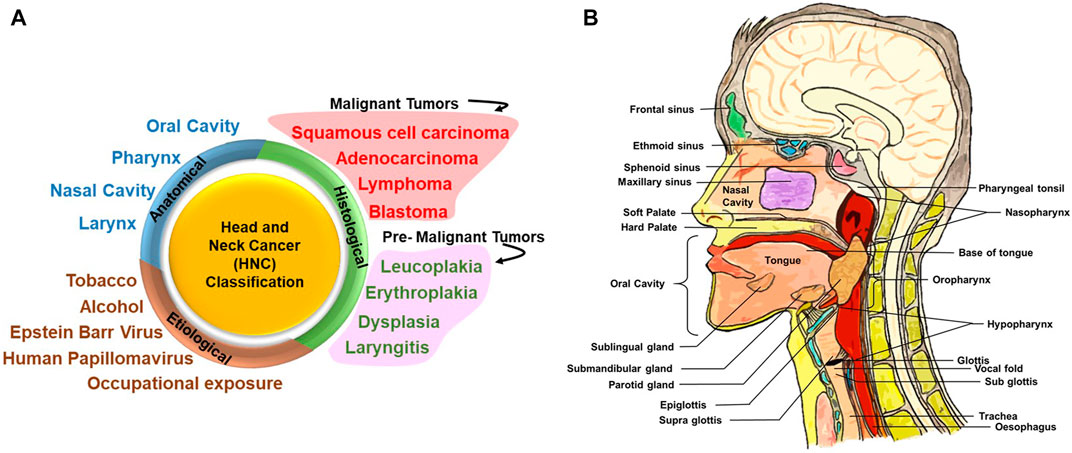
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that develop in the tissues and organs of the head and neck region. These include cancers of the oral cavity, throat, voice box, nasal cavity, and salivary glands. Often abbreviated as HNC, these cancers account for a significant number of cancer cases worldwide. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and effective management.
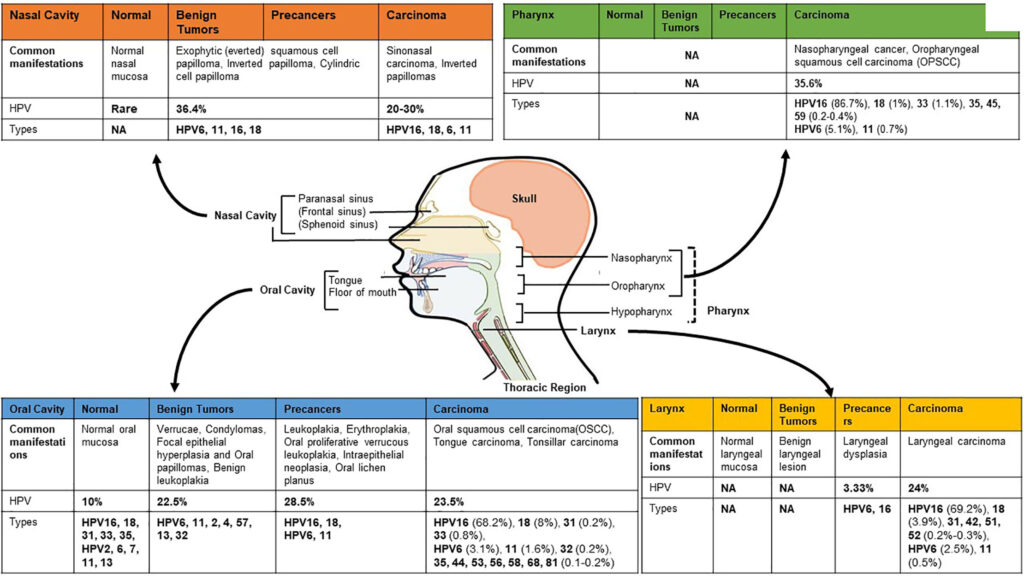
Types of Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancers are categorized based on the specific area where they originate. Below are the primary types:
Cancer of the Oral Cavity
This type of cancer develops in the mouth, including the lips, gums, inner lining of the cheeks, tongue, and the floor or roof of the mouth. It is often linked to tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption.
