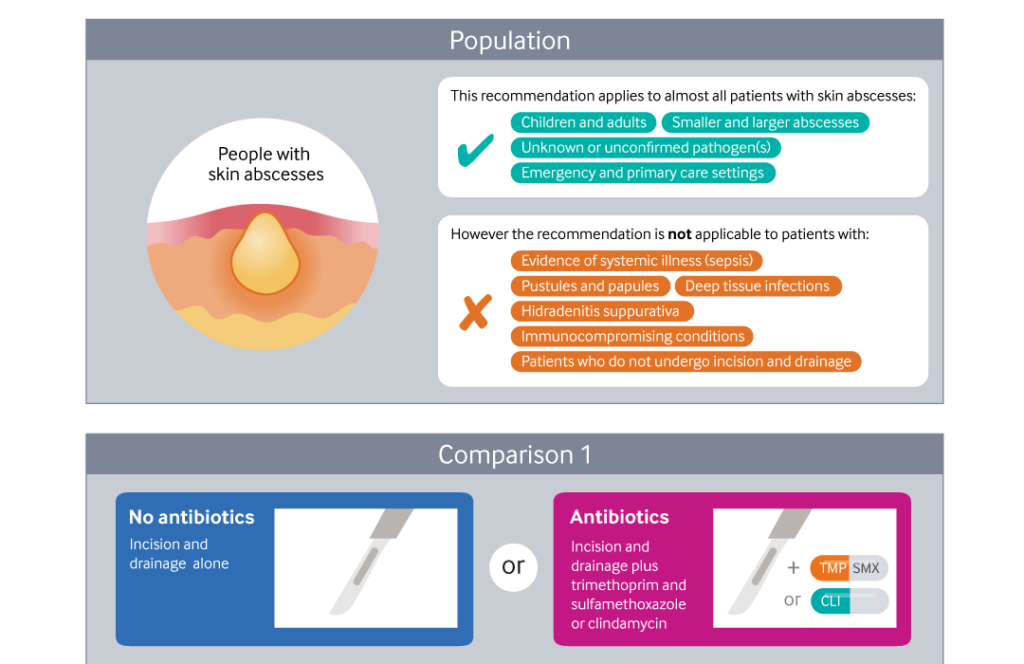
A carbuncle, often referred to as a skin abscess cluster, is a severe and painful infection of the skin that involves multiple hair follicles. It is commonly caused by bacteria and can lead to significant discomfort if left untreated. While medical professionals may use terms like “SAC” (skin abscess cluster) in discussions, this article will focus on explaining the condition in detail without relying on abbreviations.
Understanding Carbuncles
Carbuncles are clusters of boils that form under the skin. These infections typically occur when bacteria invade the deeper layers of the skin, leading to inflammation, pus formation, and swelling. Unlike a single boil, which affects one hair follicle, a carbuncle involves multiple follicles, making it more serious and harder to treat.
What Are Boils?
Before diving into carbuncles, it’s important to understand what boils are. A boil is a red, swollen, and painful lump that forms on the skin due to an infection of a hair follicle. When multiple boils develop close together and merge into a larger mass, they form a carbuncle.
Causes of Carbuncles
Carbuncles are primarily caused by bacterial infections. The most common bacterium responsible for these infections is Staphylococcus aureus, which is naturally present on the skin and inside the nose of many people. However, certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing carbuncles.
Bacterial Infection
The primary cause of carbuncles is the invasion of bacteria into the deeper layers of the skin. When bacteria enter through small cuts, abrasions, or openings in the skin, they can infect the hair follicles and surrounding tissues. This leads to inflammation and the formation of pus-filled abscesses.
Risk Factors
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, HIV, or cancer, are more susceptible to developing carbuncles.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hygiene practices can allow bacteria to thrive on the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
- Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema or dermatitis can compromise the skin’s barrier, making it easier for bacteria to penetrate.
- Close Contact: Living in crowded or unsanitary conditions can facilitate the spread of bacteria, increasing the risk of carbuncles.
- Previous History of Boils: People who have had boils in the past are more likely to develop carbuncles.
Symptoms of Carbuncles
Carbuncles often present with noticeable symptoms that can cause significant discomfort. Recognizing these symptoms early can help individuals seek prompt medical attention and prevent complications.
Common Signs
- Red, Swollen Skin: The affected area becomes red and inflamed, often accompanied by swelling.
- Pain and Tenderness: The infected area is usually painful to touch and may feel tender even without pressure.
- Pus Formation: As the infection progresses, pus accumulates under the skin, forming a large, raised lump.
- Fever and Fatigue: In severe cases, individuals may experience fever, chills, and general fatigue due to the body’s immune response.
- Drainage of Pus: Over time, the carbuncle may rupture, releasing pus and sometimes blood.
Location of Carbuncles
Carbuncles can develop anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on areas where friction or sweating occurs. These include the back of the neck, shoulders, thighs, and buttocks. The location of the carbuncle can influence the severity of symptoms and the treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Carbuncles
Treating carbuncles involves addressing the infection and alleviating symptoms. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment may range from home remedies to medical interventions.
Home Care
Mild carbuncles can often be managed at home with proper care. Here are some steps to follow:
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm, moist compresses to the affected area several times a day can help reduce pain and encourage drainage.
- Good Hygiene: Keeping the area clean and dry is essential to prevent further infection. Wash the area gently with soap and water.
- Avoid Squeezing: Do not attempt to squeeze or puncture the carbuncle, as this can worsen the infection and spread bacteria.
Medical Treatment
For more severe or persistent carbuncles, medical intervention may be necessary. Doctors may recommend the following treatments:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the bacterial infection. In some cases, topical antibiotics may also be used.
- Incision and Drainage: If the carbuncle is large or does not drain on its own, a healthcare professional may need to make a small incision to remove the pus and relieve pressure.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to seek medical attention if the carbuncle does not improve with home care or if any of the following occur:
- The carbuncle is large, deep, or extremely painful.
- Fever or other systemic symptoms develop.
- The carbuncle recurs frequently.
- The infection spreads to surrounding areas.
Preventing Recurrence
To reduce the risk of developing carbuncles in the future, consider the following preventive measures:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly wash your skin with mild soap and water, especially in areas prone to sweating.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, razors, or clothing, as these can spread bacteria.
- Boost Immunity: Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep to strengthen your immune system.
- Treat Minor Cuts Promptly: Clean and cover any cuts or abrasions to prevent bacterial entry.
Complications of Untreated Carbuncles
If left untreated, carbuncles can lead to serious complications. These may include:
- Spread of Infection: The infection can spread to nearby tissues or even enter the bloodstream, causing a condition known as sepsis.
- Scarring: Large or deep carbuncles can leave permanent scars on the skin after healing.
- Chronic Skin Infections: Some individuals may experience recurring carbuncles, requiring ongoing management and treatment.
Impact on Quality of Life
Chronic or severe carbuncles can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Pain, discomfort, and visible skin changes can lead to emotional distress and reduced self-esteem. Seeking timely treatment is crucial to minimize these effects.
Living with Carbuncles
While carbuncles can be uncomfortable and challenging to manage, understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower individuals to take control of their health. By practicing good hygiene, seeking medical care when needed, and adopting preventive measures, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing these painful skin infections.