Menopause marks a significant phase in a woman’s life, often referred to as the “change of life.” This natural biological process occurs when menstruation permanently stops, signaling the end of reproductive years. The term “menopause” is derived from two Greek words: “meno,” meaning month, and “pause,” meaning stop. While many women experience menopause between the ages of forty-five and fifty-five, the timing can vary widely. Understanding this transition, recognizing its symptoms, and learning how to manage them can help women navigate this stage with greater ease and confidence.
The Science Behind Menopause
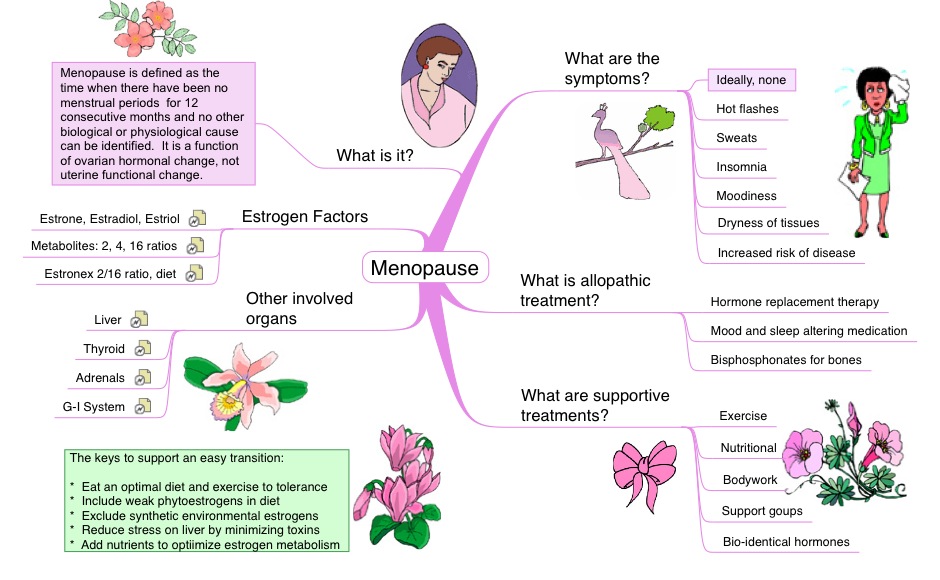
Menopause is not an overnight event but rather a gradual process that unfolds over several years. It begins with a transitional phase known as perimenopause, during which the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. This decline in hormone levels disrupts the regularity of menstrual cycles and leads to various physical and emotional changes. Eventually, the ovaries stop releasing eggs altogether, and menstruation ceases permanently.
The cessation of menstruation is confirmed when a woman has gone twelve consecutive months without a period. At this point, she is considered postmenopausal. While menopause is a natural part of aging, certain factors such as surgery, chemotherapy, or medical conditions can induce it prematurely.
Hormonal Changes During Menopause
The primary driver of menopause is the decline in estrogen and progesterone, two hormones produced by the ovaries. Estrogen plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle, maintaining bone density, and supporting cardiovascular health. As estrogen levels drop, the body undergoes a series of adjustments that manifest as physical and emotional symptoms.
Progesterone, another key hormone, also decreases during this time. Its reduction contributes to irregular periods and other changes associated with the transition. Understanding these hormonal shifts can help women better comprehend the symptoms they may experience and seek appropriate care.
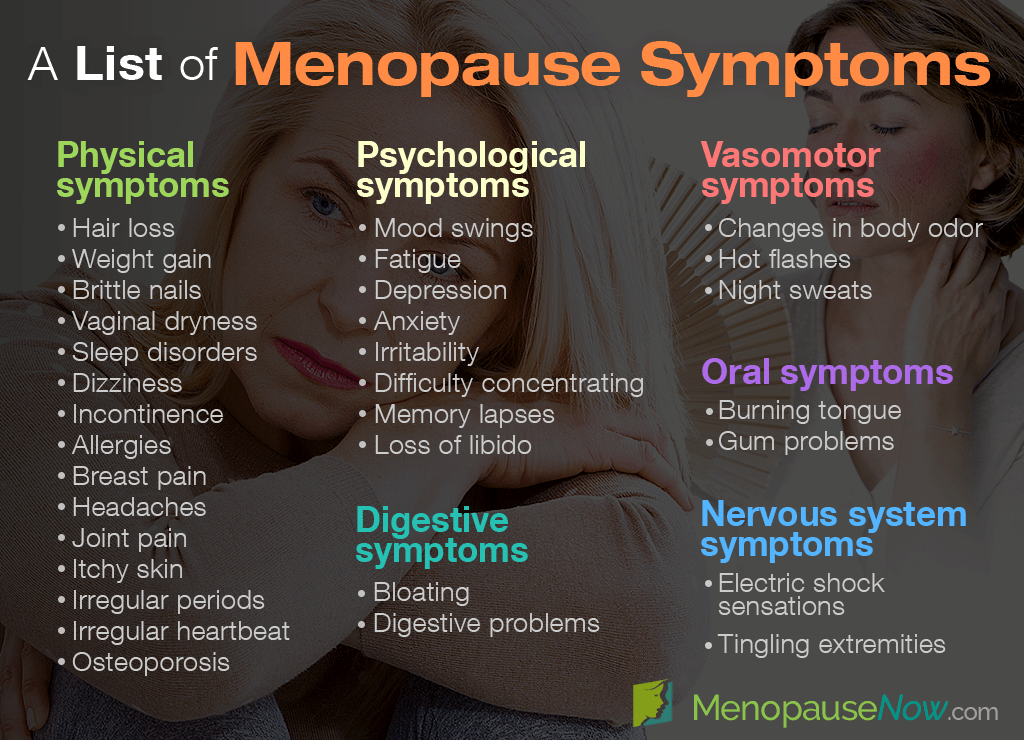
Common Symptoms of Menopause
Every woman’s experience with menopause is unique, but there are several common symptoms that many women encounter. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may persist for months or even years.
Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
One of the most well-known symptoms of menopause is hot flashes. These sudden waves of heat typically affect the upper body and face, causing flushing, sweating, and sometimes chills. Hot flashes can occur at any time of day and may last from a few seconds to several minutes. For some women, these episodes can be frequent and disruptive, affecting sleep and daily activities.
Night sweats, which are essentially hot flashes that occur during sleep, can lead to insomnia and fatigue. Disrupted sleep patterns can have a cascading effect on mood, concentration, and overall quality of life.
Vaginal Dryness and Sexual Health
As estrogen levels decline, many women experience vaginal dryness, itching, or discomfort. This condition, known as vaginal atrophy, can make sexual intercourse painful and reduce libido. Additionally, the thinning of vaginal tissues increases the risk of urinary tract infections and incontinence.
Despite these challenges, maintaining intimacy and sexual health during menopause is possible with proper care and communication. Open discussions with partners and healthcare providers can pave the way for effective solutions.
Mood Swings and Emotional Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during menopause can also impact mental health. Many women report experiencing mood swings, irritability, anxiety, or depression. These emotional changes may be exacerbated by sleep disturbances, stress, or other life transitions occurring simultaneously.
It is important to recognize that these feelings are normal and valid. Seeking support from loved ones or mental health professionals can provide valuable coping strategies and reassurance.
Other Physical Symptoms
- Weight Gain: Metabolic changes during menopause can lead to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
- Joint Pain: Some women experience stiffness or discomfort in their joints, which may be linked to declining estrogen levels.
- Hair and Skin Changes: Thinning hair, dry skin, and brittle nails are common due to reduced collagen production.
Managing Menopause Symptoms
While menopause cannot be prevented, its symptoms can often be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and alternative therapies. A personalized approach is essential, as each woman’s needs and preferences differ.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy habits can significantly alleviate menopause symptoms and improve overall well-being. Consider incorporating the following practices into your routine:
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, strengthens bones, and boosts mood. Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga are excellent options.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, which can trigger hot flashes.
- Prioritize Sleep: Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve sleep quality.
- Practice Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling can reduce stress and promote emotional balance.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy involves supplementing the body with estrogen and, in some cases, progesterone to alleviate menopause symptoms. This treatment can effectively reduce hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness while protecting against bone loss.
However, hormone replacement therapy is not suitable for everyone and carries potential risks, including an increased likelihood of blood clots, stroke, or certain cancers. Women considering this option should discuss their medical history and individual risk factors with their healthcare provider.
Non-Hormonal Treatments
For those who prefer non-hormonal approaches, several medications and therapies are available. Antidepressants, for example, can help manage mood swings and hot flashes. Vaginal moisturizers and lubricants can address vaginal dryness and improve comfort during intercourse.
Additionally, complementary therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and cognitive-behavioral therapy have shown promise in alleviating specific symptoms. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment to ensure safety and efficacy.
Embracing Menopause as a New Chapter
Menopause is more than just a biological process; it represents a profound shift in a woman’s life. While it comes with challenges, it also offers opportunities for growth, self-discovery, and renewed focus on personal well-being. By understanding the transition, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring effective management strategies, women can embrace this phase with resilience and grace.
Open conversations about menopause can help break down stigmas and empower women to seek the support they need. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, medical interventions, or community engagement, navigating menopause becomes a shared journey toward vitality and fulfillment.