An irregular heartbeat, medically referred to as arrhythmia (AH), occurs when the heart beats too fast, too slow, or in an irregular pattern. Arrhythmias can affect how well the heart works and may lead to serious complications if left untreated. This article explores the various types of irregular heartbeats, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments to help you better understand this condition.
What is an Irregular Heartbeat?
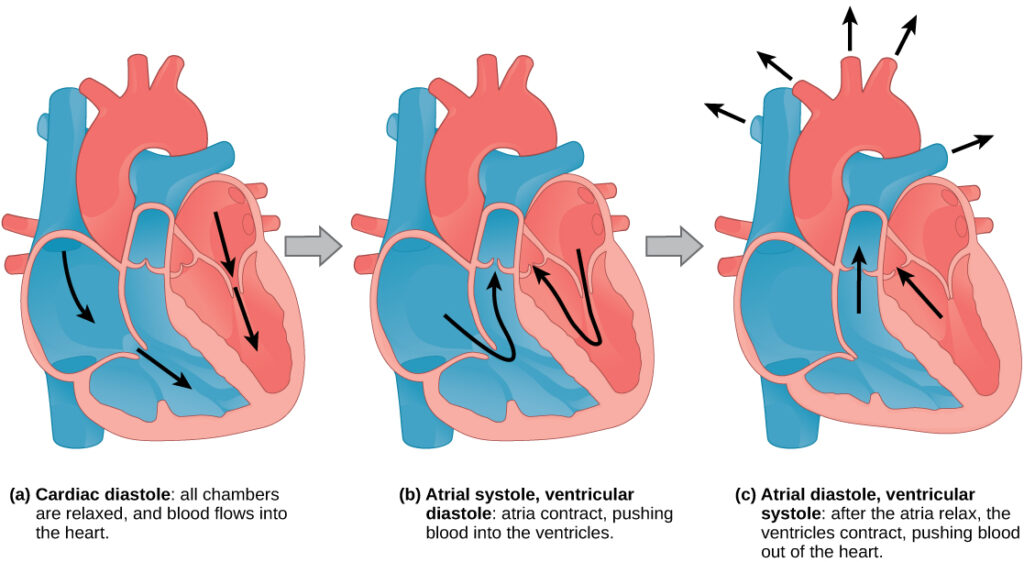
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It relies on electrical signals to maintain a steady rhythm. When these signals are disrupted, it can cause the heart to beat abnormally. An irregular heartbeat can occur in different parts of the heart and vary in severity, from harmless to life-threatening.
How Does the Heart Maintain Its Rhythm?
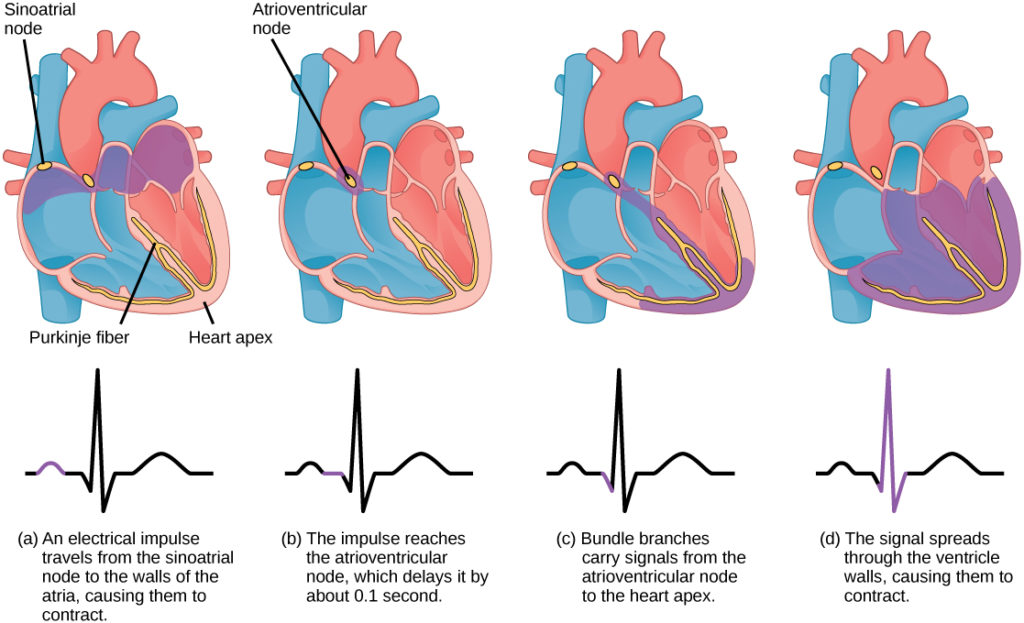
- The heart has its own natural pacemaker, called the sinoatrial node, which generates electrical impulses.
