Pregnancy is a time of joy and anticipation, but it can also bring challenges that require careful medical attention. One such challenge is HELLP Syndrome, a life-threatening condition that affects pregnant women. The acronym stands for Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, and Low Platelet Count, and it often occurs in conjunction with preeclampsia. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications of this serious pregnancy complication.
Understanding the Condition
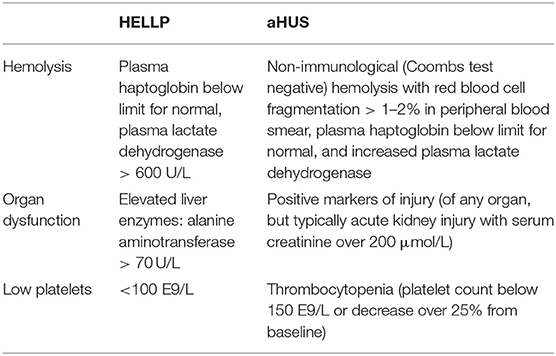
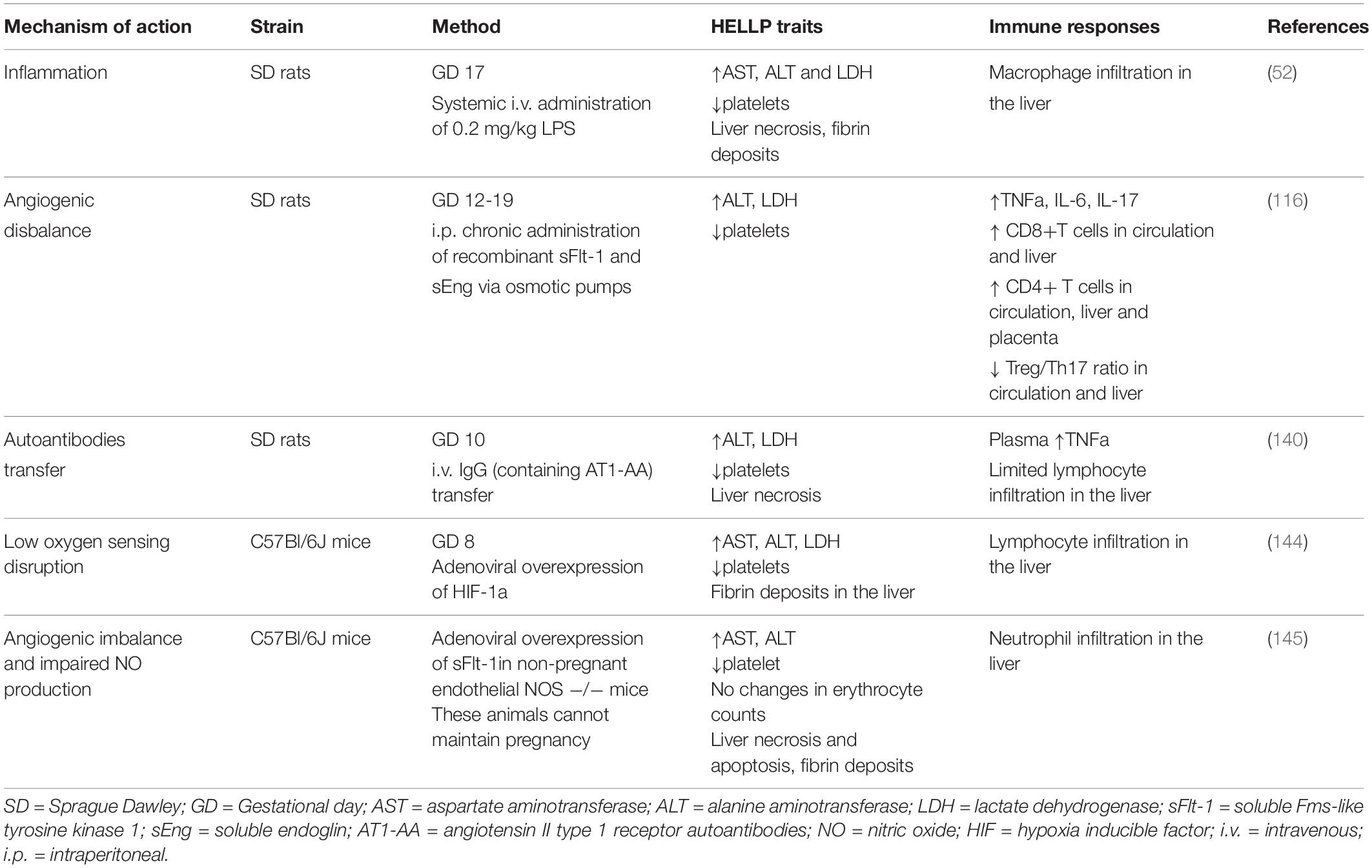
This syndrome is a rare but severe disorder that typically arises during the later stages of pregnancy, though it can also occur shortly after childbirth. It is considered a variant of preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs, most commonly the liver and kidneys. While the exact cause remains unknown, researchers believe it involves abnormalities in the placenta and the body’s immune response.
