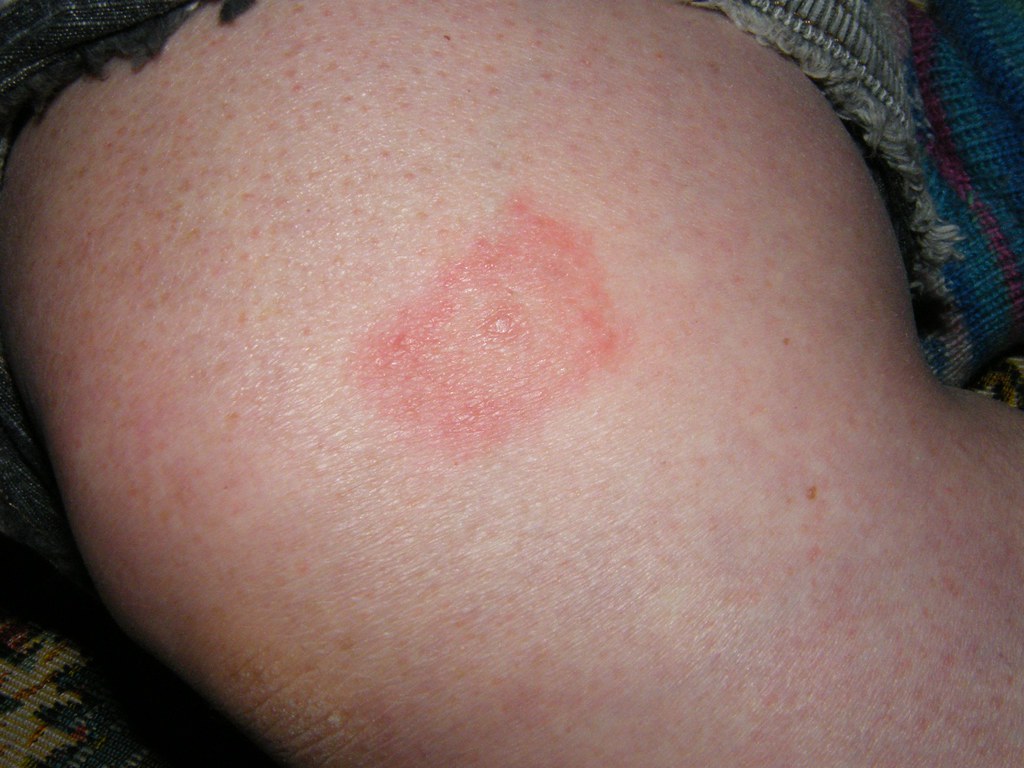
Insect bites and stings, often abbreviated as IBS, are common occurrences that can range from mildly irritating to potentially life-threatening. These encounters with insects such as mosquitoes, bees, wasps, spiders, and ticks can lead to a variety of reactions depending on the type of insect and the individual’s sensitivity. Understanding the types of bites and stings, recognizing their symptoms, and knowing how to prevent and treat them is essential for maintaining health and well-being.

Types of Insect Bites and Stings
Insects interact with humans in different ways, and their bites or stings can cause varying effects. Below are some of the most common types of insect bites and stings:
Mosquito Bites
Mosquitoes are small flying insects that feed on human blood. Their bites are usually itchy and leave behind small, red bumps. While most mosquito bites are harmless, they can transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus.
Bee and Wasp Stings
Bees and wasps use their stingers as a defense mechanism. A bee sting typically leaves a sharp pain followed by swelling and redness. Bees leave their stinger embedded in the skin, while wasps can sting multiple times without losing their stinger. In some cases, these stings can trigger severe allergic reactions.
Spider Bites
Most spider bites are harmless and cause minor irritation. However, bites from certain species, such as black widows or brown recluses, can be dangerous. These bites may result in intense pain, muscle cramps, or even systemic symptoms like fever and nausea.
Tick Bites
Ticks are small arachnids that attach themselves to the skin to feed on blood. Tick bites are often painless, but they can transmit serious illnesses such as Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Flea Bites
Fleas are tiny insects that commonly infest pets and can bite humans. Flea bites appear as small, red, itchy bumps, often clustered around the ankles or lower legs. They can cause discomfort and, in rare cases, transmit diseases.
