Chigger bites, often referred to as a nuisance during outdoor activities, are caused by tiny mites that belong to the Trombiculidae family. These pests are most commonly found in grassy or wooded areas and can cause significant discomfort to humans and animals alike. Understanding the symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures is essential for anyone who enjoys spending time outdoors. This article will delve into these aspects to help you better manage and avoid chigger bites.

What Are Chigger Bites?
Chigger bites occur when larvae of the Trombiculidae family attach themselves to the skin of humans or animals. These larvae, also known as chiggers, are microscopic and nearly invisible to the naked eye. They thrive in warm, humid environments and are most active during late spring, summer, and early fall. Once attached to the skin, they inject enzymes that break down skin cells, allowing them to feed on the liquefied tissue. Although they do not burrow into the skin or suck blood, their feeding process can lead to intense itching and irritation.
Symptoms of Chigger Bites
The symptoms of chigger bites typically appear within a few hours to a day after exposure. The severity of the symptoms can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the number of bites. Common signs include:
- Intense Itching: One of the hallmark symptoms of chigger bites is severe itching, which may worsen over time. The itching is often concentrated around areas where clothing fits tightly, such as the waist, ankles, and groin.
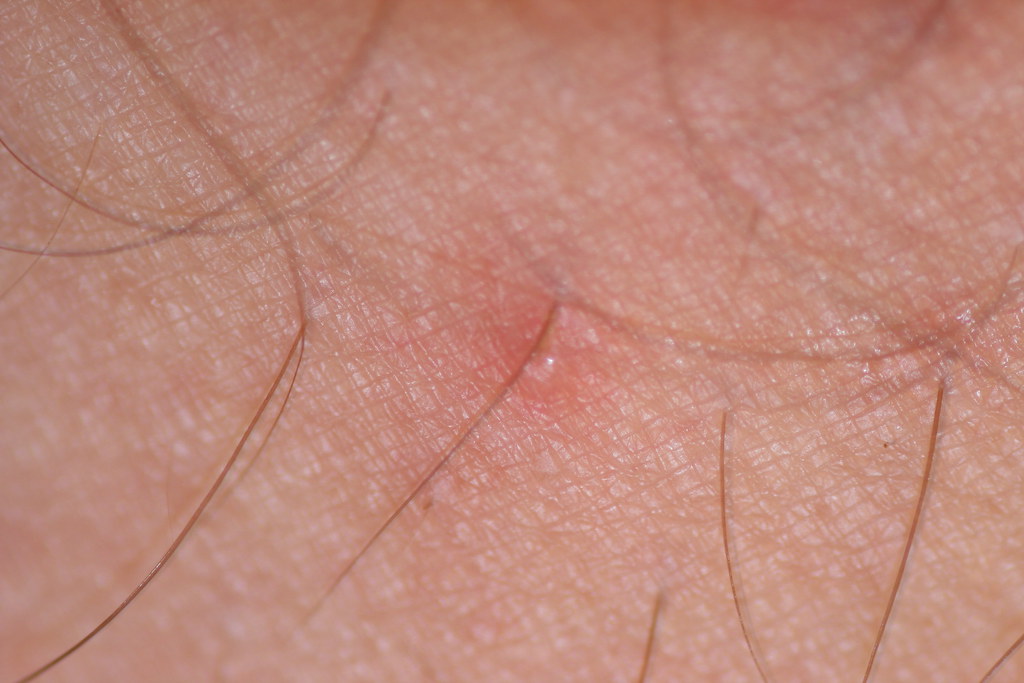
- Red Pimple-Like Bumps: The bites often appear as small, raised red bumps on the skin. These bumps may resemble pimples or blisters and can develop into larger welts if scratched excessively.
- Localized Swelling: In some cases, the affected area may become swollen and inflamed. This swelling can persist for several days, especially if the bites are scratched or irritated.
- Rash: A rash may develop around the bite sites, particularly if the individual has an allergic reaction to the enzymes injected by the chiggers.
It is important to note that while chigger bites are uncomfortable, they are generally not harmful and do not transmit diseases in most regions. However, excessive scratching can lead to secondary infections, which may require medical attention.
