A fast heartbeat originating above the ventricles is commonly referred to as SVT. This condition occurs when the heart beats faster than normal due to abnormal electrical activity in the upper chambers of the heart. While it is not always dangerous, it can cause discomfort and may require medical attention in some cases. Understanding this condition, its triggers, symptoms, and care options is essential for managing it effectively.
What Is Supraventricular Tachycardia?
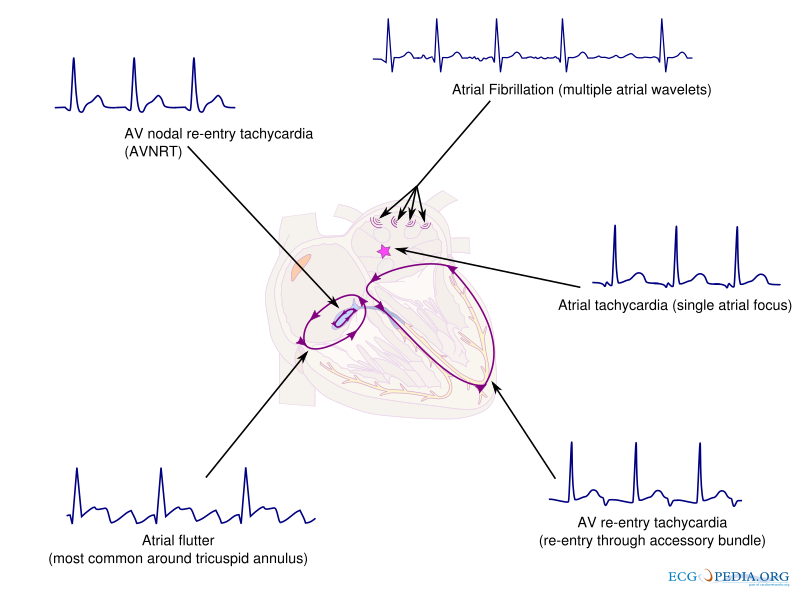
Supraventricular tachycardia refers to a group of heart rhythm disorders that originate in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. In this condition, the heart beats faster than the normal range, often exceeding 100 beats per minute. The rapid heartbeat is caused by irregular electrical signals that disrupt the heart’s natural rhythm. Unlike other types of arrhythmias, this condition specifically involves the areas above the ventricles, which are the lower chambers responsible for pumping blood to the rest of the body.
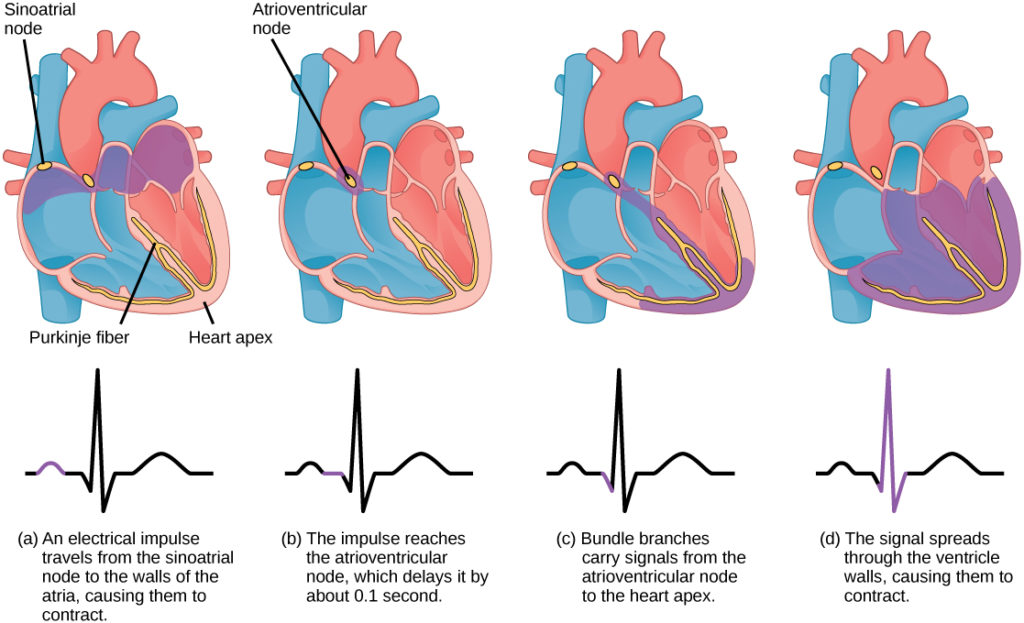
The heart’s electrical system controls the timing and sequence of heartbeats. Normally, electrical signals travel from the sinoatrial node, the heart’s natural pacemaker, through the atria and into the ventricles. In supraventricular tachycardia, however, these signals take an abnormal path or occur too frequently, causing the heart to beat faster than usual.
