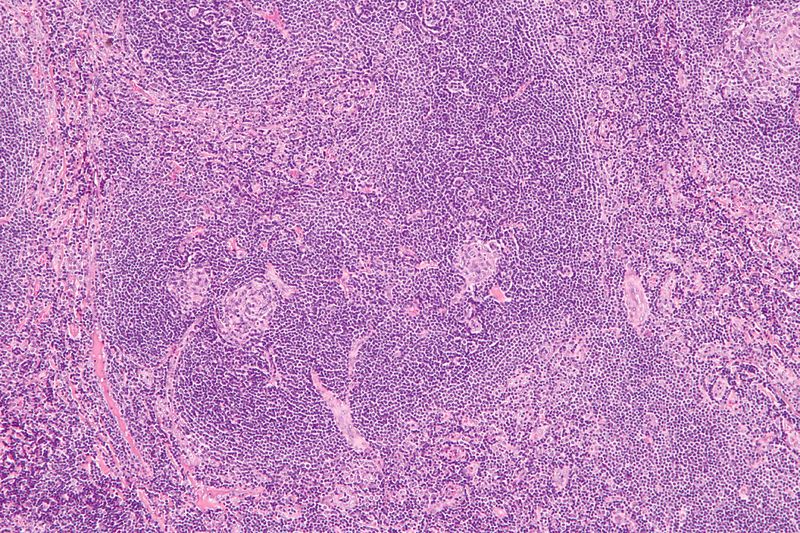
Castleman Disease, often abbreviated as CD, is a rare and complex condition that affects the lymph nodes and immune system. It belongs to a group of disorders known as lymphoproliferative disorders, where the body’s lymphocytes grow uncontrollably. This disease can manifest in various forms, each with its own set of symptoms, challenges, and treatment approaches. While it may not be widely recognized, understanding this disorder is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
What Is Castleman Disease?
Castleman Disease is a rare condition that primarily impacts the lymph nodes, which are small structures that play a critical role in the immune system. These lymph nodes help filter harmful substances from the body and house white blood cells that fight infections. In people with this disease, the lymph nodes become enlarged due to abnormal growth of cells within them. The exact cause of this abnormal growth remains unclear, but researchers believe it is linked to an overactive immune response.
This disease was first described by Dr. Benjamin Castleman in the 1950s, hence its name. Since then, medical professionals have identified two main types of the condition: unicentric and multicentric. Each type has distinct characteristics, symptoms, and treatment strategies.
Unicentric Castleman Disease
Unicentric Castleman Disease refers to a form of the condition where only one group of lymph nodes is affected. Typically, the enlarged lymph nodes are found in the chest or abdomen, though they can occur in other areas as well. People with this form of the disease often experience mild or no symptoms, and the condition may only be discovered incidentally during imaging tests for unrelated issues.
- Symptoms: When symptoms do occur, they may include fatigue, unintended weight loss, night sweats, or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen if the lymph nodes press on nearby organs.
- Treatment: Surgery to remove the affected lymph nodes is often curative for unicentric Castleman Disease. In some cases, medications may be used to shrink the lymph nodes before surgery.
Multicentric Castleman Disease
Multicentric Castleman Disease is a more severe and systemic form of the condition, affecting multiple groups of lymph nodes throughout the body. This type is often associated with more pronounced symptoms and complications, including fever, fatigue, and anemia. Multicentric Castleman Disease can also increase the risk of developing other serious conditions, such as certain cancers or autoimmune diseases.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include widespread lymph node enlargement, fever, night sweats, fatigue, weight loss, and skin rashes. Some individuals may also experience organ dysfunction due to inflammation.
- Treatment: Managing multicentric Castleman Disease typically involves a combination of therapies, including medications to suppress the immune system, chemotherapy, or targeted treatments that address specific proteins involved in the disease process.
The Role of the Immune System in Castleman Disease
The immune system plays a central role in Castleman Disease. Normally, the immune system protects the body by identifying and attacking harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses. However, in people with this condition, the immune system becomes overactive and starts producing excessive amounts of certain proteins, particularly interleukin-6. Interleukin-6 is a molecule that promotes inflammation and stimulates the growth of lymphocytes.
This overproduction of interleukin-6 leads to the characteristic swelling of lymph nodes and other symptoms associated with the disease. Researchers are still working to understand why the immune system behaves this way in individuals with Castleman Disease. Some studies suggest that viral infections, such as human herpesvirus 8, may trigger the condition in certain cases, especially in those with weakened immune systems.