Causes of Chigger Bites
Chigger bites occur due to the feeding behavior of chigger larvae. These larvae are parasitic and rely on hosts to survive during their early stages of development. Several factors contribute to the likelihood of encountering chiggers:
Habitat
Chiggers are commonly found in moist, grassy, or wooded areas. They thrive in environments with tall grass, shrubs, and dense vegetation, where they can easily attach to passing hosts. Some common habitats include:
- Forests and woodlands
- Grassy fields and meadows
- Gardens and parks
- Near bodies of water, such as lakes and streams
Host Preference
While chiggers can attach to a wide range of hosts, including birds, reptiles, and small mammals, humans are often accidental targets. Chiggers are attracted to the carbon dioxide and heat emitted by potential hosts, making humans an easy target during outdoor activities. They tend to congregate in areas where clothing is tight against the skin, such as the waistband, armpits, and behind the knees.
Seasonal Activity
Chiggers are most active during warm and humid months, typically from late spring to early fall. Their activity decreases during colder months, as they require specific environmental conditions to survive. Understanding their seasonal patterns can help individuals plan outdoor activities more strategically to minimize exposure.
Treatment for Chigger Bites
If you suspect you have been bitten by chiggers, prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. While there is no specific medication to eliminate chigger larvae, several home remedies and over-the-counter treatments can provide relief.
Cleaning the Affected Area
The first step in treating chigger bites is to clean the affected area thoroughly. Use mild soap and water to wash away any remaining larvae or debris. Gently pat the skin dry with a clean towel to avoid further irritation. Avoid scrubbing the area, as this can exacerbate the itching and inflammation.
Relieving Itchiness
To reduce itching and discomfort, consider the following remedies:
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the bites can help numb the area and reduce swelling. Wrap the ice pack in a cloth to prevent direct contact with the skin.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamine medications, such as diphenhydramine, can help alleviate itching and reduce allergic reactions.
- Topical Creams: Hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion can be applied to the bites to soothe the skin and relieve itching. These products are widely available at pharmacies and grocery stores.
Avoiding Scratching
Scratching the bites can worsen the symptoms and increase the risk of infection. To prevent scratching, keep your nails short and avoid touching the affected area. Wearing loose-fitting clothing can also help minimize irritation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
In most cases, chigger bites resolve on their own within one to two weeks. However, you should seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Signs of infection, such as pus, increased redness, or warmth around the bites
- Persistent or worsening symptoms despite treatment
- Allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing or widespread hives
Prevention of Chigger Bites
Preventing chigger bites is key to enjoying outdoor activities without the discomfort of itching and irritation. By taking a few simple precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of encountering these pests.
Dressing Appropriately
One of the most effective ways to prevent chigger bites is to wear protective clothing. Consider the following tips:
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants to minimize exposed skin.
- Tuck your pants into your socks and your shirt into your pants to create a barrier against chiggers.
- Choose light-colored clothing, as it makes it easier to spot and remove chiggers before they attach to your skin.
Using Insect Repellents
Insect repellents containing DEET, permethrin, or citronella can help deter chiggers. Apply the repellent to both your skin and clothing, following the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Permethrin-treated clothing is particularly effective, as it remains protective even after multiple washes.
Avoiding High-Risk Areas
Steer clear of areas known to harbor chiggers, such as tall grass, dense vegetation, and wooded trails. If you must venture into these areas, stay on designated paths and avoid brushing against plants or sitting directly on the ground.
Showering After Outdoor Activities
After spending time outdoors, take a shower as soon as possible to wash away any chiggers that may be clinging to your skin. Pay special attention to areas where clothing fits tightly, as these are common sites for chigger bites. Washing your clothes in hot water can also help eliminate any lingering larvae.
Maintaining Your Yard
If you live in an area prone to chiggers, take steps to reduce their presence in your yard. Regularly mow the lawn, trim bushes, and remove debris to eliminate potential habitats. Using insecticides specifically designed for chiggers can also help control their population.
Understanding the Importance of Prevention
While chigger bites are rarely dangerous, they can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily activities. By understanding the causes and symptoms of these bites, as well as implementing preventive measures, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from these pesky pests. Whether you’re hiking, gardening, or simply enjoying a picnic, being proactive about prevention can ensure a more pleasant outdoor experience.