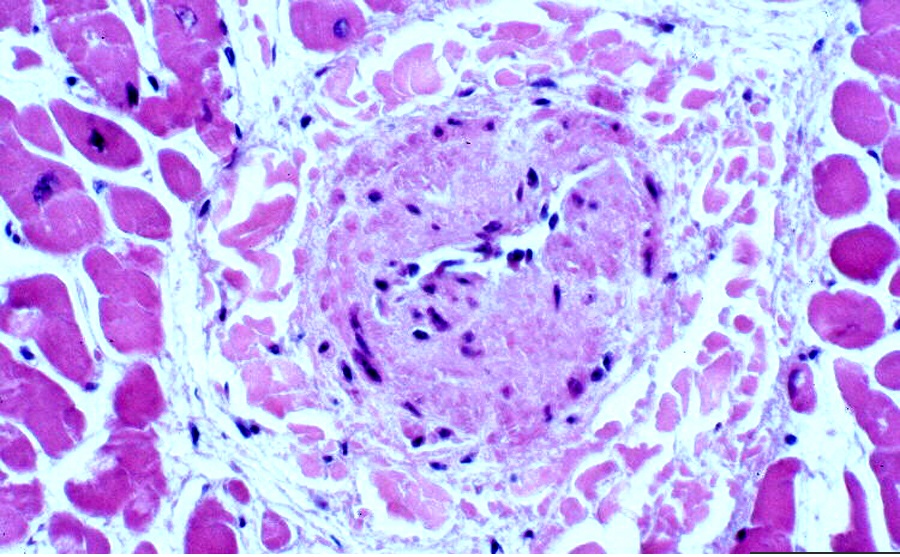
Fibromuscular dysplasia, often abbreviated as FMD, is a rare medical condition that affects the arteries of the body. This disorder causes abnormal cell development in the walls of the arteries, leading to narrowing, bulging, or tearing of the blood vessels. Although it can occur in any artery, it most commonly affects the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys and brain. Despite being relatively uncommon, fibromyalgia dysplasia has significant implications for cardiovascular health and requires careful management. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options associated with this complex condition.
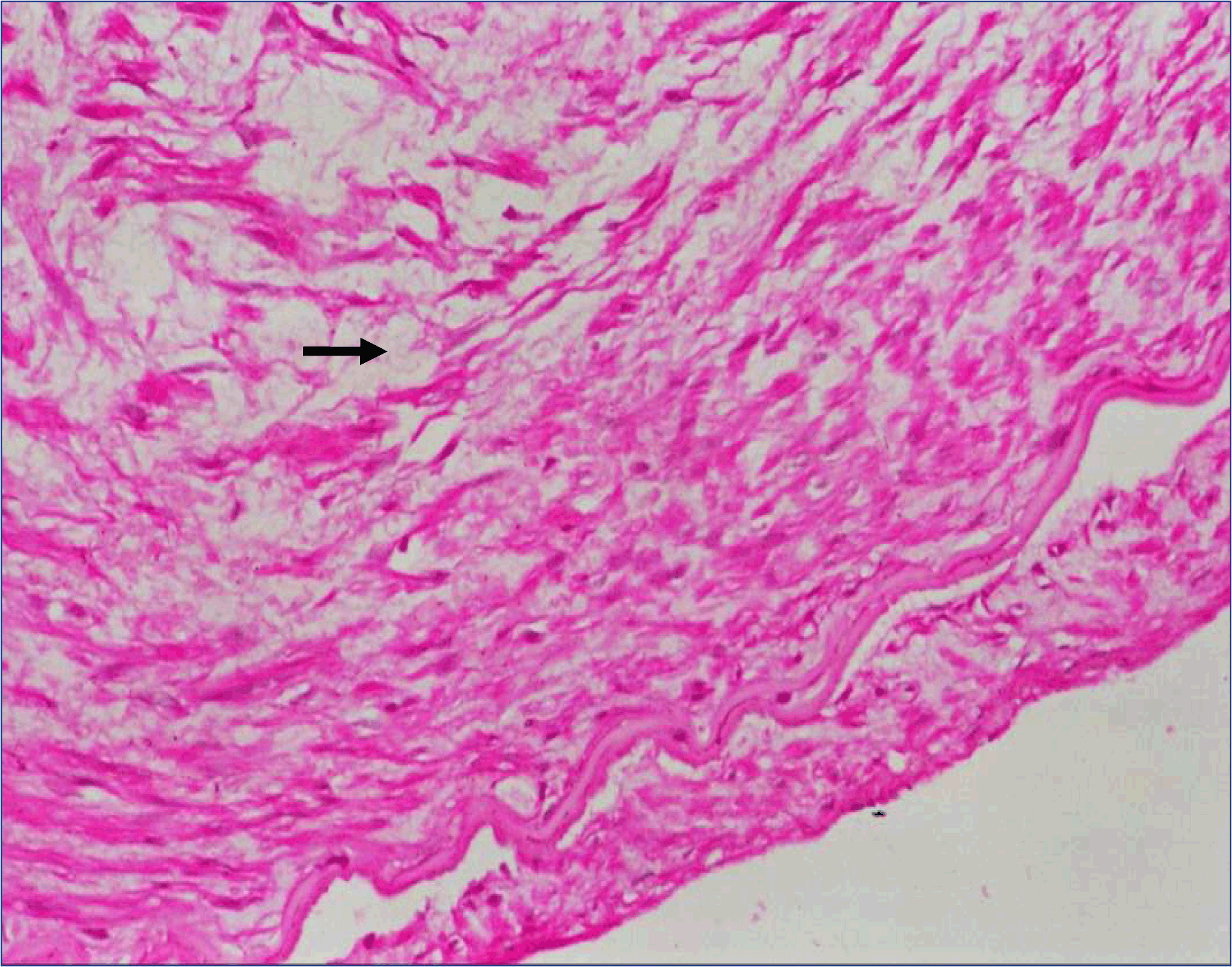
Understanding Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Fibromuscular dysplasia is a non-inflammatory vascular disease that primarily impacts medium-sized arteries. The condition leads to irregular thickening or thinning of the arterial walls, causing structural abnormalities such as stenosis (narrowing), aneurysms (bulging), or dissections (tearing). These changes can restrict blood flow, increase the risk of clot formation, or lead to complications like high blood pressure or stroke.
