Inflammation of veins, commonly referred to as phlebitis, is a condition that affects the vascular system. It occurs when a vein becomes inflamed, leading to discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. Phlebitis can occur in both superficial veins, which are close to the surface of the skin, and deep veins, which are located deeper within the body. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options are essential for managing this condition effectively.

What is Inflammation of Veins?
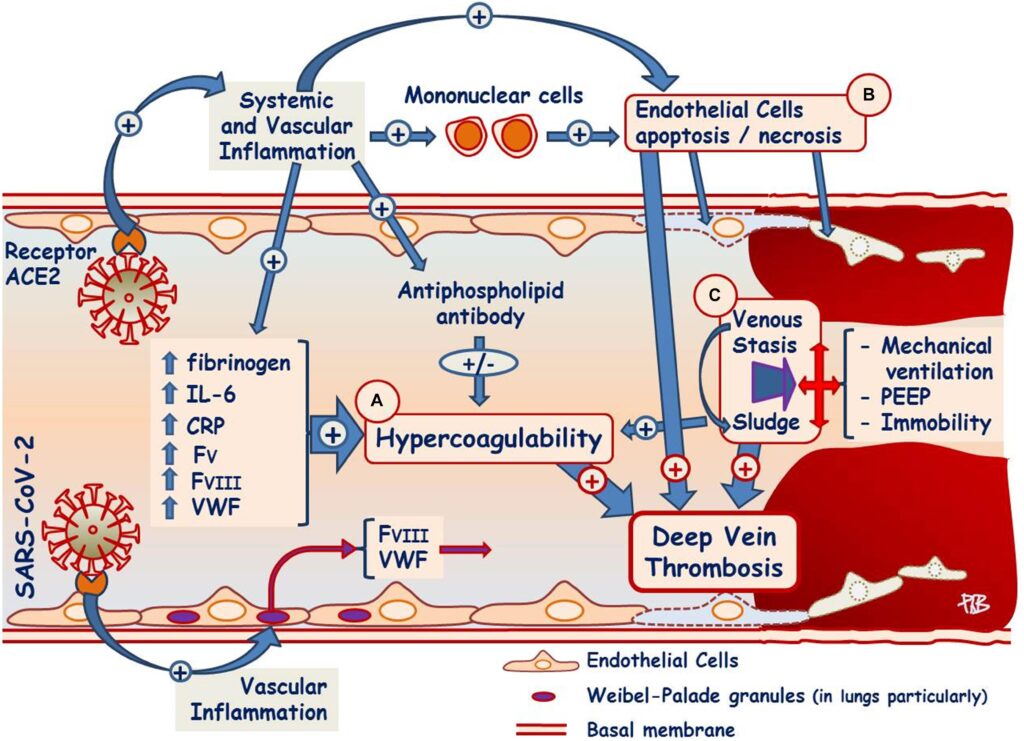
Inflammation of veins refers to the swelling and irritation of the walls of a vein. This condition can develop due to various factors, including injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions. When a vein becomes inflamed, it can lead to pain, redness, and warmth around the affected area. The severity of the condition depends on whether it affects superficial or deep veins.
Superficial inflammation of veins typically occurs in veins near the surface of the skin and is often less serious. On the other hand, deep vein inflammation, also known as deep vein thrombophlebitis, involves veins located deeper in the body and can pose more significant health risks, such as blood clots.
Causes of Inflammation of Veins
The inflammation of veins can result from a variety of causes. Below are some of the most common factors that contribute to this condition:
1. Prolonged Inactivity
- Prolonged periods of sitting or lying down can slow blood flow through the veins, increasing the risk of inflammation.
- This is particularly common during long flights, bed rest after surgery, or extended periods of immobility.
2. Trauma or Injury
- Injuries to the veins, such as those caused by intravenous catheters or needles, can irritate the vein walls and lead to inflammation.
- Physical trauma, such as bruising or damage to the veins, can also trigger this condition.
3. Blood Clot Formation
- Blood clots can form within the veins, obstructing blood flow and causing inflammation.
- This is especially common in individuals with conditions like deep vein thrombosis.