- These impulses travel through the heart, causing it to contract and pump blood efficiently.
- When something interferes with this process, an irregular heartbeat can occur.
Types of Irregular Heartbeats
There are several types of irregular heartbeats, each with unique characteristics. These types are classified based on where they originate in the heart and whether they cause the heart to beat too fast or too slow.
Tachycardia: A Fast Heart Rate
Tachycardia refers to a condition where the heart beats faster than normal. There are several subtypes of tachycardia:
- Atrial Fibrillation: The upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria, beat irregularly and often too quickly. This is one of the most common types of irregular heartbeat.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: The lower chambers of the heart, called the ventricles, beat too fast. This type can be dangerous if not treated promptly.
- Supraventricular Tachycardia: This involves rapid heartbeats that start above the ventricles. It is often less severe but can still cause discomfort.
Bradycardia: A Slow Heart Rate
Bradycardia occurs when the heart beats slower than normal. This can lead to insufficient blood flow to the body’s organs. Common forms include:
- Sick Sinus Syndrome: The sinoatrial node does not function properly, leading to alternating periods of fast and slow heart rates.
- Heart Block: Electrical signals between the upper and lower chambers of the heart are delayed or blocked, causing a slow heartbeat.
Premature Contractions
Premature contractions happen when the heart beats earlier than expected. These can occur in the atria or ventricles and are often harmless but may cause palpitations.
Causes of Irregular Heartbeats
Several factors can contribute to the development of an irregular heartbeat. Understanding these causes can help in prevention and management.
Lifestyle Factors
- Excessive consumption of alcohol or caffeine
- Smoking
- Stress or anxiety
- Lack of physical activity
Medical Conditions
- High blood pressure
- Coronary artery disease
- Thyroid disorders
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Medications and Substances
- Certain prescription medications
- Over-the-counter cold and allergy drugs
- Recreational drug use
Structural Changes in the Heart
In some cases, structural abnormalities in the heart, such as scarring from a previous heart attack or congenital defects, can disrupt the heart’s electrical system and lead to irregular heartbeats.
Symptoms of Irregular Heartbeats
Not all irregular heartbeats cause noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can range from mild to severe. Common signs include:
- Fluttering sensations in the chest
- Racing or pounding heartbeats
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting or near-fainting episodes
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately:
- Chest pain lasting more than a few minutes
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
- Severe shortness of breath
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat accompanied by confusion or extreme fatigue
Treatments for Irregular Heartbeats
The treatment for an irregular heartbeat depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle changes may be sufficient, while others may require medication or surgical intervention.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain changes to your daily habits can help manage and prevent irregular heartbeats:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Reducing salt intake to control blood pressure
- Limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption
- Quitting smoking
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation
Medications
Doctors may prescribe medications to control heart rate, restore normal rhythm, or prevent blood clots. Common medications include:
- Beta-blockers to slow the heart rate
- Antiarrhythmic drugs to stabilize the heart’s rhythm
- Anticoagulants to reduce the risk of stroke
Procedures and Surgeries
In more severe cases, medical procedures or surgeries may be necessary:
- Cardioversion: A procedure that uses electrical shocks to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure where abnormal heart tissue is destroyed to stop irregular signals.
- Pacemaker Implantation: A small device is placed under the skin to help regulate the heart’s rhythm.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: A device that monitors the heart and delivers shocks if dangerous rhythms are detected.
Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief through alternative therapies, although these should always be discussed with a healthcare provider:
- Acupuncture
- Herbal supplements (with caution, as some can interact with medications)
- Biofeedback techniques to manage stress
Living with an Irregular Heartbeat
While an irregular heartbeat can be concerning, many people live full and active lives with proper management. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, adherence to prescribed treatments, and a commitment to healthy living can make a significant difference.
Monitoring Your Condition
Keeping track of your symptoms and reporting any changes to your doctor is essential. Some individuals may benefit from wearable devices that monitor heart rate and rhythm continuously.
Support Systems
Living with an irregular heartbeat can sometimes feel overwhelming. Joining support groups or connecting with others who have similar conditions can provide emotional support and practical advice.