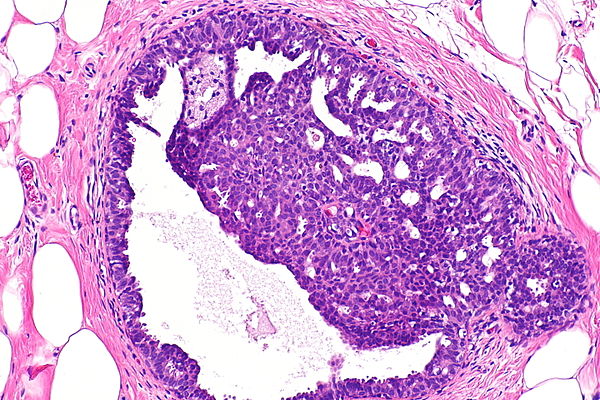
Fibrocystic breast changes, often abbreviated as FBC, are a common condition that affects many women at some point in their lives. These changes are not harmful and are considered a normal variation of breast tissue. Understanding what fibrocystic breast changes are, what causes them, how to identify their symptoms, and how to manage them can help alleviate concerns and promote better breast health.
What Are Fibrocystic Breast Changes?
Fibrocystic breast changes refer to the development of lumpy or rope-like areas in the breasts. These changes are not a disease but rather a benign condition that occurs due to fluctuations in hormone levels. The term “fibrocystic” describes two characteristics of the breast tissue: fibrous and cystic. Fibrous tissue feels firm and rubbery, while cystic tissue consists of fluid-filled sacs. Together, these changes create a texture that may feel uneven or dense.
It is important to note that fibrocystic breast changes do not increase the risk of developing breast cancer. However, because they can cause discomfort and mimic other breast conditions, it is essential to monitor any changes and consult a healthcare provider if needed.
Causes of Fibrocystic Breast Changes
The exact cause of fibrocystic breast changes is not fully understood, but researchers believe that hormonal fluctuations play a significant role. Here are some factors that contribute to this condition:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Changes in estrogen and progesterone levels during the menstrual cycle can lead to the formation of lumps and cysts in the breast tissue. Estrogen promotes cell growth, while progesterone helps regulate this growth. An imbalance between these hormones can result in excessive tissue development.
- Monthly Menstrual Cycle: Many women experience fibrocystic changes in relation to their menstrual periods. As hormone levels rise and fall, the breast tissue may become more tender, swollen, or lumpy.
- Caffeine Consumption: Some studies suggest that caffeine may exacerbate fibrocystic breast changes, although the evidence is not conclusive. Reducing caffeine intake may help alleviate symptoms for some women.
- Genetic Predisposition: Women with a family history of fibrocystic breast changes may be more likely to experience this condition themselves.
While these factors are commonly associated with fibrocystic breast changes, it is important to remember that every woman’s body is unique. Not all women will experience the same triggers or symptoms.
Symptoms of Fibrocystic Breast Changes
The symptoms of fibrocystic breast changes can vary from person to person. Some women may experience mild discomfort, while others may have more pronounced symptoms. Common signs include:
- Breast Lumps: The most noticeable symptom is the presence of lumps or thickened areas in the breast tissue. These lumps are usually movable and may feel rubbery or firm.
- Breast Pain: Many women report tenderness, soreness, or aching in the breasts. This pain is often cyclical, meaning it occurs in relation to the menstrual cycle and subsides afterward.
- Breast Swelling: The breasts may feel fuller or heavier than usual, especially before menstruation.
- Nipple Discharge: In some cases, women may notice a clear or milky discharge from the nipples. This is typically harmless but should be evaluated by a healthcare provider if it occurs frequently or is accompanied by other symptoms.
It is worth noting that fibrocystic breast changes are more common in women of reproductive age and tend to decrease after menopause when hormone levels stabilize.
Diagnosis of Fibrocystic Breast Changes
If you notice any unusual changes in your breasts, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can perform a clinical breast examination to assess the texture and consistency of the breast tissue. In some cases, additional tests may be recommended to rule out other conditions, such as:
- Mammogram: This imaging test uses low-dose X-rays to examine the breast tissue. It can help identify any abnormalities and determine whether further evaluation is needed.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the breast tissue. It is particularly useful for distinguishing between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts.
- Breast Biopsy: If a lump appears suspicious, a biopsy may be performed to remove a small sample of tissue for analysis. This test can confirm whether the lump is benign or requires further treatment.
While fibrocystic breast changes are generally harmless, it is always better to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare provider about any concerns.
Care and Management of Fibrocystic Breast Changes
Although fibrocystic breast changes cannot be cured, there are several strategies to manage symptoms and improve comfort. Here are some approaches to consider:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing caffeine intake, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and maintaining a healthy weight can help minimize symptoms. Some women find relief by increasing their intake of foods rich in vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, so incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises may be beneficial.
Medications and Supplements
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, can help reduce breast pain and inflammation.
- Vitamin Supplements: Some studies suggest that vitamin E and evening primrose oil may help alleviate symptoms. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Medical Interventions
- Aspiration of Cysts: If a cyst is particularly large or painful, a healthcare provider may use a fine needle to drain the fluid. This procedure can provide immediate relief.
- Hormonal Therapy: In rare cases, hormonal medications may be prescribed to regulate hormone levels and reduce symptoms. This approach is typically reserved for women with severe symptoms that do not respond to other treatments.
Regular Monitoring
Women with fibrocystic breast changes should perform regular self-examinations to monitor their breast tissue for any new or unusual changes. Familiarizing yourself with the normal texture and appearance of your breasts can help you detect potential issues early. Additionally, scheduling routine mammograms and clinical breast exams as recommended by your healthcare provider is crucial for maintaining breast health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While fibrocystic breast changes are generally benign, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. These include:
- A lump that feels hard, immovable, or irregular in shape
- Persistent nipple discharge, especially if it is bloody
- Redness, warmth, or swelling in the breast tissue
- Unexplained changes in the size or shape of the breast
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider promptly to rule out other conditions, such as infection or malignancy.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with fibrocystic breast changes can sometimes cause anxiety or stress, especially if the symptoms are uncomfortable or persistent. It is important to remember that this condition is common and not harmful. Seeking support from loved ones or joining a support group can help alleviate emotional distress. Additionally, discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider can provide reassurance and guidance.