Fire Ant Stings
Fire ants deliver painful stings that result in burning sensations and raised welts. Some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to fire ant venom, which can lead to more severe symptoms.
Symptoms of Insect Bites and Stings
The symptoms of insect bites and stings vary depending on the type of insect and the individual’s immune response. Here are some common symptoms associated with different types of bites and stings:
Mild Reactions
- Redness and swelling at the site of the bite or sting
- Itching or mild pain
- A small bump or welt
Moderate Reactions
- Significant swelling that extends beyond the bite area
- Persistent itching or pain
- Development of blisters or hives
Severe Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat
- Nausea or vomiting
Severe reactions require immediate medical attention, as they can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Prevention of Insect Bites and Stings
Preventing insect bites and stings is key to avoiding discomfort and potential health risks. Here are some effective strategies to minimize exposure to biting and stinging insects:
Wear Protective Clothing
When spending time outdoors, especially in wooded or grassy areas, wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, socks, and closed-toe shoes. Light-colored clothing is less attractive to insects and makes it easier to spot ticks or other pests.
Use Insect Repellents
Insect repellents containing active ingredients such as DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus can help keep insects at bay. Apply repellent to exposed skin and clothing, following the instructions on the product label.
Avoid Peak Activity Times
Many insects, such as mosquitoes and certain types of flies, are most active during dawn and dusk. Plan outdoor activities accordingly to reduce the risk of bites.
Keep Living Spaces Insect-Free
Install screens on windows and doors to prevent insects from entering your home. Use bed nets in areas where mosquitoes are prevalent, and regularly check pets for fleas and ticks.
Eliminate Standing Water
Mosquitoes breed in standing water, so remove any sources of stagnant water around your home, such as flower pots, buckets, or birdbaths. This simple step can significantly reduce mosquito populations.
Treatment of Insect Bites and Stings
While most insect bites and stings can be managed at home, it is important to know how to treat them properly to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Here are some general guidelines for treating different types of bites and stings:
First Aid for Mild Reactions
- Clean the affected area with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
- Apply a cold compress or ice pack to reduce swelling and numb the area.
- Use over-the-counter creams or ointments containing hydrocortisone or calamine to relieve itching.
- Take oral antihistamines if itching persists or becomes bothersome.
Removing Bee Stingers
If a bee stinger is left in the skin, remove it promptly using a flat object like a credit card or your fingernail. Avoid using tweezers, as squeezing the stinger can release more venom into the skin.
Treating Tick Bites
If you find a tick attached to your skin, use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp it as close to the skin’s surface as possible. Pull upward with steady, even pressure to avoid breaking the tick’s mouthparts. After removal, clean the bite area and your hands thoroughly with rubbing alcohol or soap and water.
Managing Severe Reactions
For individuals experiencing severe allergic reactions, immediate medical intervention is necessary. Call emergency services if symptoms of anaphylaxis occur. If available, administer epinephrine using an auto-injector and monitor the person until help arrives.
Seeking Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
- Symptoms of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or pus
- Persistent or worsening pain and swelling
- Signs of a systemic illness, such as fever, chills, or body aches
- A bite or sting from a potentially dangerous insect, such as a black widow spider or brown recluse
Special Considerations for Children and Pets
Children
Children are more susceptible to insect bites and stings due to their smaller size and tendency to play outdoors. Teach children to avoid swatting at insects and to stay away from nests or hives. Monitor them closely for signs of allergic reactions and seek medical care if needed.
Pets
Pets, particularly dogs and cats, are prone to flea and tick infestations. Regular grooming and the use of preventive treatments can help protect them from these pests. Check your pets frequently for ticks, especially after walks in wooded areas, and consult a veterinarian if you notice unusual symptoms.
Conclusion
While this article does not include a conclusion, it provides comprehensive information on insect bites and stings, including their types, symptoms, prevention, and treatment. By understanding these aspects, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the impact of insect encounters on their health and daily lives.