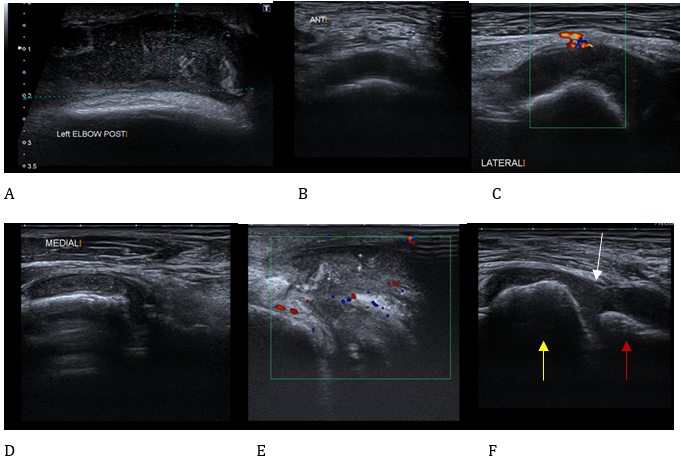
Elbow bursitis, also known as olecranon bursitis or OB, is a common condition that affects the small fluid-filled sac located at the tip of the elbow. This sac, called the bursa, plays a vital role in reducing friction and cushioning the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joint. When this bursa becomes inflamed, it can lead to discomfort, swelling, and limited mobility. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition.

Understanding Elbow Bursitis
Elbow bursitis occurs when the bursa at the back of the elbow becomes irritated or inflamed. The bursa is a thin, slippery sac that helps the skin slide smoothly over the bone when you bend or straighten your arm. Without this protective cushion, even simple movements could cause pain and discomfort. However, when the bursa swells, it can make everyday activities challenging.
Common Causes of Elbow Bursitis
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of elbow bursitis. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment.
- Prolonged Pressure: Repeatedly leaning on the elbows, such as during activities like writing, typing, or resting the elbows on hard surfaces, can irritate the bursa and lead to inflammation.
- Trauma or Injury: A direct blow to the elbow, such as falling onto a hard surface or bumping the elbow against an object, can damage the bursa and trigger inflammation.
- Infection: Bacteria can enter the bursa through cuts, scrapes, or puncture wounds on the skin near the elbow. This can result in an infected bursa, which often requires more aggressive treatment.
- Rheumatoid Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can increase the risk of developing bursitis due to systemic inflammation in the body.
- Overuse: Repetitive motions involving the elbow joint, such as lifting heavy objects or participating in sports like tennis or golf, can strain the bursa and lead to irritation.
Symptoms of Elbow Bursitis
The symptoms of elbow bursitis can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation and whether an infection is present. Some of the most common signs include:
- Swelling: One of the earliest and most noticeable symptoms is swelling at the back of the elbow. The area may appear puffy or balloon-like.
- Pain: While mild cases may not cause significant pain, more severe inflammation can lead to discomfort, especially when pressing on the elbow or moving the joint.
- Redness and Warmth: If the bursa is infected, the skin over the elbow may become red, warm to the touch, and tender.
- Limited Mobility: Swelling and pain can restrict the range of motion in the elbow, making it difficult to bend or straighten the arm fully.
- Fever: In cases of infected bursitis, individuals may experience fever or chills as the body tries to fight off the infection.
Diagnosing Elbow Bursitis
If you suspect you have elbow bursitis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. During the evaluation, the doctor will likely perform the following steps:
Physical Examination
The doctor will examine the affected elbow, looking for signs of swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness. They may also assess your range of motion to determine how much the inflammation is affecting your ability to use the joint.
Medical History
Your doctor will ask about any recent injuries, repetitive activities, or underlying health conditions that could contribute to the development of bursitis. Providing a detailed history can help guide the diagnostic process.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of elbow pain, such as fractures or arthritis. These tests can also help identify any calcifications or fluid buildup within the bursa.
Aspiration and Laboratory Analysis
If an infection is suspected, the doctor may perform a procedure called aspiration. This involves using a needle to remove fluid from the swollen bursa. The fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis to check for the presence of bacteria or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Elbow Bursitis
The treatment for elbow bursitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In most cases, conservative measures are effective in relieving symptoms and promoting healing. However, more aggressive interventions may be necessary for severe or persistent cases.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For non-infected cases of elbow bursitis, the following approaches are typically recommended:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that put pressure on the elbow can help reduce irritation and allow the bursa to heal. Using padding or cushions can also minimize stress on the joint.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Compression: Wrapping the elbow with an elastic bandage can provide support and limit swelling. However, care should be taken to avoid wrapping too tightly, as this can restrict blood flow.
- Elevation: Keeping the elbow elevated above heart level whenever possible can help reduce fluid accumulation and promote drainage.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Draining the Bursa
In cases where the swelling is significant or does not improve with conservative measures, the doctor may recommend draining the excess fluid from the bursa. This procedure, known as aspiration, is performed using a sterile needle and syringe. Afterward, a compression bandage is applied to prevent the fluid from reaccumulating.
Treatment for Infected Bursitis
When the bursa is infected, additional steps are necessary to address the underlying infection. These may include:
- Antibiotics: Oral or intravenous antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria identified during laboratory analysis.
- Repeated Aspiration: If the infection persists, multiple aspirations may be required to remove infected fluid and prevent complications.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases where the infection does not respond to antibiotics or repeated drainage, surgical removal of the bursa may be necessary. This procedure, called bursectomy, is typically reserved for chronic or recurrent infections.
Preventing Recurrence
To reduce the risk of developing elbow bursitis again, consider adopting the following preventive measures:
- Avoid prolonged pressure on the elbows by using padded surfaces or supports.
- Take regular breaks during activities that involve repetitive elbow movements.
- Protect the elbows from trauma by wearing protective gear during sports or high-risk activities.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle to manage underlying conditions like arthritis or gout.
Living with Elbow Bursitis
While elbow bursitis can be uncomfortable and inconvenient, most cases resolve with proper care and treatment. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following the recommended treatment plan, individuals can effectively manage this condition and regain full function of their elbows.