Types of Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation: A chaotic and irregular heartbeat that originates in the atria.
- Atrial Flutter: A rapid but regular heartbeat caused by a looping electrical circuit in the atria.
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia: A condition where an extra electrical pathway in the heart causes a fast heartbeat.
- Atrioventricular Reciprocating Tachycardia: Similar to the previous type but involves an accessory pathway between the atria and ventricles.
Common Triggers of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Several factors can trigger episodes of this condition. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Below are some common triggers:
Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress and anxiety can have a significant impact on heart rhythm. When the body experiences stress, it releases hormones like adrenaline, which can increase the heart rate. People with a history of this condition may find that stressful situations exacerbate their symptoms.
Caffeine and Stimulants
Caffeinated beverages such as coffee, tea, and energy drinks can stimulate the heart and trigger episodes. Similarly, nicotine and certain medications, including over-the-counter cold remedies, may act as stimulants and contribute to a faster heartbeat.
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake can disrupt the heart’s electrical system and lead to episodes of this condition. Even moderate drinking may pose a risk for individuals who are particularly sensitive to its effects.
Dehydration
Dehydration can affect the balance of electrolytes in the body, which are essential for maintaining a regular heartbeat. Low levels of potassium, magnesium, or calcium can increase the likelihood of developing an irregular heart rhythm.
Physical Exertion
Intense physical activity or exercise can sometimes trigger episodes, especially in individuals who are not accustomed to regular exercise. However, it is important to note that moderate exercise is generally beneficial for heart health and should not be avoided unless advised by a healthcare provider.
Symptoms of Supraventricular Tachycardia
The symptoms of this condition can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others may find them more severe and disruptive. Below are the most common symptoms associated with this condition:
Rapid Heartbeat
The hallmark symptom is a sudden and rapid heartbeat. This may feel like the heart is racing, pounding, or fluttering. Episodes can last anywhere from a few seconds to several hours.
Chest Pain
Some people may experience chest pain or discomfort during an episode. This symptom can be alarming and may prompt individuals to seek immediate medical attention.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness
A fast heartbeat can reduce the amount of blood reaching the brain, leading to feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness. In severe cases, this may result in fainting.
Shortness of Breath
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath is another common symptom. This occurs because the heart is working harder than usual to pump blood, which can make it challenging to catch one’s breath.
Fatigue
Episodes can leave individuals feeling tired or fatigued, even after the episode has ended. This is because the heart has been working overtime to maintain circulation during the episode.
Pounding Sensation in the Neck
Some people report feeling a pounding sensation in their neck during an episode. This is caused by the rapid contractions of the heart, which can be felt in the neck due to the proximity of major blood vessels.
Diagnosis of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Diagnosing this condition typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers will assess the individual’s symptoms, lifestyle, and family history to determine the likelihood of this condition.
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It can help identify abnormal rhythms and confirm the presence of this condition. In some cases, a portable monitor may be used to record the heart’s activity over a longer period.
Holter Monitor
A Holter monitor is a small device worn for 24 to 48 hours to continuously record the heart’s electrical activity. This test is useful for capturing episodes that occur intermittently.
Event Monitor
An event monitor is similar to a Holter monitor but is used for longer periods, often up to a month. Individuals activate the device when they experience symptoms, allowing healthcare providers to analyze the heart’s activity during an episode.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart. This test helps evaluate the structure and function of the heart and can rule out other underlying conditions.
Treatment and Care Options
Treatment for this condition depends on the severity of symptoms, the frequency of episodes, and the individual’s overall health. In many cases, lifestyle changes and simple techniques can help manage the condition effectively.
Vagal Maneuvers
Vagal maneuvers are simple techniques that can help slow down the heart rate during an episode. These include actions such as bearing down as if having a bowel movement, placing an ice pack on the face, or coughing forcefully. These maneuvers work by stimulating the vagus nerve, which helps regulate the heart’s rhythm.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to control the heart rate or prevent episodes. Commonly used medications include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs. These medications work by stabilizing the heart’s electrical activity and reducing the frequency of episodes.
Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat certain types of this condition. During the procedure, a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. The catheter delivers energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways causing the irregular heartbeat.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. These changes may include reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, managing stress through relaxation techniques, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Emergency Care
In rare cases, episodes may require emergency medical attention. If symptoms such as chest pain, fainting, or severe shortness of breath occur, it is important to seek immediate care. Healthcare providers may use medications or electrical cardioversion to restore a normal heart rhythm.
Living with Supraventricular Tachycardia
While this condition can be unsettling, many individuals are able to live full and active lives with proper management. Understanding the condition, recognizing triggers, and following a treatment plan can help minimize its impact on daily life. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.