Hidradenitis Suppurativa, often abbreviated as HS, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition is characterized by painful lumps, abscesses, and scarring under the skin, primarily in areas where the skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, and buttocks. Despite its prevalence, it remains one of the most misunderstood and underdiagnosed conditions in dermatology. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and care options for Hidradenitis Suppurativa to help raise awareness and provide guidance for those affected.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
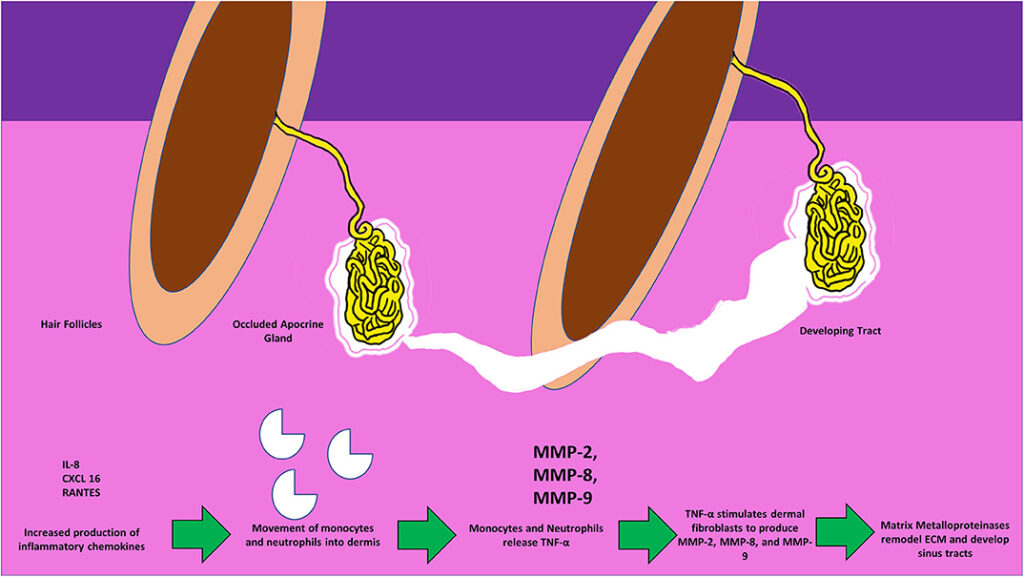
Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a long-term skin disorder that causes small, painful lumps to form under the skin. These lumps can break open and lead to abscesses, tunnels under the skin, and significant scarring. The condition typically begins after puberty and tends to worsen over time if left untreated. It is not contagious, but it can have a profound impact on a person’s quality of life due to the pain, discomfort, and emotional distress it causes.
Common Areas Affected
- Armpits
- Groin
- Buttocks
- Under the breasts
- Inner thighs
Causes of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
The exact cause of this condition is still not fully understood, but researchers believe it involves a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Below are some of the leading theories about what contributes to the development of this condition:
Genetic Factors
Many individuals with this condition have a family history of the disorder, suggesting that genetics may play a role. Specific genes related to the immune system and inflammation have been identified in some cases, but more research is needed to understand how these genes contribute to the condition.
Immune System Dysfunction
This condition is thought to be linked to an abnormal immune response. Instead of targeting harmful invaders like bacteria or viruses, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, causing inflammation and blockages. This leads to the formation of painful lumps and abscesses.
Hormonal Influence
Hormones, particularly sex hormones like androgens, may also play a role in the development of this condition. Many people notice that their symptoms worsen during hormonal changes, such as during menstruation or pregnancy. This suggests that hormonal fluctuations could trigger flare-ups.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking and obesity, are strongly associated with this condition. Smoking can increase inflammation in the body, while excess weight can create friction and pressure in areas prone to outbreaks. Stress and poor hygiene practices may also exacerbate symptoms.
Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
The symptoms of this condition vary from person to person, depending on the severity of the disease. However, there are some common signs that most individuals experience. Recognizing these symptoms early can help with timely diagnosis and treatment.
Early Symptoms
- Small, painful bumps under the skin
- Blackheads or pitted scars in areas where the skin rubs together
- Mild itching or discomfort in affected areas
Advanced Symptoms
- Persistent abscesses or boils that rupture and drain pus
- Tunnels or tracts forming under the skin, connecting multiple abscesses
- Thick, rope-like scars in areas where the skin has healed
- Chronic pain and discomfort, especially during movement
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Beyond the physical symptoms, this condition can take a toll on mental health. Many individuals experience feelings of embarrassment, shame, or isolation due to the visible nature of the condition. Anxiety and depression are common among those living with this condition, highlighting the need for both medical and psychological support.
Diagnosis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Diagnosing this condition can be challenging because its symptoms often mimic other skin disorders, such as acne, boils, or folliculitis. There is no specific test to confirm the presence of this condition, so healthcare providers rely on a combination of physical exams, medical history, and ruling out other potential causes.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will examine the affected areas of the skin, looking for characteristic signs such as recurring abscesses, blackheads, and scarring. They may also ask about the frequency and duration of flare-ups.
Ruling Out Other Conditions
To ensure an accurate diagnosis, doctors may perform tests to rule out infections, cysts, or other skin conditions. For example, a sample of pus or fluid from an abscess may be sent to a lab to check for bacterial infections.
Severity Staging
Once diagnosed, the condition is often classified into stages based on its severity. This helps guide treatment decisions and monitor progression over time. The stages include:
- Mild: Occasional boils and abscesses with minimal scarring
- Moderate: Recurrent abscesses, some tunneling, and moderate scarring
- Severe: Widespread abscesses, extensive tunneling, and significant scarring
Treatment and Care Options
While there is currently no cure for this condition, various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s needs and the severity of their condition.
Medications
Several medications are commonly used to treat this condition, including:
- Antibiotics: These help reduce inflammation and prevent secondary infections.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Oral or topical medications can help control inflammation and relieve pain.
- Hormonal therapies: Birth control pills or other hormone-regulating medications may help manage symptoms in some individuals.
- Biologics: Advanced treatments like biologic drugs target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue, drain abscesses, or eliminate tunnels under the skin. Surgical options include:
- Incision and drainage: A temporary solution to relieve pain and remove pus from abscesses.
- Excision: Removing affected skin and allowing healthy tissue to heal.
- Laser therapy: Used to destroy hair follicles and reduce the risk of future flare-ups.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups:
- Weight management: Losing excess weight can reduce friction and pressure on affected areas.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can lower inflammation and improve overall health.
- Wearing loose clothing: Avoiding tight-fitting clothes can minimize irritation and discomfort.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or therapy can help reduce stress-related flare-ups.
Supportive Therapies
In addition to medical treatments, supportive therapies can play a crucial role in managing this condition:
- Pain management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
- Psychological support: Counseling or support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of the condition.
- Nutritional counseling: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce symptoms.
Living with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Living with this condition requires patience, resilience, and a proactive approach to managing symptoms. While it can be challenging, many individuals find ways to adapt and lead fulfilling lives. Building a strong support network, staying informed about treatment options, and advocating for oneself in healthcare settings are essential steps toward better management of the condition.
Tips for Managing Daily Life
- Keep affected areas clean and dry to prevent infections.
- Use warm compresses to soothe pain and promote drainage of abscesses.
- Follow a consistent skincare routine to minimize irritation.
- Educate friends and family about the condition to foster understanding and support.