The Eustachian tube, a vital part of the ear anatomy, plays a crucial role in maintaining ear health. When this tube malfunctions, it leads to a condition known as ETD, or Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. This dysfunction can cause discomfort, pain, and even hearing difficulties. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring treatment options are essential for managing this condition effectively.
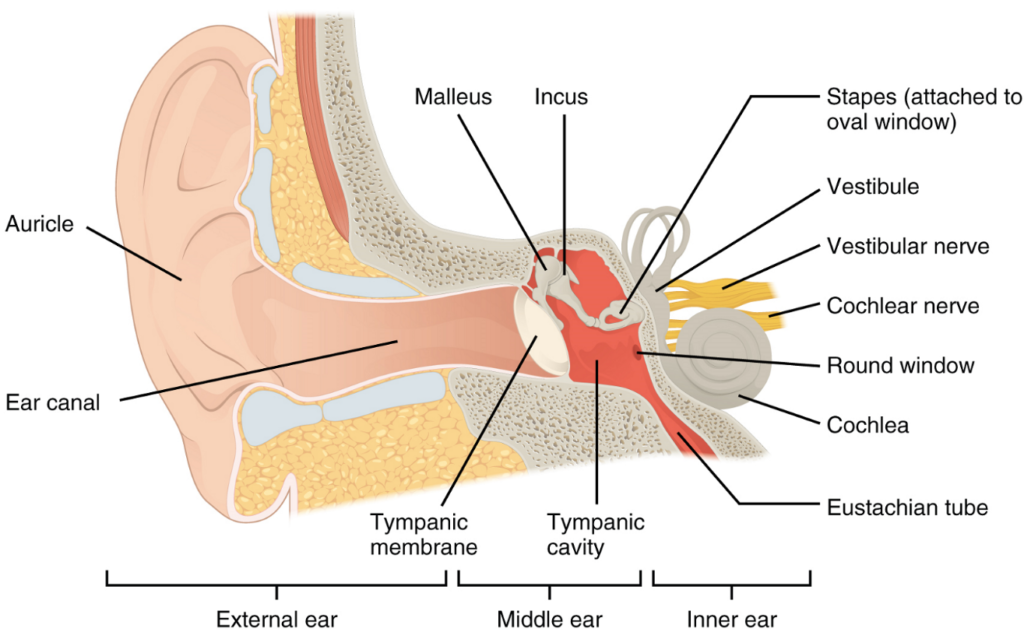
What is the Eustachian Tube?
The Eustachian tube is a narrow passage that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. Its primary function is to equalize air pressure between the middle ear and the external environment. It also helps drain mucus from the middle ear, preventing fluid buildup that could lead to infections. Normally, the tube remains closed but opens briefly during activities like swallowing, yawning, or chewing to allow air to flow in and out of the middle ear.
How Does the Eustachian Tube Work?
- Air Pressure Regulation: The tube ensures that the pressure on both sides of the eardrum remains balanced, which is critical for proper hearing and comfort.
- Mucus Drainage: By allowing mucus to drain from the middle ear into the throat, the tube prevents blockages that could harbor bacteria or viruses.
- Protection: The tube acts as a barrier, preventing harmful substances like bacteria and viruses from entering the middle ear.
Causes of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Several factors can contribute to the malfunctioning of the Eustachian tube. These causes can be broadly categorized into physical, environmental, and pathological factors.
Physical Factors
Physical issues often stem from structural abnormalities or conditions that affect the tube’s ability to open and close properly.
- Nasal Congestion: Swelling in the nasal passages due to allergies, colds, or sinus infections can block the opening of the Eustachian tube.
- Anatomical Abnormalities: Some individuals may have naturally narrow or malformed Eustachian tubes, making them more prone to dysfunction.
- Tumors or Growths: Benign growths such as nasal polyps can obstruct the tube, leading to dysfunction.
Environmental Factors
Changes in environmental conditions can also impact the functioning of the Eustachian tube.
- Altitude Changes: Rapid changes in altitude, such as during flights or while driving through mountainous regions, can create pressure imbalances that the tube struggles to manage.
