Geographic Tongue, also known as Benign Migratory Glossitis or Erythema Migrans, is a harmless yet often misunderstood condition that affects the surface of the tongue. While it may sound alarming due to its name, this condition is neither serious nor contagious. It is characterized by irregular, smooth, red patches on the tongue that resemble a map, hence the term “geographic.” This article delves into the details of Geographic Tongue, exploring its symptoms, potential causes, and ways to manage and care for it.
Understanding Geographic Tongue
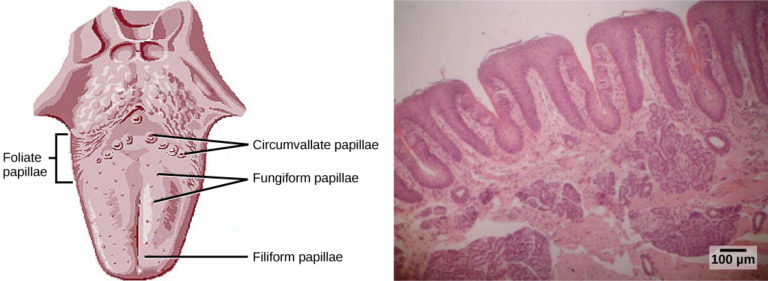
Geographic Tongue is a condition that primarily affects the top surface of the tongue. The tongue normally has tiny bumps called papillae, which give it a rough texture. In individuals with Geographic Tongue, some areas lose these papillae, leading to the formation of smooth, red patches. These patches can change in size, shape, and location over time, creating a migratory pattern.
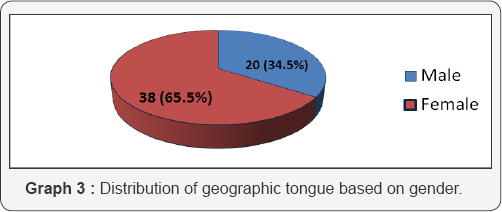
This condition is relatively common, affecting between one and three percent of the population. It can occur at any age but is more frequently observed in adults. Interestingly, Geographic Tongue does not seem to have a gender bias, affecting both men and women equally. Despite its prevalence, many people remain unaware of what it is and how it manifests.
Symptoms of Geographic Tongue
The most noticeable symptom of Geographic Tongue is the appearance of irregular, red patches on the tongue’s surface. These patches are typically smooth and lack the small bumps that cover the rest of the tongue. Below are some key characteristics of the symptoms:
- Map-like Appearance: The patches often resemble a map, with distinct borders that may be slightly raised and white in color.
- Migratory Nature: The affected areas tend to shift over time, changing in size, shape, and location. This movement gives the condition its descriptive name.
- Painless in Most Cases: For many individuals, Geographic Tongue is asymptomatic, meaning it does not cause pain or discomfort. However, some may experience mild irritation or sensitivity.
- Sensitivity to Certain Foods: People with Geographic Tongue might find that spicy, acidic, or hot foods trigger a burning sensation or discomfort.
It is important to note that while Geographic Tongue is generally harmless, its unusual appearance can sometimes cause anxiety or concern. If you notice persistent changes in your tongue’s appearance, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and reassurance.
Potential Causes of Geographic Tongue
The exact cause of Geographic Tongue remains unknown, but researchers have identified several factors that may contribute to its development. While no definitive answers exist, the following possibilities have been explored:
Genetic Factors
There is evidence to suggest that Geographic Tongue may have a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. This indicates that certain inherited traits could predispose someone to Geographic Tongue.
Psoriasis Connection
Some studies have found a link between Geographic Tongue and psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin. Both conditions involve abnormal cell turnover and inflammation, leading researchers to speculate that they may share underlying mechanisms.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty, have been associated with Geographic Tongue. This suggests that hormonal imbalances may play a role in triggering or exacerbating the condition.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Certain nutritional deficiencies, particularly those involving vitamins B and zinc, have been linked to Geographic Tongue. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients may help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Stress and Immune System Factors
Stress and immune system dysfunction are other potential contributors. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to various conditions, including Geographic Tongue.
While these factors provide some insight into the possible causes, it is important to recognize that Geographic Tongue can occur without any identifiable triggers. Its unpredictable nature makes it challenging to pinpoint a single cause.
Caring for Geographic Tongue
Since Geographic Tongue is benign and typically resolves on its own, treatment is usually unnecessary. However, there are steps you can take to manage any discomfort and maintain oral health:
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Practicing good oral hygiene is crucial for overall oral health and can help minimize irritation caused by Geographic Tongue. Brush your teeth twice a day, floss daily, and use an antibacterial mouthwash to keep your mouth clean and free of harmful bacteria.
Avoid Irritating Foods
If you experience sensitivity or discomfort, try avoiding foods that irritate the tongue. Spicy, acidic, or very hot foods can exacerbate symptoms. Opt for milder options and see if your symptoms improve.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can worsen dryness and irritation in the mouth. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps keep the mouth moist and reduces the likelihood of discomfort.
Use a Soft Toothbrush
Using a soft-bristled toothbrush can prevent further irritation of the tongue. Harsh brushing can aggravate the sensitive areas and lead to increased discomfort.
Consider Dietary Supplements
If nutritional deficiencies are suspected, consider incorporating supplements into your diet under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Vitamins B and zinc, in particular, may support tongue health.
Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience persistent symptoms or are concerned about the appearance of your tongue, seek advice from a dentist or doctor. They can rule out other conditions and provide personalized recommendations for managing Geographic Tongue.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While Geographic Tongue is generally harmless, there are instances where medical attention may be necessary. If you notice any of the following, consult a healthcare professional promptly:
- Persistent pain or discomfort that does not improve with self-care measures.
- Signs of infection, such as swelling, pus, or fever.
- Changes in the tongue’s appearance accompanied by other systemic symptoms, such as fatigue or weight loss.
These could indicate an underlying issue that requires further investigation. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough examination and recommend appropriate tests to determine the cause of your symptoms.
Living with Geographic Tongue
For most individuals, Geographic Tongue is a temporary and manageable condition. Its benign nature means that it rarely impacts daily life significantly. However, understanding the condition and knowing how to care for your tongue can make a difference in minimizing discomfort and maintaining peace of mind.
Education and awareness are key to addressing concerns related to Geographic Tongue. By staying informed and adopting healthy habits, you can effectively manage this condition and focus on enjoying a healthy, balanced lifestyle.