Gynecomastia, commonly referred to as enlarged breast tissue in men, is a condition that affects a significant number of males at some point in their lives. This medical issue can occur due to a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and underlying health conditions. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options are essential for those affected by this condition. In this article, we will delve into these aspects to provide a comprehensive overview of Gynecomastia.
What is Enlarged Breast Tissue in Men?
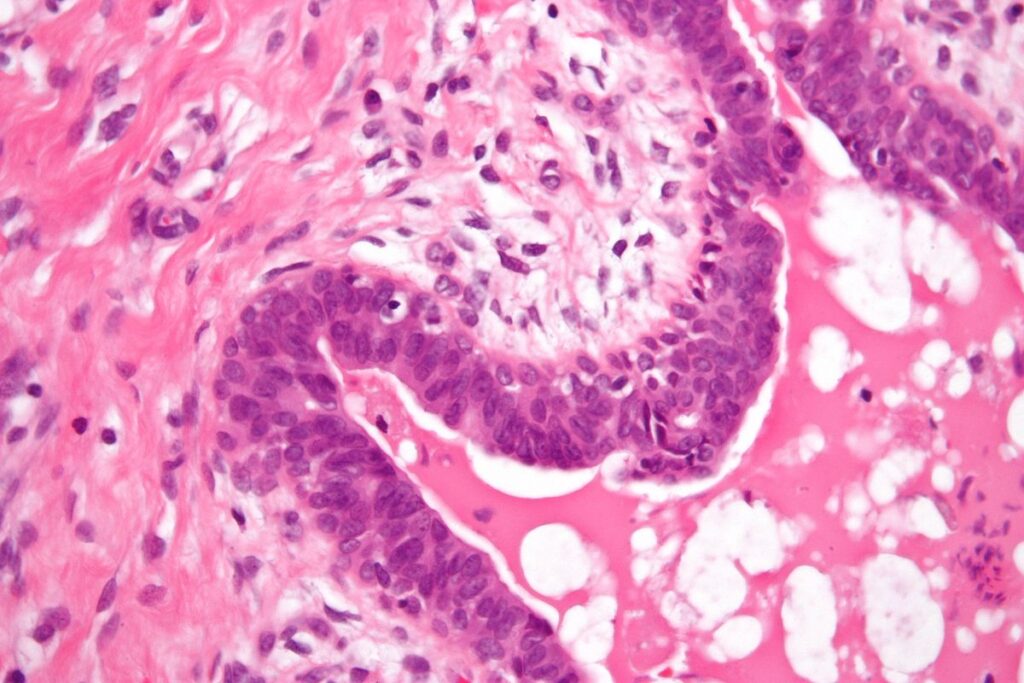
Enlarged breast tissue in men occurs when there is an abnormal increase in the size of the breast glandular tissue. Unlike pseudogynecomastia, which is caused by excess fat accumulation, true gynecomastia involves the growth of glandular tissue. This condition can affect one or both breasts and may result in tenderness or discomfort. While it is not typically harmful, it can lead to emotional distress and self-consciousness in affected individuals.
Common Causes of Enlarged Breast Tissue in Men
The development of enlarged breast tissue in men can be attributed to several factors. Below, we explore the most common causes:
Hormonal Imbalance
- Estrogen and Testosterone Levels: The primary cause of enlarged breast tissue in men is an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. Estrogen, often considered a female hormone, plays a role in breast tissue development. When estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels fall, it can lead to the growth of breast tissue in men.
- Puberty: During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common. Many adolescent boys experience temporary breast enlargement due to these changes. In most cases, the condition resolves on its own within a few months to a couple of years.
- Aging: As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decline, while estrogen levels may remain stable or increase. This shift can contribute to the development of enlarged breast tissue later in life.
Medications and Substances
- Prescription Medications: Certain medications can cause breast tissue enlargement as a side effect. These include anti-androgens used to treat prostate cancer, anabolic steroids, antibiotics, and drugs used to treat heart conditions or mental health disorders.
- Recreational Drugs: The use of substances such as marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines has been linked to the development of enlarged breast tissue in men.
- Alcohol Consumption: Chronic alcohol use can disrupt liver function, leading to hormonal imbalances that may result in breast tissue growth.
Health Conditions
- Hypogonadism: This condition occurs when the body produces insufficient amounts of testosterone, leading to an imbalance that can cause breast enlargement.
