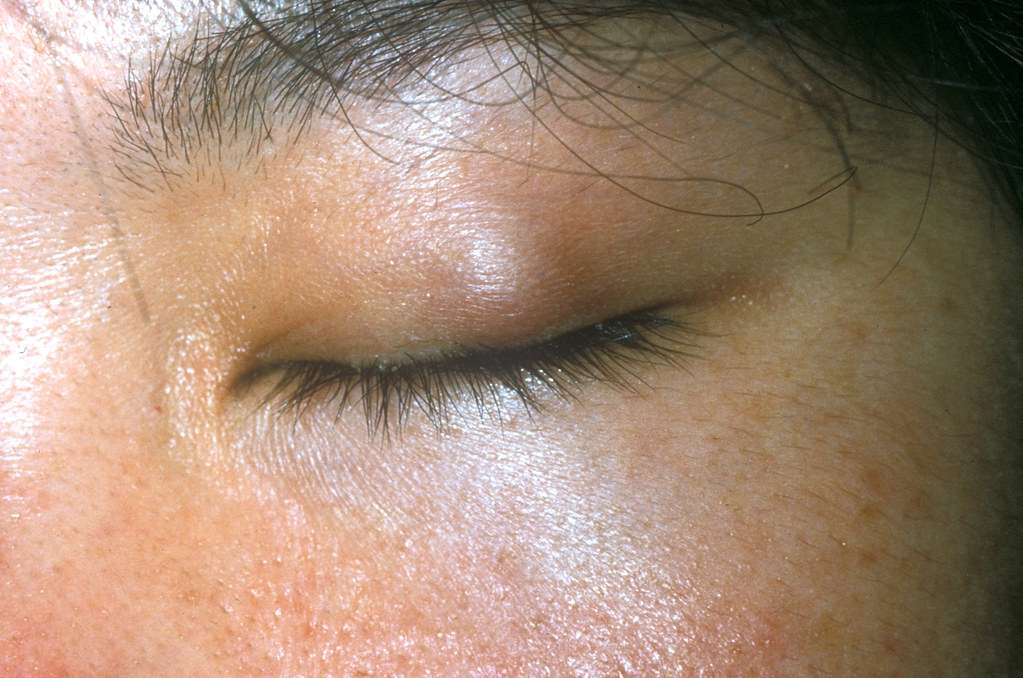
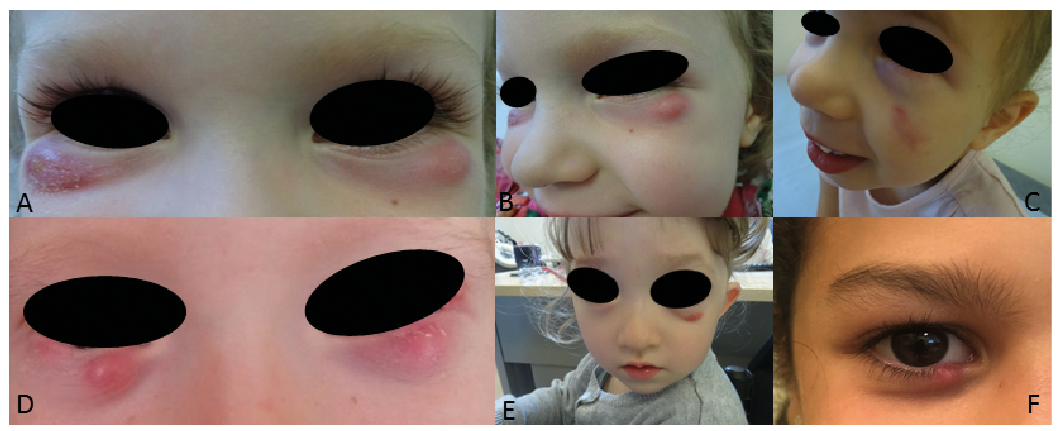
A chalazion, often referred to as a meibomian cyst, is a common condition that affects the eyelids. It occurs when an oil gland in the eyelid becomes blocked, leading to inflammation and swelling. While this condition is typically harmless, it can cause discomfort and affect vision if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options available for individuals dealing with this condition.
What Causes a Chalazion?
The primary cause of a chalazion is the blockage of an oil gland located in the eyelid. These glands are responsible for producing the oily layer of tears, which helps prevent the evaporation of moisture from the surface of the eye. When one of these glands becomes clogged, the oil builds up inside, leading to inflammation and the formation of a lump.