How Does It Develop?
The exact cause of fibromuscular dysplasia remains unknown, but researchers believe it may result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies suggest that hormonal influences could play a role, as the condition is more frequently observed in women than in men. Additionally, certain genetic predispositions might make individuals more susceptible to developing the disorder. While trauma or injury to the arteries is not considered a direct cause, these factors could potentially exacerbate existing abnormalities.
Symptoms of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
The symptoms of this artery disorder vary depending on which arteries are affected and the severity of the condition. In some cases, individuals may remain asymptomatic until complications arise. However, common signs and symptoms include:
- High Blood Pressure: Narrowed arteries supplying the kidneys can lead to elevated blood pressure levels, a condition known as renovascular hypertension.
- Headaches and Dizziness: When the arteries supplying the brain are involved, patients may experience frequent headaches, dizziness, or ringing in the ears.
- Neck Pain: Dissections or aneurysms in the carotid arteries can cause neck pain or discomfort.
- Chest Pain: If the coronary arteries are affected, chest pain or heart-related issues may occur.
- Pulsatile Tinnitus: A whooshing sound in the ears caused by turbulent blood flow near the auditory system.
It is important to note that symptoms can mimic other conditions, making diagnosis challenging without proper evaluation.
Diagnosing Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Diagnosing fibromuscular dysplasia typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging tests, and sometimes invasive procedures. Early detection is crucial to prevent complications and manage the condition effectively.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination. They will inquire about symptoms, family history of vascular diseases, and any risk factors such as smoking or hormonal imbalances. During the physical exam, they may check for signs of high blood pressure, abnormal pulses, or bruits (abnormal sounds heard over narrowed arteries).
Imaging Tests
Several imaging techniques are used to visualize the arteries and identify abnormalities:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the arteries. Doppler ultrasound can assess blood flow patterns.
- CT Angiography: This test combines X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the arteries.
- MRI Angiography: Magnetic resonance imaging provides highly detailed images of the arteries without using radiation.
- Catheter-Based Angiography: An invasive procedure where a contrast dye is injected into the arteries, allowing them to be visualized under X-ray. This method is considered the gold standard for diagnosing fibromuscular dysplasia.
Treatment Options for Fibromuscular Dysplasia
While there is no cure for fibromuscular dysplasia, various treatments aim to manage symptoms, improve blood flow, and reduce the risk of complications. The approach depends on the location and severity of the affected arteries.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making healthy lifestyle choices can help manage symptoms and prevent further progression of the disease:
- Blood Pressure Control: Maintaining optimal blood pressure through diet, exercise, and medications if necessary is essential to protect the arteries.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking damages blood vessels and worsens vascular conditions, so quitting is strongly recommended.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall cardiovascular health.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate physical activity improves circulation and reduces stress on the arteries.
Medications
Medications are often prescribed to address specific symptoms or complications:
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Medications such as ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers help lower blood pressure.
- Antiplatelet Therapy: Aspirin or similar drugs reduce the risk of blood clots forming in narrowed arteries.
- Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels and support artery health.
Interventional Procedures
In cases where medication and lifestyle changes are insufficient, interventional procedures may be necessary:
- Angioplasty: A minimally invasive procedure where a balloon-tipped catheter is used to widen narrowed arteries. Stents may also be placed to keep the artery open.
- Surgical Repair: For severe cases involving aneurysms or dissections, surgery may be required to repair or bypass the damaged artery.
Complications Associated with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
If left untreated, fibromuscular dysplasia can lead to serious complications, including:
- Stroke: Narrowed or torn arteries supplying the brain increase the risk of stroke.
- Kidney Failure: Reduced blood flow to the kidneys can impair their function over time.
- Heart Attack: Coronary artery involvement raises the likelihood of myocardial infarction.
- Ruptured Aneurysm: Bulging arteries may rupture, causing life-threatening internal bleeding.
Living with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Managing fibromuscular dysplasia requires ongoing care and vigilance. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed. Patients should also stay informed about their health and advocate for themselves when seeking care.
Support Resources
Connecting with support groups or organizations dedicated to fibromuscular dysplasia can provide valuable resources and emotional support. Sharing experiences with others who understand the challenges of living with this condition can foster a sense of community and empowerment.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research continues to shed light on the underlying mechanisms of fibromuscular dysplasia and explore new treatment options. Participating in clinical trials or staying updated on scientific advancements can offer hope for improved therapies in the future.