Inflammatory Processes and Their Impact
The chronic inflammation caused by Castleman Disease can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. For example, prolonged inflammation may lead to kidney damage, liver dysfunction, or even heart problems. Additionally, the overactive immune response can result in anemia, low platelet counts, and other blood-related abnormalities.
Understanding these inflammatory processes is essential for developing effective treatments. By targeting the underlying mechanisms driving the disease, healthcare providers can better manage symptoms and improve quality of life for patients.
Diagnosis Challenges and Approaches
Diagnosing Castleman Disease can be challenging due to its rarity and the fact that its symptoms often mimic those of other conditions, such as lymphoma or autoimmune disorders. As a result, many individuals may go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed for extended periods.
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm a diagnosis of Castleman Disease, doctors typically rely on a combination of tests and evaluations. These may include:
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as CT scans, MRI, or PET scans are used to identify enlarged lymph nodes and assess their location and extent.
- Lymph Node Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from an affected lymph node for examination under a microscope. This test is crucial for distinguishing Castleman Disease from other conditions with similar features.
- Blood Tests: Blood work can reveal abnormalities such as elevated levels of interleukin-6, anemia, or abnormal white blood cell counts, which may support the diagnosis.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is vital for improving outcomes in Castleman Disease. Delayed diagnosis can lead to complications, worsening symptoms, and reduced effectiveness of treatments. Therefore, individuals experiencing persistent symptoms such as unexplained fatigue, night sweats, or swollen lymph nodes should seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment Options and Advances
The treatment approach for Castleman Disease depends on the type and severity of the condition. While there is currently no cure for the multicentric form, significant advancements have been made in managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
Unicentric Castleman Disease Treatments
For unicentric Castleman Disease, surgical removal of the affected lymph nodes is usually sufficient to resolve the condition. In cases where surgery is not immediately possible, medications such as corticosteroids or rituximab may be used to reduce the size of the lymph nodes prior to the procedure.
Multicentric Castleman Disease Treatments
Treating multicentric Castleman Disease requires a multifaceted approach. Common treatment options include:
- Immunosuppressive Medications: Drugs like corticosteroids and immunomodulators help reduce inflammation and suppress the overactive immune response.
- Targeted Therapies: Medications such as siltuximab target interleukin-6, helping to block its effects and alleviate symptoms.
- Chemotherapy: In severe cases, chemotherapy may be used to control the rapid growth of lymphocytes.
- Antiviral Therapy: If the disease is linked to a viral infection, antiviral medications may be prescribed to address the underlying cause.
Emerging Research and Clinical Trials
Researchers continue to explore new therapies and treatment strategies for Castleman Disease. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of novel drugs and combinations of existing treatments. Participation in these trials offers hope for improved outcomes and potential breakthroughs in managing this challenging condition.
Living with Castleman Disease
Living with Castleman Disease can be physically and emotionally demanding. Individuals with the condition often face uncertainty about their health and may need to make lifestyle adjustments to cope with symptoms and treatment side effects.
Support Systems and Resources
Building a strong support network is essential for those living with Castleman Disease. Support groups, both online and in-person, provide opportunities to connect with others who understand the unique challenges of the condition. Additionally, organizations dedicated to rare diseases offer valuable resources, including educational materials and advocacy initiatives.
Managing Symptoms and Side Effects
Effective symptom management is key to maintaining quality of life. Strategies may include:
- Adopting a balanced diet to support overall health and energy levels.
- Engaging in light physical activity to combat fatigue and improve mood.
- Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Working closely with healthcare providers to monitor and address treatment side effects.
Raising Awareness and Advocacy
Despite its rarity, raising awareness about Castleman Disease is critical for advancing research and improving patient care. Advocacy efforts aim to educate the public, secure funding for studies, and ensure that individuals with the condition receive timely and accurate diagnoses.
How You Can Help
There are several ways to contribute to the fight against Castleman Disease:
- Participate in fundraising events or donate to organizations supporting rare disease research.
- Share information about the condition with friends, family, and your community to spread awareness.
- Encourage policymakers to prioritize funding for rare disease initiatives.
By working together, we can make strides toward a better understanding of Castleman Disease and ultimately improve the lives of those affected by it.