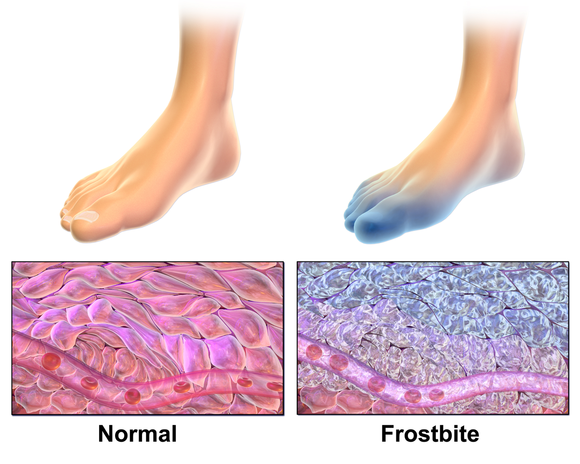
Frostbite, also known as congelatio in medical terms, is a condition that occurs when skin and underlying tissues freeze due to prolonged exposure to cold temperatures. It is most commonly seen in regions with extreme winter climates but can occur anywhere if conditions are right. Frostbite requires prompt attention to prevent long-term damage or complications. This article explores the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for frostbite.

What Causes Frostbite?
Frostbite occurs when the body’s natural response to cold leads to reduced blood flow to extremities such as fingers, toes, ears, and the nose. The body prioritizes keeping vital organs warm, which can result in decreased circulation to areas farthest from the heart. When these areas remain exposed to freezing temperatures for too long, ice crystals form in the tissues, causing cell damage.
Factors That Increase Risk
- Prolonged Exposure to Cold: Staying outside in freezing temperatures without proper protection significantly raises the risk of frostbite.
- Wet Conditions: Moisture accelerates heat loss from the body, making wet clothing or skin more susceptible to frostbite.
- Wind Chill: Wind increases the rate at which heat escapes from exposed skin, lowering the effective temperature experienced by the body.
- Tight Clothing: Wearing tight shoes, gloves, or other garments can restrict blood flow, increasing vulnerability to frostbite.
- Health Conditions: Certain medical issues like diabetes, poor circulation, or peripheral neuropathy can heighten the risk of developing frostbite.
Symptoms of Frostbite
The severity of frostbite can vary depending on how deeply the tissue has been affected. Symptoms often progress through stages, starting with mild discomfort and potentially leading to severe damage if untreated.
Early Signs
- Cold Skin: Affected areas may feel unusually cold compared to surrounding parts of the body.
- Numbness: A tingling sensation or complete numbness may develop in the affected area.
- Red or Pale Skin: Initially, the skin might appear red, but it can quickly turn pale or even blue as frostbite worsens.
Advanced Symptoms
- Hardened Skin: As frostbite progresses, the skin may become hard and waxy to the touch.
- Blisters: In moderate to severe cases, blisters filled with clear fluid or blood may form after rewarming.
- Loss of Function: Muscles and joints near the frostbitten area may lose their ability to move properly.
- Gangrene: If left untreated, frostbite can lead to tissue death, resulting in blackened skin and potential amputation.
Treatment Options for Frostbite
Immediate action is critical when treating frostbite. Delayed or improper care can exacerbate the injury and increase the likelihood of permanent damage.
First Aid Measures
- Seek Shelter: Move the person out of the cold environment into a warm, dry space as soon as possible.
- Remove Wet Clothing: Take off any damp or restrictive clothing to prevent further heat loss.
- Rewarm Gradually: Immerse the affected area in warm (not hot) water between ninety-nine and one hundred four degrees Fahrenheit for twenty to thirty minutes. Avoid using direct heat sources like stoves or heating pads, as they can cause burns.
- Avoid Rubbing: Do not rub or massage the frostbitten area, as this can cause additional tissue damage.
- Elevate the Area: Keep the frostbitten part elevated to reduce swelling.
Medical Intervention
In cases where frostbite is severe, professional medical treatment is essential. Healthcare providers may administer medications to improve blood flow and manage pain. They might also use specialized techniques such as:
- Thrombolytic Therapy: Medications that dissolve blood clots and restore circulation to damaged tissues.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: This involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber to promote healing.
- Surgical Procedures: In extreme cases, surgery may be necessary to remove dead tissue or amputate severely damaged areas.
Preventing Frostbite
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when dealing with frostbite. By taking simple precautions, you can protect yourself and others from this painful condition.
Dress Appropriately
- Layer Clothing: Wear multiple layers of loose-fitting, moisture-wicking fabrics to trap warmth and allow sweat to evaporate.
- Cover Extremities: Use waterproof gloves, socks, hats, and scarves to shield vulnerable areas from the cold.
- Choose Insulated Footwear: Opt for boots with good insulation and traction to keep feet warm and safe.
Stay Dry
Moisture significantly increases the risk of frostbite. To stay dry:
- Change out of wet clothes immediately.
- Use waterproof gear during snowy or rainy weather.
- Avoid activities that cause excessive sweating in cold environments.
Limit Time Outdoors
If temperatures are dangerously low, limit your time outside. Plan breaks indoors to warm up periodically, and never ignore signs of discomfort or early frostbite symptoms.
Monitor Weather Conditions
Check forecasts regularly before heading outdoors. Pay attention to both air temperature and wind chill, as these factors combined determine how quickly frostbite can occur.
Travel Safely
When traveling in cold climates, carry emergency supplies such as blankets, hand warmers, and extra clothing. Let someone know your plans and expected return time so help can be sent if needed.
Educate Yourself and Others
Understanding the risks and recognizing early warning signs can make all the difference. Share knowledge about frostbite prevention and treatment with family, friends, and colleagues who spend time in cold environments.