Cellulite, often referred to as “orange peel” or “cottage cheese” skin, is a common condition that affects the appearance of the skin. Medically known as gynoid lipodystrophy, cellulite manifests as dimpled or lumpy skin, most commonly found on the thighs, buttocks, and abdomen. While it is not harmful or indicative of any underlying health issue, many individuals seek ways to reduce its appearance due to aesthetic concerns. In this article, we will explore the causes of cellulite, how it appears on the skin, and the various treatment options available.

What Is Cellulite?
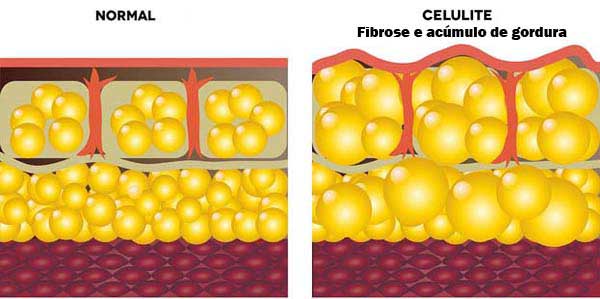
Cellulite is a condition characterized by the uneven texture of the skin, often described as dimpling or lumpiness. It occurs when fat deposits push through the connective tissue beneath the skin, creating an irregular surface. This condition is more common in women than in men, with estimates suggesting that up to 90 percent of women experience cellulite at some point in their lives.
The appearance of cellulite can vary from mild to severe. In mild cases, the skin may have a slightly uneven texture that is only noticeable when the skin is pinched. In more severe cases, the skin may have a pronounced dimpled appearance even when relaxed. Understanding the factors that contribute to cellulite can help individuals make informed decisions about managing or treating it.
Causes of Cellulite
The exact cause of cellulite is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These include hormonal influences, genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and the natural aging process.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones play a significant role in the formation of cellulite. Estrogen, insulin, noradrenaline, thyroid hormones, and prolactin are thought to influence the production and distribution of fat cells. Fluctuations in estrogen levels, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can exacerbate the appearance of cellulite. Women are more prone to cellulite because their fat cells are distributed differently compared to men, and their connective tissue is arranged vertically, making it easier for fat to protrude.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a crucial role in determining whether an individual is likely to develop cellulite. Certain genes can influence factors such as metabolism, fat distribution, circulation, and skin structure, all of which contribute to cellulite formation. If your family members have cellulite, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: A diet high in fat, carbohydrates, and salt, combined with low fiber intake, can contribute to cellulite formation.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to poor circulation and weakened muscle tone, both of which may worsen cellulite.
- Smoking: Smoking damages collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for maintaining skin elasticity, making cellulite more visible.
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake can lead to dry, less elastic skin, which may accentuate cellulite.
Aging Process
As people age, their skin naturally loses elasticity and thickness due to a decrease in collagen and elastin production. The connective tissue beneath the skin also weakens over time, making cellulite more prominent. Aging-related changes in fat distribution can further contribute to the appearance of cellulite.
Appearance of Cellulite
Cellulite typically appears as dimpled or lumpy skin, often resembling the texture of orange peel or cottage cheese. It is most commonly found on the thighs, buttocks, and abdomen but can also occur on the arms and other areas of the body. The severity of cellulite can range from mild to severe, depending on factors such as skin thickness, fat distribution, and connective tissue structure.
Grades of Cellulite Severity
- Grade 1: No visible cellulite when the skin is relaxed, but a slight dimpling may appear when the skin is pinched.
- Grade 2: Visible cellulite when standing, but not when lying down.
- Grade 3: Prominent cellulite visible both when standing and lying down.
The appearance of cellulite can vary based on skin tone and texture. Individuals with fair skin may find cellulite more noticeable due to the contrast between the dimpled areas and the surrounding skin. Conversely, those with darker skin tones may experience less visible cellulite, although the condition is still present.
Treatment Options for Cellulite
While there is no permanent cure for cellulite, several treatment options are available to reduce its appearance. These treatments range from topical creams and non-invasive procedures to surgical interventions. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine the best approach for your specific needs.
Topical Treatments
Topical creams and lotions are among the most accessible and affordable options for addressing cellulite. These products often contain ingredients such as caffeine, retinol, or herbal extracts that claim to improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of cellulite. While they may provide temporary improvements, their effectiveness is generally limited and short-lived.
- Caffeine Creams: Caffeine is believed to stimulate blood flow and break down fat cells, potentially reducing the appearance of cellulite.
- Retinol Creams: Retinol promotes collagen production, which can improve skin elasticity and smoothness over time.
- Herbal Extracts: Some creams incorporate plant-based ingredients like ginkgo biloba or horse chestnut, which are thought to enhance circulation and reduce inflammation.
Non-Invasive Procedures
Non-invasive treatments are popular for their minimal downtime and reduced risk compared to surgical options. These procedures target cellulite by breaking down fat cells, improving circulation, or tightening the skin.
- Laser and Radiofrequency Therapy: These treatments use heat energy to stimulate collagen production and tighten the skin, reducing the appearance of cellulite.
- Cryolipolysis: Also known as “fat freezing,” this procedure targets and destroys fat cells without damaging the surrounding tissue.
- Acoustic Wave Therapy: This technique uses sound waves to break down cellulite and improve skin texture.
Invasive Procedures
For individuals seeking more dramatic results, invasive procedures may be an option. These treatments involve surgery or injections and typically require a longer recovery period.
- Liposuction: Liposuction removes excess fat from beneath the skin, but it does not address the connective tissue responsible for cellulite. As a result, it may not significantly improve cellulite appearance.
- Subcision: This procedure involves inserting a needle under the skin to break up the fibrous bands that cause cellulite dimples.
- Cellulite Reduction Injections: Injectable treatments aim to dissolve fat cells or stimulate collagen production, leading to smoother skin.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce the appearance of cellulite. These changes focus on improving overall skin health, circulation, and body composition.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, including strength training and cardiovascular exercise, can build muscle tone and reduce fat deposits.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a nutrient-rich diet with adequate protein, healthy fats, and fiber can support skin health and reduce cellulite visibility.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin elasticity and flush out toxins that may contribute to cellulite.
- Massage: Massaging the affected areas can improve blood flow and lymphatic drainage, potentially reducing cellulite appearance.
Myths About Cellulite
There are several misconceptions about cellulite that can lead to confusion and misinformation. Addressing these myths can help individuals better understand the condition and manage their expectations regarding treatment.
Myth 1: Only Overweight People Get Cellulite
While excess body fat can exacerbate cellulite, it is not exclusive to overweight individuals. Even people with low body fat percentages can develop cellulite due to genetic and hormonal factors.
Myth 2: Cellulite Indicates Poor Health
Cellulite is purely a cosmetic concern and does not indicate any underlying health issues. It is a natural occurrence caused by the structure of the skin and connective tissue.
Myth 3: Creams Can Permanently Eliminate Cellulite
While topical treatments may temporarily improve skin texture, they cannot permanently eliminate cellulite. Long-term results often require a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes.