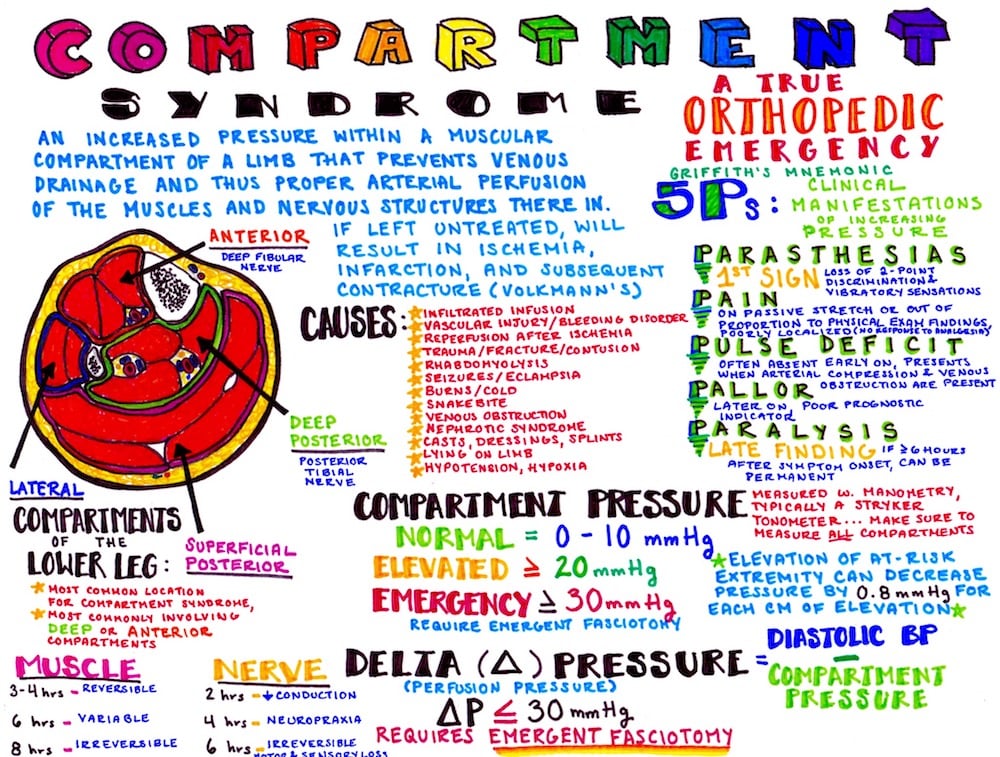
Compartment syndrome, often abbreviated as CS, is a serious medical condition that occurs when pressure within the muscles builds to dangerous levels. This elevated pressure can reduce blood flow, leading to insufficient oxygen and nutrients reaching the tissues. If left untreated, compartment syndrome can result in permanent muscle and nerve damage or even loss of function. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this critical condition.
Understanding Compartment Syndrome
Before diving into the specifics, it is important to understand what compartment syndrome is. The human body has groups of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels enclosed within compartments formed by strong connective tissue called fascia. When the pressure inside these compartments rises, it compresses the structures within, potentially causing significant harm.
Types of Compartment Syndrome
- Acute Compartment Syndrome: This form develops rapidly, often due to an injury. It is considered a medical emergency.
- Chronic Compartment Syndrome: Also known as exertional compartment syndrome, this type develops gradually and is typically associated with physical activity.
Causes of Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome can occur due to various reasons, depending on whether it is acute or chronic.
Causes of Acute Compartment Syndrome
Acute compartment syndrome is usually caused by trauma or injury to the affected area. Common causes include:
- Fractures, particularly those involving long bones such as the tibia or forearm
- Crush injuries
- Burns
- Bleeding within a muscle compartment, often following surgery or anticoagulant therapy
- Tight bandages or casts that restrict blood flow
Causes of Chronic Compartment Syndrome
Chronic compartment syndrome is most commonly seen in athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive physical activities. Contributing factors include:
- Intense exercise, especially running or cycling
- Poor biomechanics during physical activity
- Inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines
- Overtraining without sufficient recovery time
Symptoms of Compartment Syndrome
The symptoms of compartment syndrome vary depending on its type but share some common features.
Symptoms of Acute Compartment Syndrome
Acute compartment syndrome typically presents with severe symptoms that develop quickly. These include:
- Intense pain that seems disproportionate to the injury
- Swelling and tightness in the affected area
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Weakness in the affected limb
- Pale or shiny skin over the affected area
- Severe pain when the muscles are stretched or used
Symptoms of Chronic Compartment Syndrome
Chronic compartment syndrome tends to have milder symptoms that worsen with activity and improve with rest. These symptoms include:
- Aching or cramping pain during exercise
- Tightness or fullness in the affected muscles
- Numbness or tingling during physical activity
- Visible swelling or bulging of the muscles
- Relief of symptoms after stopping the activity
Diagnosis of Compartment Syndrome
Accurate diagnosis of compartment syndrome is crucial to prevent complications. The diagnostic process involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specialized tests.
Clinical Evaluation
Doctors begin by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. They will assess the patient’s pain levels, look for signs of swelling or discoloration, and evaluate muscle strength and sensation in the affected area.
Measurement of Compartment Pressure
To confirm the diagnosis, healthcare providers may use a device to measure the pressure within the muscle compartments. This test involves inserting a needle or catheter into the compartment and recording the pressure readings. Elevated pressure readings indicate compartment syndrome.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography scans may be ordered to rule out other conditions or identify underlying causes like fractures or bleeding.