- Weather Conditions: Cold weather or high humidity can exacerbate nasal congestion, indirectly affecting the tube’s function.
Pathological Factors
Certain medical conditions can directly or indirectly lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Infections: Middle ear infections or upper respiratory tract infections can cause inflammation and swelling around the tube.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can lead to persistent nasal congestion, which interferes with the tube’s ability to open.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Acid reflux can irritate the throat and nasal passages, potentially affecting the tube’s function.
Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction can vary in severity and duration. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others may face significant disruptions in their daily lives.
Ear Fullness or Pressure
One of the most common symptoms is a sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear. This occurs when the tube fails to equalize pressure, leaving the ear feeling blocked or clogged.
Hearing Difficulties
Individuals with this condition may notice a decrease in their ability to hear clearly. Sounds may seem muffled, as if they are underwater, due to the pressure imbalance in the middle ear.
Ear Pain
Pain or discomfort in the ear is another frequent symptom. This pain can range from mild to severe and may worsen with changes in altitude or during activities like swallowing.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, can occur as a result of Eustachian tube dysfunction. This symptom can be particularly bothersome, especially in quiet environments.
Balance Issues
Since the inner ear is closely linked to balance, dysfunction in the Eustachian tube can sometimes lead to dizziness or unsteadiness.
Diagnosis of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically rely on a combination of physical examinations, patient history, and specialized tests to confirm the presence of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will examine the ears, nose, and throat to check for signs of inflammation, blockages, or other abnormalities. They may use an otoscope to look inside the ear canal and assess the condition of the eardrum.
Patient History
Understanding the patient’s medical history, including any recent illnesses, allergies, or exposure to environmental factors, can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause of the dysfunction.
Specialized Tests
In some cases, additional tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
- Tympanometry: This test measures the movement of the eardrum in response to changes in air pressure, helping to identify issues with the Eustachian tube.
- Nasal Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is used to examine the nasal passages and the opening of the Eustachian tube.
Treatment Options for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Treatment for Eustachian tube dysfunction depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. In many cases, simple home remedies and lifestyle changes can alleviate the condition. However, more persistent or severe cases may require medical intervention.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
For mild cases, individuals can try several self-care strategies to relieve symptoms.
- Yawning or Swallowing: These actions can help open the Eustachian tube temporarily, providing relief from pressure.
- Chewing Gum: Chewing gum encourages frequent swallowing, which can help equalize pressure in the ear.
- Nasal Decongestants: Over-the-counter nasal sprays or decongestants can reduce swelling in the nasal passages, improving tube function.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help soothe pain and discomfort.
Medical Treatments
If home remedies fail to provide relief, medical treatments may be necessary.
- Antihistamines: For individuals with allergies, antihistamines can reduce nasal congestion and improve Eustachian tube function.
- Steroid Nasal Sprays: These sprays can reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and around the Eustachian tube.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection and reduce swelling.
Advanced Procedures
In cases where conservative treatments are ineffective, more advanced procedures may be considered.
- Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small balloon into the Eustachian tube and inflating it to widen the passage.
- Tympanostomy Tubes: Small tubes may be inserted into the eardrum to help equalize pressure and drain fluid from the middle ear.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgical correction of anatomical abnormalities may be required to restore proper function.
Preventing Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
While not all cases of Eustachian tube dysfunction can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing the condition.
- Manage Allergies: Keeping allergies under control through medication or avoidance of triggers can prevent nasal congestion.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain healthy mucus consistency, reducing the likelihood of blockages.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can irritate the nasal passages and throat, increasing the risk of dysfunction.
- Use Earplugs During Flights: Specialized earplugs designed for air travel can help equalize pressure during altitude changes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of Eustachian tube dysfunction resolve on their own or with simple interventions, there are instances when medical attention is necessary.
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms last for more than a few weeks despite home remedies, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider.
- Severe Pain: Intense or worsening ear pain should not be ignored, as it could indicate a more serious underlying issue.
- Hearing Loss: Significant or sudden hearing loss requires prompt evaluation to rule out complications.
- Fever or Discharge: The presence of fever or ear discharge may signal an infection that needs treatment.