Oropharyngeal Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer occurs in the oropharynx, which includes the base of the tongue, tonsils, and the middle part of the throat. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a significant risk factor for this type of cancer.
Laryngeal Cancer
Laryngeal cancer affects the voice box, an organ involved in breathing, speaking, and protecting the airway during swallowing. Chronic smoking and heavy alcohol use are common causes.
Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer arises in the lower part of the throat, near the esophagus and trachea. This type is relatively rare but often diagnosed at advanced stages due to its subtle early symptoms.
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancer originates in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nose. It is more prevalent in certain regions, such as Southeast Asia, and is associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection.
Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer
This type involves the nasal passages and the hollow spaces in the bones around the nose, known as paranasal sinuses. Exposure to wood dust and certain chemicals increases the risk.
Salivary Gland Cancer
Salivary gland cancer develops in the glands responsible for producing saliva. While most salivary gland tumors are benign, some can be malignant.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of head and neck cancers is influenced by various factors. Some of the most common causes and risk factors include:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, as well as chewing tobacco, significantly increases the risk of head and neck cancers.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking, especially when combined with tobacco use, raises the likelihood of developing these cancers.
- Infections: Certain viral infections, such as human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus, are linked to specific types of head and neck cancers.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting dental care and oral health can contribute to the development of oral cavity cancers.
- Exposure to Harmful Substances: Prolonged exposure to asbestos, wood dust, and industrial chemicals increases the risk.
- Family History: A family history of head and neck cancers may predispose individuals to these conditions.
Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancer
The symptoms of head and neck cancers vary depending on the location and stage of the disease. Some common signs include:
- A persistent sore throat or hoarseness that does not improve
- Difficulty swallowing or pain while swallowing
- Unexplained weight loss
- A lump or sore in the mouth or throat that does not heal
- Swelling or a mass in the neck
- Chronic ear pain or hearing problems
- Nosebleeds or blocked sinuses
- Changes in voice or speech
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by less serious conditions. However, if they persist for more than two weeks, medical evaluation is recommended.
Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer
Diagnosing head and neck cancers involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory procedures. The following steps are typically taken:
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will examine the head and neck region for any abnormalities, such as lumps, sores, or discoloration. They may also assess the function of the voice box and throat.
Imaging Tests
Imaging techniques like X-rays, computed tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography scans help identify tumors and determine their size and location.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from the suspected area for microscopic examination. This is the definitive method for diagnosing cancer.
Endoscopy
An endoscope, a thin tube with a camera, may be used to examine the throat, voice box, and other areas that are difficult to see externally.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests and other laboratory analyses may be conducted to assess overall health and detect markers of cancer.
Treatment Options for Head and Neck Cancer
Treatment for head and neck cancers depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment approaches include:
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is often the first line of treatment. Depending on the extent of the cancer, surgeons may remove part or all of the affected organ. In some cases, reconstructive surgery is required to restore appearance and function.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery and chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often administered intravenously and may cause side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. This approach minimizes damage to healthy cells and is often used for advanced or recurrent cancers.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It has shown promise in treating certain types of head and neck cancers, particularly those associated with human papillomavirus.
Rehabilitation and Supportive Care
After treatment, patients may require rehabilitation to regain speech, swallowing, and other functions. Supportive care, including nutritional support and pain management, is also essential for improving quality of life.
Prevention Strategies
While not all head and neck cancers can be prevented, adopting certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
- Avoid tobacco products and limit alcohol consumption.
- Maintain good oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly.
- Get vaccinated against human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus.
- Use protective equipment when exposed to harmful substances at work.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
By understanding the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for head and neck cancers, individuals can take proactive steps toward early detection and better outcomes.