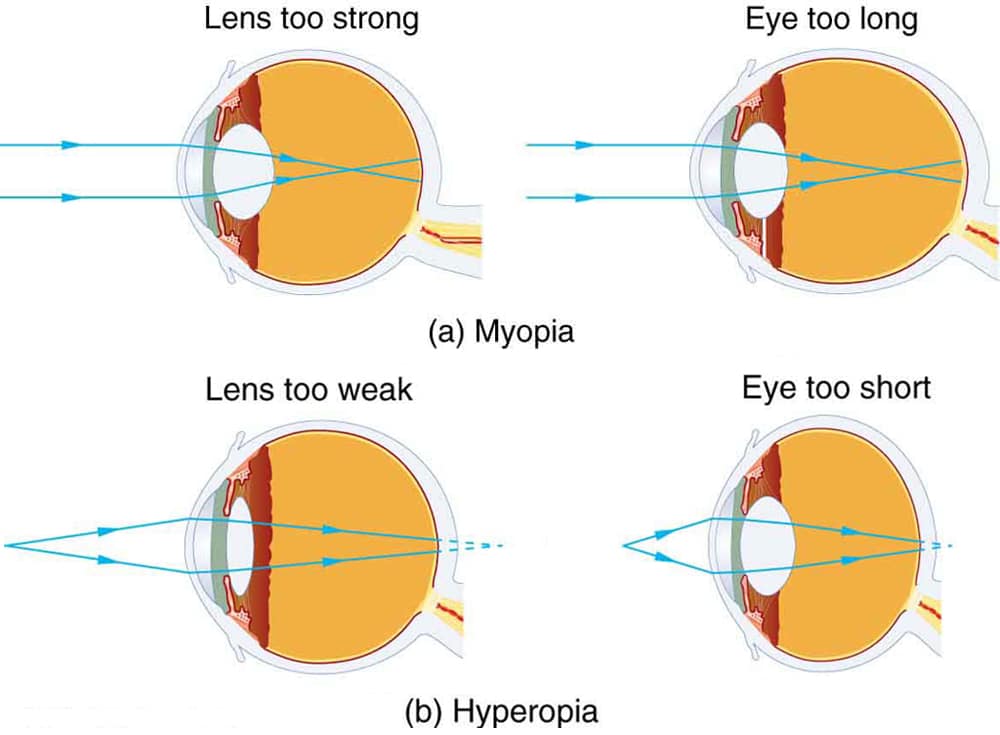
Nearsightedness is a refractive error of the eye where light focuses in front of the retina instead of directly on it. This misalignment prevents the eye from forming a clear image of distant objects. People who experience nearsightedness often find themselves squinting or moving closer to objects to see them more clearly. It is one of the most common vision problems, particularly among children and young adults.
How Does Nearsightedness Develop?
The development of nearsightedness is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding how this condition arises can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment.
Genetic Factors
Research has shown that genetics play a significant role in the development of nearsightedness. If one or both parents have the condition, their children are more likely to develop it as well. Specific genes associated with eye growth and development can predispose individuals to nearsightedness. However, genetics alone do not determine whether someone will develop the condition; environmental factors also play a crucial role.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors such as prolonged near work, limited outdoor activity, and excessive screen time have been linked to the onset and progression of nearsightedness. Studies suggest that spending less time outdoors during childhood may increase the risk of developing the condition. Additionally, focusing on close-up tasks like reading, writing, or using digital devices for extended periods can strain the eyes and contribute to its development.
Symptoms of Nearsightedness
Recognizing the symptoms of nearsightedness is essential for early detection and management. While some symptoms may seem mild at first, they can worsen over time if left untreated. Below are the most common signs associated with this condition:
- Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly
- Frequent squinting to improve focus
- Headaches caused by eye strain
- Trouble seeing while driving, especially at night
- Needing to sit closer to screens or blackboards
- Holding books or other materials very close to the face
If you or your child experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to consult an eye care professional for a comprehensive eye examination.
Causes of Nearsightedness
While the exact cause of nearsightedness varies from person to person, several key factors contribute to its development. These include structural changes in the eye, lifestyle habits, and certain medical conditions.
Anatomical Changes in the Eye
In individuals with nearsightedness, the eyeball is often longer than normal or the cornea is too curved. This causes light entering the eye to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. As a result, distant images appear blurry. These anatomical changes typically occur during childhood and adolescence when the eyes are still growing.