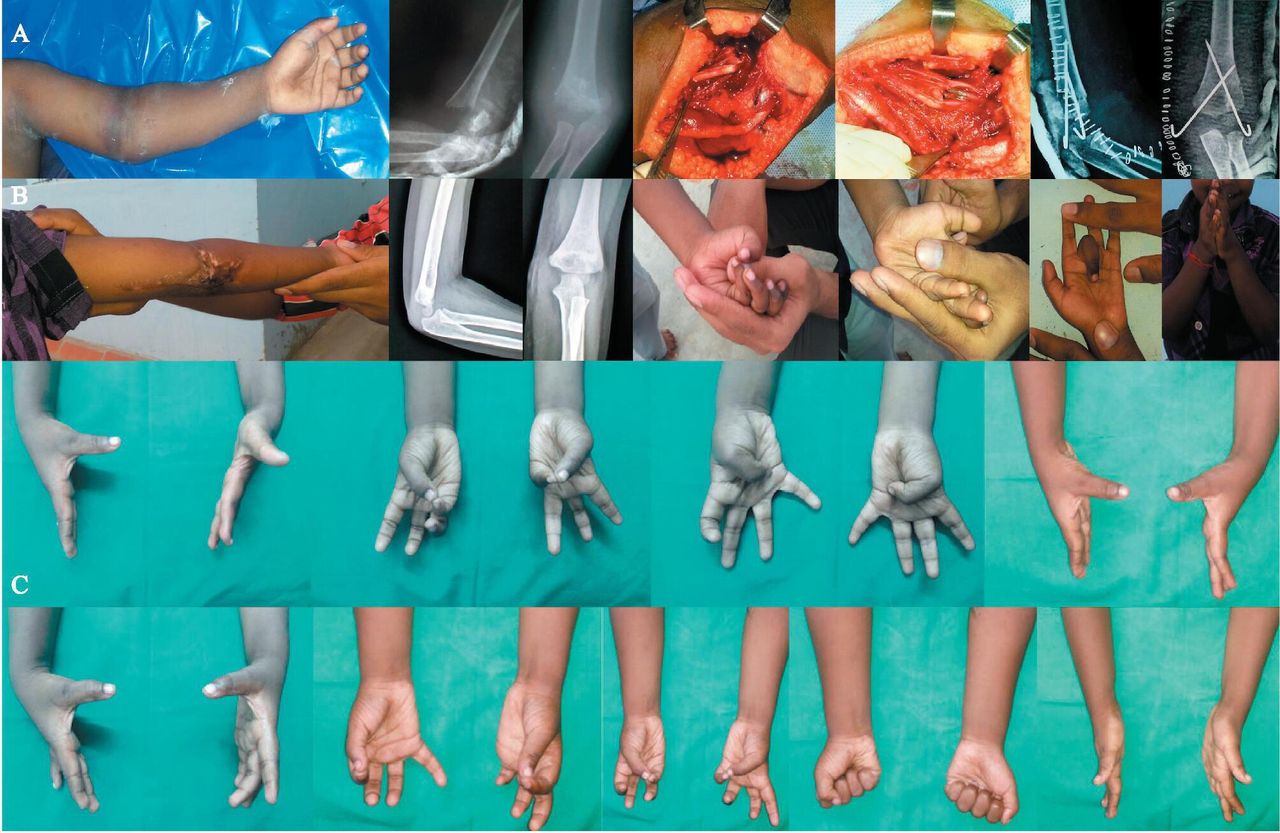
Treatment Options for Compartment Syndrome
The treatment approach for compartment syndrome depends on its type and severity. Prompt intervention is essential to prevent long-term damage.
Treatment for Acute Compartment Syndrome
Acute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. The primary treatment option is:
Fasciotomy
A fasciotomy is a surgical procedure in which the fascia is cut open to relieve pressure within the compartment. This allows the muscles and nerves to recover and restores blood flow. Delaying this procedure can lead to irreversible damage.
Treatment for Chronic Compartment Syndrome
Chronic compartment syndrome is typically managed conservatively before considering surgical options.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Initial treatment focuses on modifying physical activity and addressing contributing factors. These include:
- Rest and avoiding activities that trigger symptoms
- Physical therapy to improve flexibility and biomechanics
- Orthotic devices to correct alignment issues
- Ice and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling
Surgical Treatments
If non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be recommended. Similar to acute compartment syndrome, a fasciotomy is performed to release the pressure in the affected compartment.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from compartment syndrome varies depending on the type and treatment received. For acute cases, patients may require weeks to months of rehabilitation to regain strength and function. Physical therapy plays a key role in restoring mobility and preventing complications.
For chronic compartment syndrome, recovery is generally quicker, especially if conservative measures are effective. Patients are encouraged to gradually return to physical activity under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Preventing Compartment Syndrome
While not all cases of compartment syndrome can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Using proper techniques and equipment during physical activity
- Wearing well-fitted shoes and protective gear
- Avoiding overtraining and allowing adequate recovery time
- Seeking prompt medical attention for injuries or unexplained pain
Living with Compartment Syndrome
For individuals diagnosed with compartment syndrome, understanding the condition and adhering to treatment recommendations is vital. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that the condition is managed effectively and complications are minimized.
By staying informed and proactive, patients can achieve better outcomes and maintain their quality of life despite the challenges posed by compartment syndrome.