- Liver Disease: Liver dysfunction can interfere with hormone metabolism, potentially resulting in elevated estrogen levels and breast tissue growth.
- Kidney Disease: Men undergoing dialysis for kidney failure may experience hormonal changes that contribute to enlarged breast tissue.
- Tumors: Rarely, tumors in the testicles, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland can produce hormones that lead to breast tissue enlargement.
Symptoms of Enlarged Breast Tissue in Men
Recognizing the symptoms of enlarged breast tissue in men is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
- Swelling or enlargement of one or both breasts
- Breast tenderness or pain
- Firm or rubbery tissue beneath the nipple area
- Nipple discharge in rare cases
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary in severity and duration depending on the underlying cause of the condition.
Diagnosis of Enlarged Breast Tissue in Men
To determine whether a man is experiencing enlarged breast tissue, healthcare providers typically perform a thorough evaluation. This process may include:
Physical Examination
A doctor will examine the breast tissue to assess its size, texture, and symmetry. They may also check for any signs of discharge or lumps that could indicate an underlying issue.
Medical History Review
Understanding the patient’s medical history is essential for identifying potential causes. The doctor may ask about medication use, substance abuse, family history of breast conditions, and any recent changes in health.
Diagnostic Tests
- Blood Tests: These tests measure hormone levels, liver function, and kidney function to identify any abnormalities that could contribute to breast tissue enlargement.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound or mammography may be used to differentiate between glandular tissue and fatty tissue. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out cancerous growths.
Treatment Options for Enlarged Breast Tissue in Men
The treatment for enlarged breast tissue in men depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the individual’s preferences. Below are the most common approaches:
Observation and Monitoring
In many cases, especially during puberty or mild cases in older men, enlarged breast tissue resolves on its own without intervention. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is recommended to ensure the condition does not worsen or persist longer than expected.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help address the root cause of enlarged breast tissue:
- Diet and Exercise: Losing excess weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise can reduce fat deposits in the chest area, particularly in cases of pseudogynecomastia.
- Avoiding Substances: Cutting back on alcohol consumption and discontinuing the use of recreational drugs or medications known to cause breast enlargement can lead to improvement.
Medication Adjustments
If a specific medication is causing the condition, a healthcare provider may recommend switching to an alternative drug or adjusting the dosage. It is important to consult a doctor before making any changes to prescribed medications.
Hormone Therapy
In cases where hormonal imbalances are the primary cause, hormone therapy may be prescribed to restore balance. For example, medications that block estrogen production or increase testosterone levels may be used to reduce breast tissue growth.
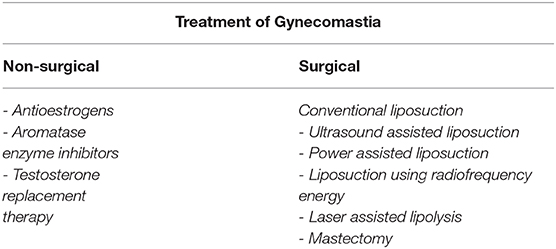
Surgical Intervention
For persistent or severe cases of enlarged breast tissue, surgery may be the most effective solution. The two main surgical procedures are:
- Liposuction: This procedure removes excess fat from the breast area and is typically used for cases of pseudogynecomastia.
- Mastectomy: A mastectomy involves the removal of glandular breast tissue and is often recommended for true gynecomastia. This procedure is minimally invasive and results in minimal scarring.
Post-Surgical Care
After surgery, patients are advised to follow their doctor’s instructions for recovery. This may include wearing compression garments, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Enlarged breast tissue in men can have a significant emotional and psychological impact. Many individuals feel embarrassed or self-conscious about their appearance, which can affect their self-esteem and social interactions. Seeking support from a counselor or joining a support group can help individuals cope with these feelings and improve their quality of life.
Prevention Tips
While not all cases of enlarged breast tissue can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Avoid the use of anabolic steroids and recreational drugs
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Consult a healthcare provider before starting new medications
When to Seek Medical Attention
While enlarged breast tissue is often benign, certain signs warrant immediate medical attention:
- Persistent or worsening breast enlargement
- Severe pain or discomfort
- Nipple discharge, especially if it is bloody
- A lump or hard mass in the breast tissue
These symptoms could indicate an underlying condition that requires prompt evaluation and treatment.