Nail Fold Infection, commonly referred to as Paronychia, is a condition that affects the skin surrounding the nails. This infection can occur in both fingers and toes and may lead to discomfort, swelling, and other complications if left untreated. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and knowing the available treatments are essential for managing this common yet often overlooked issue.
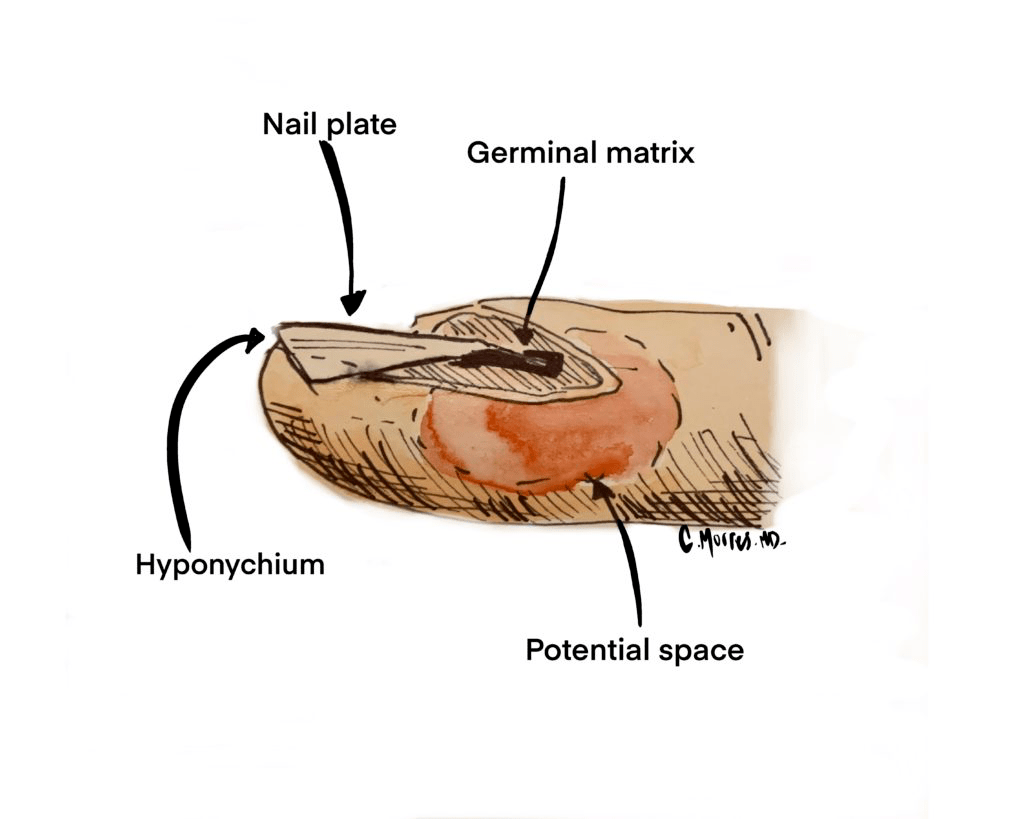
What is Nail Fold Infection?
A nail fold infection occurs when bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms invade the skin around the nails. The skin in this area, known as the nail fold, serves as a protective barrier. When this barrier is compromised, it becomes susceptible to infections. These infections can be acute, lasting for a short period, or chronic, persisting over weeks or months.
Types of Nail Fold Infections
- Acute Nail Fold Infection: This type develops suddenly and is often caused by bacteria. It typically lasts for less than six weeks.
- Chronic Nail Fold Infection: This type develops gradually and is usually caused by fungi or repeated exposure to irritants. It persists for more than six weeks.
Causes of Nail Fold Infections
Several factors can contribute to the development of nail fold infections. Understanding these causes can help prevent the condition and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Bacterial Causes
Bacteria are the most common culprits behind acute nail fold infections. Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species are frequently responsible for these infections. Bacteria can enter the skin through small cuts, cracks, or breaks in the nail fold. Common scenarios that increase the risk of bacterial infections include:
- Biting or picking at the nails
- Cutting the cuticles too aggressively
- Trauma to the nail area, such as stubbing a toe or finger
- Frequent exposure to water or moisture
Fungal Causes
Fungi are often responsible for chronic nail fold infections. Candida species, particularly Candida albicans, are the primary fungal agents involved. Fungal infections tend to develop slowly and are more common in individuals who frequently immerse their hands or feet in water. Factors that increase the risk of fungal nail fold infections include:
- Prolonged exposure to damp environments
- Weakened immune system
- Underlying health conditions like diabetes
- Wearing tight or poorly ventilated footwear
Other Contributing Factors
In addition to bacteria and fungi, several other factors can predispose individuals to nail fold infections:
- Allergic Reactions: Contact with harsh chemicals or allergens can irritate the skin and create an entry point for infections.