Lifestyle Habits
Modern lifestyles characterized by increased screen time and reduced outdoor activities have been linked to the rising rates of nearsightedness. Children and adults who spend long hours reading, studying, or using electronic devices are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Similarly, insufficient exposure to natural light and outdoor environments may hinder the eye’s ability to regulate its growth properly.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of developing nearsightedness. Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can temporarily affect the shape of the lens in the eye, leading to blurred vision. Additionally, premature birth or complications during infancy may predispose individuals to refractive errors later in life.
Solutions for Nearsightedness
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to manage and correct nearsightedness. From corrective lenses to surgical procedures, individuals have multiple options to improve their vision and quality of life.
Corrective Lenses
One of the most common solutions for nearsightedness is the use of corrective lenses. These include eyeglasses and contact lenses, which help refocus light onto the retina to produce clear images.
Eyeglasses
Eyeglasses are a simple and non-invasive way to correct nearsightedness. They come in various styles and lens types, including single-vision lenses designed specifically for distance correction. For individuals with additional vision issues, such as astigmatism or presbyopia, multifocal lenses may be recommended.
Contact Lenses
Contact lenses offer an alternative to eyeglasses and provide a wider field of view without obstructing peripheral vision. There are different types of contact lenses available, including soft lenses, rigid gas-permeable lenses, and specialty lenses for specific needs. Orthokeratology, or ortho-k lenses, is another option that involves wearing specially designed rigid lenses overnight to temporarily reshape the cornea.
Refractive Surgery
For those seeking a more permanent solution, refractive surgery may be an option. These procedures aim to reshape the cornea to improve how light enters the eye.
Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis
Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis, commonly known as LASIK, is a popular surgical procedure for correcting nearsightedness. During the procedure, a laser reshapes the cornea to allow light to focus correctly on the retina. Most patients experience significant improvement in their vision after LASIK, although it is not suitable for everyone.
Photorefractive Keratectomy
Photorefractive keratectomy, or PRK, is another type of laser surgery used to treat nearsightedness. Unlike LASIK, PRK removes the outer layer of the cornea before reshaping it. While recovery time may be longer compared to LASIK, PRK is often recommended for individuals with thin corneas.
Vision Therapy
Vision therapy involves a series of exercises and activities designed to improve visual skills and coordination. While it is not a direct treatment for nearsightedness, vision therapy can help address underlying issues such as eye strain or focusing difficulties. This approach is particularly beneficial for children whose eyes are still developing.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage nearsightedness and prevent its progression. Encouraging children to spend more time outdoors, reducing screen time, and taking regular breaks during near work are effective strategies. The “20-20-20” rule—taking a 20-second break every 20 minutes to look at something 20 feet away—is a practical tip to reduce eye strain.
Preventing the Progression of Nearsightedness
While nearsightedness cannot always be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to slow its progression, especially in children. Early intervention and consistent monitoring are key to managing the condition effectively.
Regular Eye Examinations
Scheduling routine eye exams is crucial for detecting nearsightedness early and addressing any changes in vision promptly. Eye care professionals can recommend appropriate interventions based on the individual’s age, lifestyle, and severity of the condition.
Encouraging Outdoor Activities
Studies have shown that spending time outdoors can reduce the risk of developing nearsightedness in children. Natural light and open spaces encourage the eyes to focus on distant objects, promoting healthy eye development.
Balancing Screen Time
Limiting screen time and ensuring proper lighting while using digital devices can help minimize eye strain. Parents should establish guidelines for technology use and encourage breaks to protect their children’s vision.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Ongoing research continues to explore new treatments and technologies for managing nearsightedness. Innovations such as specialized contact lenses, pharmaceutical interventions, and advanced surgical techniques hold promise for improving outcomes in the future.
Atropine Eye Drops
Low-dose atropine eye drops have gained attention as a potential treatment for slowing the progression of nearsightedness in children. While the exact mechanism is not fully understood, studies suggest that these drops may help regulate eye growth and reduce the rate of myopia progression.
Smart Contact Lenses
Researchers are also developing smart contact lenses equipped with sensors and microchips to monitor eye health and deliver targeted treatments. Although still in experimental stages, these lenses could revolutionize how nearsightedness and other eye conditions are managed.
By staying informed about advancements in eye care, individuals can make educated decisions about their vision health and explore emerging options that best suit their needs.