4. Infections
- Infections in the surrounding tissues can spread to the veins, leading to inflammation.
- Bacterial infections are a common cause of this type of vein inflammation.
5. Underlying Medical Conditions
- Certain medical conditions, such as varicose veins, autoimmune disorders, and cancer, can increase the likelihood of vein inflammation.
- Conditions that affect blood clotting, such as thrombophilia, can also contribute to this problem.
6. Medications and Treatments
- Some medications, particularly those administered intravenously, can irritate the veins and cause inflammation.
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy may also increase the risk of vein inflammation.
Symptoms of Inflammation of Veins
The symptoms of inflammation of veins vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Some of the most common signs include:
1. Pain and Tenderness
- Affected veins often become painful to the touch, with tenderness extending along the length of the vein.
- The pain may worsen when pressure is applied to the area or during movement.
2. Redness and Warmth
- The skin over the inflamed vein may appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- This is a result of increased blood flow and immune response in the affected area.
3. Swelling
- Swelling may occur around the inflamed vein, leading to puffiness and discomfort.
- In cases of deep vein inflammation, swelling may extend to the surrounding tissues.
4. Visible Veins
- In superficial inflammation, the affected vein may become more prominent and visible under the skin.
- The vein may feel hard or cord-like to the touch.
5. Fever and Chills
- In cases where an infection is present, individuals may experience fever and chills.
- These systemic symptoms indicate that the body is fighting off an infection.
6. Skin Discoloration
- Chronic inflammation of veins can lead to changes in skin color, such as darkening or discoloration.
- This is often seen in individuals with long-standing varicose veins.
Treatment Options for Inflammation of Veins
Treating inflammation of veins involves addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms. The approach to treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Below are some of the most common treatment options:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoiding prolonged periods of inactivity is crucial for preventing and managing vein inflammation.
- Regular movement, such as walking or stretching, can improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of blood clots.
2. Compression Therapy
- Compression stockings or bandages can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow in the affected area.
- This is particularly effective for individuals with superficial vein inflammation.
3. Medications
- Anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can help reduce pain and swelling.
- In cases of deep vein inflammation, blood thinners may be prescribed to prevent blood clots.
- Antibiotics may be necessary if an infection is present.
4. Warm Compresses
- Applying warm compresses to the affected area can provide relief from pain and discomfort.
- This method helps improve blood flow and reduce inflammation.
5. Elevation
- Elevating the affected limb above heart level can reduce swelling and promote healing.
- This is particularly beneficial for individuals with leg vein inflammation.
6. Surgical Interventions
- In severe cases, surgical removal of the affected vein may be necessary.
- This is typically reserved for individuals with recurrent or chronic vein inflammation.
7. Thrombolytic Therapy
- For deep vein inflammation accompanied by blood clots, thrombolytic therapy may be used to dissolve the clot.
- This treatment involves the administration of medications that break down blood clots.
Preventing Inflammation of Veins
While not all cases of vein inflammation can be prevented, certain measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition:
1. Stay Active
- Engaging in regular physical activity promotes healthy blood circulation and reduces the risk of blood clots.
- Simple exercises, such as walking or swimming, can be highly beneficial.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins, increasing the likelihood of inflammation.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and exercise can help prevent this condition.
3. Avoid Smoking
- Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs circulation, making individuals more susceptible to vein inflammation.
- Quitting smoking can improve overall vascular health.
4. Stay Hydrated
- Proper hydration supports healthy blood flow and reduces the risk of clot formation.
- Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential for maintaining vascular health.
5. Monitor Medical Conditions
- Individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or varicose veins, should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage these issues effectively.
- Regular check-ups can help detect and address potential problems early.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild cases of vein inflammation can often be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. These include:
- Sudden swelling, pain, or redness in the leg, which may indicate deep vein thrombosis.
- Fever, chills, or signs of infection, such as pus or drainage from the affected area.
- Shortness of breath or chest pain, which could suggest a pulmonary embolism.
- Persistent symptoms that do not improve with self-care measures.
If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical evaluation promptly to prevent complications.