- Nail Disorders: Conditions like ingrown nails or psoriasis can damage the nail fold and increase susceptibility to infections.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hand or foot care can allow germs to thrive in the nail area.
Symptoms of Nail Fold Infections
The symptoms of nail fold infections vary depending on whether the infection is acute or chronic. Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent complications and ensure timely treatment.
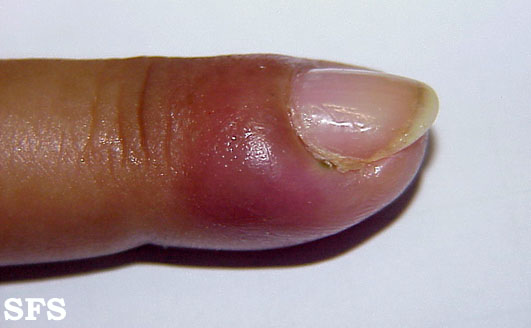
Symptoms of Acute Nail Fold Infections
Acute infections often present with sudden and noticeable symptoms. These may include:
- Redness and swelling around the nail
- Tenderness or pain in the affected area
- Pus-filled blisters or abscesses
- Warmth or heat emanating from the infected area
Symptoms of Chronic Nail Fold Infections
Chronic infections develop more gradually and may not cause immediate discomfort. However, they can lead to long-term damage if untreated. Symptoms of chronic infections include:
- Thickening or discoloration of the nail
- Persistent redness and swelling
- Dry, cracked skin around the nail
- Separation of the nail from the nail bed
Diagnosis of Nail Fold Infections
Diagnosing a nail fold infection typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. During the examination, the doctor will assess the appearance of the affected area and inquire about the patient’s medical history and potential risk factors. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis:
- Culture Test: A sample of pus or tissue may be collected to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
- Laboratory Analysis: Blood tests may be conducted to check for underlying conditions like diabetes or immune system disorders.
Treatment Options for Nail Fold Infections
The treatment for nail fold infections depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Both home remedies and medical interventions can effectively manage and resolve infections.
Home Remedies
Mild cases of nail fold infections can often be treated at home using simple remedies. These approaches focus on reducing inflammation and promoting healing:
- Warm Soaks: Soaking the affected area in warm water several times a day can help reduce swelling and draw out pus.
- Epsom Salt Baths: Adding Epsom salt to warm water can provide additional relief and aid in disinfection.
- Antiseptic Solutions: Applying over-the-counter antiseptic solutions can help kill bacteria and prevent the spread of infection.
Medical Treatments
For more severe or persistent infections, medical intervention may be necessary. Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections. Commonly used antibiotics include penicillin and clindamycin.
- Antifungal Medications: Antifungal creams or oral medications may be recommended for chronic infections caused by fungi.
- Incision and Drainage: If an abscess forms, a healthcare provider may need to make a small incision to drain the pus.
- Steroid Creams: In cases where inflammation is significant, steroid creams may be prescribed to reduce swelling.
Preventive Measures
Preventing nail fold infections involves adopting good hygiene practices and minimizing exposure to risk factors. Some effective preventive measures include:
- Avoid biting or picking at the nails
- Keep the hands and feet clean and dry
- Use gloves when handling chemicals or working in wet environments
- Trim nails carefully and avoid cutting the cuticles
- Choose breathable footwear and change socks regularly
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many nail fold infections can be managed at home, certain signs indicate the need for professional medical attention. These include:
- Severe pain or swelling that does not improve with home treatment
- Spreading redness or warmth around the affected area
- Fever or chills accompanying the infection
- Signs of nail deformity or permanent damage
Seeking prompt medical care in these situations can prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Complications of Untreated Nail Fold Infections
If left untreated, nail fold infections can lead to serious complications. These may include:
- Spread of Infection: The infection can spread to nearby tissues, leading to cellulitis or abscess formation.
- Nail Deformities: Chronic infections can cause permanent changes in the shape or structure of the nail.
- Osteomyelitis: In rare cases, the infection can spread to the bone, resulting in a condition known as osteomyelitis.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Individuals
Certain groups of people are more prone to developing nail fold infections due to underlying health conditions or lifestyle factors. These include:
- Individuals with Diabetes: Poor circulation and reduced immunity increase the risk of infections.
- Healthcare Workers: Frequent handwashing and exposure to moisture can damage the skin barrier.
- People with Immune System Disorders: Conditions like HIV or autoimmune diseases can impair the body’s ability to fight infections.
For these individuals, extra precautions and regular monitoring are essential to prevent and manage nail fold infections effectively.