Key Components of the Disorder
- Hemolysis: This refers to the breakdown of red blood cells, which can lead to anemia and other complications.
- Elevated Liver Enzymes: When liver cells are damaged, enzymes leak into the bloodstream, causing elevated levels that indicate liver dysfunction.
- Low Platelet Count: Platelets are essential for blood clotting. A reduced count increases the risk of bleeding and complicates any necessary medical procedures.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Understanding these risks can help healthcare providers identify at-risk patients and take preventive measures.
Common Risk Factors
- A history of preeclampsia or similar conditions in previous pregnancies.
- Being over the age of 35.
- Having a multiple pregnancy, such as twins or triplets.
- Preexisting health conditions like diabetes, obesity, or kidney disease.
- First-time pregnancy or a gap of more than ten years between pregnancies.
Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of this condition can be vague and easily mistaken for other issues, making early detection challenging. However, recognizing these signs is crucial for timely intervention.
Common Symptoms
- Severe headaches that do not respond to pain relievers.
- Pain in the upper right abdomen, often under the ribs.
- Nausea and vomiting, especially if sudden and persistent.
- Swelling, particularly in the hands and face.
- High blood pressure and protein in the urine, which may indicate preeclampsia.
- Fatigue and general malaise.
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing this condition requires a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Early and accurate diagnosis is critical to prevent complications for both the mother and the baby.
Steps Involved in Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess symptoms such as abdominal pain, swelling, and high blood pressure.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure liver enzyme levels, platelet count, and signs of red blood cell breakdown.
- Urine Analysis: Checking for protein in the urine helps determine if preeclampsia is present.
- Ultrasound: Imaging may be used to evaluate the health of the fetus and the placenta.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, prompt treatment is essential to manage the condition and reduce risks to both the mother and the baby. The primary goal is to stabilize the mother’s condition while preparing for the safe delivery of the baby.
Immediate Interventions
- Hospitalization: Most cases require close monitoring in a hospital setting to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Medications: Blood pressure medications may be prescribed to control hypertension. Steroids might be administered to improve platelet count and accelerate fetal lung development.
- Delivery: In many cases, delivering the baby is the most effective way to resolve the condition. The timing depends on the severity of the symptoms and the gestational age of the baby.
Post-Delivery Care
Even after childbirth, the mother may require ongoing care to ensure her body recovers fully. Liver function and blood counts are monitored closely, and additional treatments may be necessary to address lingering issues.
Potential Complications
If left untreated, this condition can lead to severe and potentially fatal complications for both the mother and the baby. Awareness of these risks underscores the importance of early detection and treatment.
Complications for the Mother
- Liver rupture or hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening.
- Kidney failure or acute respiratory distress syndrome.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation, a condition where blood clots form throughout the body.
- Stroke due to uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Complications for the Baby
- Premature birth, which can result in developmental delays and health issues.
- Low birth weight due to restricted growth in the womb.
- Stillbirth in severe cases where the condition is not managed promptly.
Preventive Measures
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent this condition, certain steps can reduce the risk and promote a healthier pregnancy.
Strategies for Prevention
- Attend all prenatal appointments to monitor blood pressure and overall health.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Manage preexisting conditions like diabetes and hypertension with the help of a healthcare provider.
- Be vigilant about reporting unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Living with the Condition
For women who have experienced this condition, understanding its long-term implications is important. While most women recover fully after delivery, some may face ongoing health challenges.
Long-Term Considerations
- Follow-up appointments to monitor liver function and blood pressure.
- Emotional support to cope with the stress and anxiety of a high-risk pregnancy.
- Planning for future pregnancies with guidance from healthcare professionals.
Raising Awareness
Education and awareness play a vital role in reducing the impact of this condition. By understanding its symptoms and risks, women and their families can advocate for timely medical care and better outcomes.
How to Spread Awareness
- Share information with friends, family, and community groups.
- Support organizations dedicated to maternal health and pregnancy-related research.
- Encourage open conversations about pregnancy complications to reduce stigma and fear.