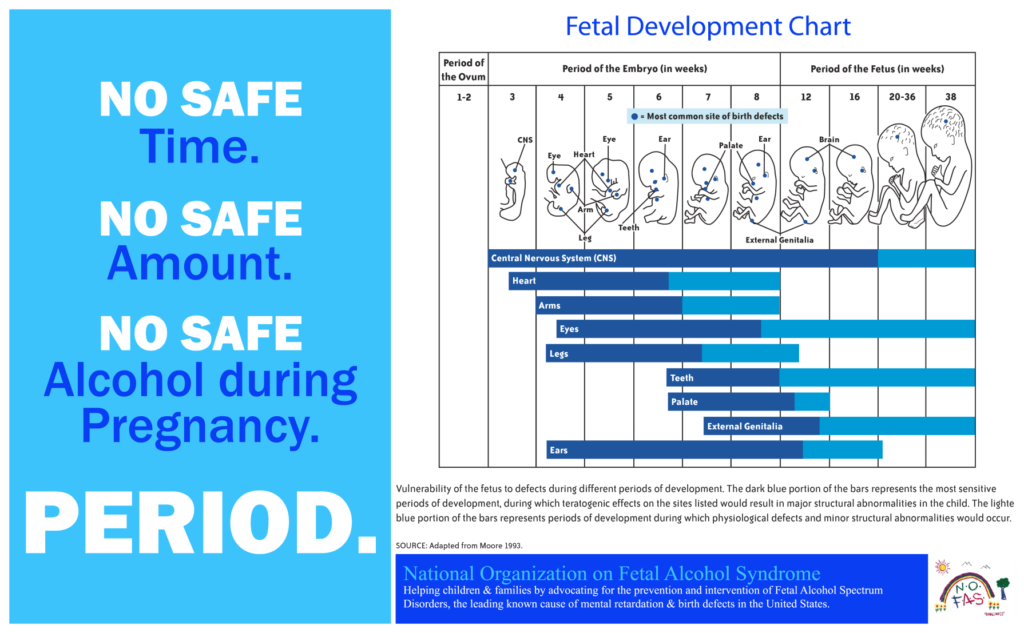
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, often abbreviated as FAS, is a serious condition that affects children whose mothers consumed alcohol during pregnancy. This condition can lead to lifelong physical, behavioral, and cognitive challenges for the child. Understanding the causes, recognizing the effects, and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial steps in addressing this preventable yet devastating condition.

Understanding the Causes of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
The primary cause of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy. When a pregnant woman drinks alcohol, it passes through the placenta and enters the bloodstream of the developing fetus. The fetus metabolizes alcohol much more slowly than an adult, leading to higher concentrations of alcohol in its system. This prolonged exposure disrupts normal development, particularly affecting the brain and other vital organs.
How Alcohol Affects the Developing Fetus
- Brain Development: Alcohol interferes with the growth and organization of brain cells, leading to structural abnormalities in the brain. This disruption can result in cognitive impairments, learning difficulties, and behavioral problems.
- Growth Restriction: Exposure to alcohol can hinder the overall growth of the fetus, resulting in low birth weight and stunted physical development.
- Facial Deformities: Alcohol consumption during critical stages of fetal development can lead to distinctive facial features, such as a smooth ridge between the nose and upper lip, small eye openings, and a thin upper lip.
Risk Factors That Increase the Likelihood of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Certain factors can increase the risk of a child being born with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. These include:
- Binge Drinking: Consuming large amounts of alcohol in a short period significantly raises the risk of harm to the fetus.
- Chronic Alcohol Use: Regular and heavy drinking throughout pregnancy poses a greater threat to fetal development.
- Poor Nutrition: A lack of proper nutrition during pregnancy can exacerbate the harmful effects of alcohol on the developing fetus.
- Lack of Prenatal Care: Women who do not receive adequate prenatal care may be unaware of the risks associated with alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
The Effects of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
The effects of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome can vary widely depending on the timing, frequency, and amount of alcohol exposure during pregnancy. However, the consequences are often severe and long-lasting, impacting multiple aspects of a child’s life.
Physical Effects
Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome often exhibit a range of physical abnormalities, including:
- Distinctive Facial Features: As mentioned earlier, these include a smooth philtrum (the groove between the nose and upper lip), a thin upper lip, and small eye openings.
- Growth Deficiencies: Many affected children experience slow growth both before and after birth, leading to shorter-than-average height and lower-than-average weight.
- Organ Abnormalities: Alcohol exposure can cause malformations in the heart, kidneys, and other organs, potentially leading to chronic health issues.
Cognitive and Behavioral Effects
The cognitive and behavioral effects of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome are among the most challenging aspects of the condition. These effects can include:
- Learning Disabilities: Children with this syndrome often struggle with reading, writing, math, and problem-solving skills.
- Memory Problems: Impaired memory can make it difficult for children to retain information and apply it in various situations.
- Attention Deficits: Many affected children have difficulty focusing, staying organized, and completing tasks.
- Behavioral Issues: Hyperactivity, impulsivity, and poor social skills are common, making it challenging for children to interact with peers and authority figures.
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome can extend into adulthood. Individuals with this condition may face challenges such as:
- Difficulty Maintaining Employment: Cognitive and behavioral impairments can hinder job performance and career advancement.
- Mental Health Disorders: Depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues are prevalent among individuals with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome.
- Substance Abuse: There is a higher risk of developing substance abuse problems later in life.
- Legal and Social Challenges: Poor decision-making and impulsive behavior can lead to legal troubles and strained relationships.
Prevention Strategies for Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
The good news is that Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is entirely preventable. By taking proactive measures, women can ensure the health and well-being of their unborn children. Below are some effective prevention strategies:
Avoiding Alcohol During Pregnancy
The single most important step in preventing Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is abstaining from alcohol during pregnancy. Even small amounts of alcohol can pose risks, so complete avoidance is recommended. Women who are planning to become pregnant should also stop drinking alcohol to ensure a healthy start to their pregnancy.
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the dangers of alcohol consumption during pregnancy is critical. Educational campaigns targeting women of childbearing age, healthcare providers, and the general public can help spread the message that no amount of alcohol is safe during pregnancy. Schools, community organizations, and healthcare facilities can play a vital role in disseminating this information.
Access to Prenatal Care
Regular prenatal care is essential for monitoring the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Healthcare providers can offer guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including avoiding alcohol, smoking, and other harmful substances. Early and consistent prenatal care can also help identify potential risks and address them promptly.
Support for Women Struggling with Alcohol Dependence
Some women may find it challenging to stop drinking due to addiction or other underlying issues. Providing access to support services, such as counseling, rehabilitation programs, and support groups, can help these women overcome their dependence on alcohol. Friends, family members, and healthcare providers should encourage women to seek help without judgment or stigma.
Policy Measures and Public Health Initiatives
Governments and public health organizations can implement policies to reduce alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Examples include:
- Warning Labels: Requiring clear warning labels on alcoholic beverages about the risks of drinking during pregnancy.
- Screening Programs: Incorporating alcohol screening into routine healthcare visits for women of childbearing age.
- Funding for Research: Supporting research efforts to better understand the effects of alcohol on fetal development and improve prevention strategies.
Community Involvement
Communities can also contribute to prevention efforts by creating supportive environments for pregnant women. This includes offering resources such as parenting classes, affordable childcare, and access to nutritious food. Encouraging open conversations about pregnancy and alcohol use can reduce stigma and promote healthier choices.