Risk Factors
- Poor Eyelid Hygiene: Failing to clean the eyelids regularly can lead to the accumulation of debris, increasing the risk of blockages.
- Blepharitis: This condition involves inflammation of the eyelids, often due to bacterial infection or skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels can affect the consistency of the oil produced by the glands, making blockages more likely.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Conditions such as rosacea or acne can increase the likelihood of developing a chalazion.
Symptoms of a Chalazion
Recognizing the symptoms of a chalazion is essential for early intervention and effective management. The most common signs include:
Visible Lump on the Eyelid
A chalazion typically presents as a small, painless lump on the upper or lower eyelid. Over time, the lump may grow larger, causing mild discomfort or pressure on the eye.
Redness and Swelling
In some cases, the affected area of the eyelid may appear red and swollen. This is due to the inflammatory response triggered by the blocked gland.
Mild Discomfort
While a chalazion is generally painless, some individuals may experience mild discomfort, especially if the lump presses against the eyeball or surrounding tissues.
Blurry Vision
If the chalazion grows large enough, it may press on the cornea, leading to temporary blurry vision. This symptom usually resolves once the lump shrinks or is treated.
Diagnosing a Chalazion
Diagnosing a chalazion typically involves a physical examination by an eye care professional. The process is straightforward and may include the following steps:
Medical History Review
The doctor will begin by asking about your medical history, including any previous eye conditions, skin issues, or recurring eyelid problems. This information helps rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Physical Examination
The healthcare provider will examine the affected eyelid closely, looking for signs of a lump, redness, or swelling. They may also check for tenderness or discharge, which could indicate an infection.
Differential Diagnosis
It is important to differentiate a chalazion from other similar conditions, such as a stye or a tumor. A stye, for example, is often painful and caused by an infection, whereas a chalazion is typically painless and results from a blocked gland.
Additional Tests
In rare cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests, such as a biopsy, to rule out more serious conditions if the lump does not respond to treatment or exhibits unusual characteristics.
Treatment Options for a Chalazion
The treatment approach for a chalazion depends on its size, duration, and impact on daily life. Most cases resolve on their own within a few weeks, but certain interventions can speed up recovery or address persistent lumps.
Warm Compresses
One of the simplest and most effective treatments for a chalazion is applying warm compresses to the affected eyelid. This method helps soften the hardened oil blocking the gland, promoting drainage and reducing inflammation. To use this technique:
- Soak a clean cloth in warm water and wring out the excess.
- Place the warm cloth over the closed eyelid for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Repeat this process three to four times daily until the lump subsides.
Massage
Gently massaging the eyelid after applying a warm compress can further aid in draining the blocked gland. Use clean hands and apply light pressure in a circular motion around the lump.
Topical Treatments
In some cases, doctors may prescribe antibiotic ointments or steroid creams to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. These medications should only be used under medical supervision.
Oral Medications
If the chalazion is associated with an underlying condition like blepharitis or rosacea, oral antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended to address the root cause.
Incision and Curettage
For persistent or large chalazia that do not respond to conservative treatments, a minor surgical procedure called incision and curettage may be necessary. During this procedure:
- The patient is given local anesthesia to numb the area.
- A small incision is made on the inner surface of the eyelid to access the blocked gland.
- The contents of the gland are removed using specialized tools.
This outpatient procedure is safe and effective, with minimal downtime required for recovery.
Laser Therapy
In recent years, laser therapy has emerged as an alternative treatment option for stubborn chalazia. This minimally invasive technique uses focused laser energy to break down the lump without damaging surrounding tissues.
Preventive Measures
To reduce the risk of developing another chalazion, consider adopting the following preventive measures:
- Clean your eyelids regularly with a gentle cleanser or baby shampoo.
- Avoid rubbing or touching your eyes with unwashed hands.
- Manage underlying skin conditions like rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis.
- Stay hydrated to maintain healthy tear production.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most chalazia are harmless and resolve on their own, certain situations warrant prompt medical attention. Contact an eye care professional if you experience any of the following:
- The lump grows rapidly or becomes very large.
- You notice significant pain, redness, or discharge from the affected area.
- Your vision becomes increasingly blurry or distorted.
- The chalazion does not improve after several weeks of home treatment.
Living with a Chalazion
Dealing with a chalazion can be frustrating, especially if it affects your appearance or comfort. However, understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the available treatment options can empower you to manage the condition effectively. By maintaining good eyelid hygiene and seeking timely medical advice, you can minimize the impact of a chalazion on your daily life.