Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. Among these, Bulimia Nervosa (BN) stands out as one of the most prevalent and challenging to address. Characterized by cycles of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors, this disorder can have devastating effects on both physical and mental health. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Bulimia Nervosa, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the profound impact it has on individuals and their loved ones.
What is Bulimia Nervosa?
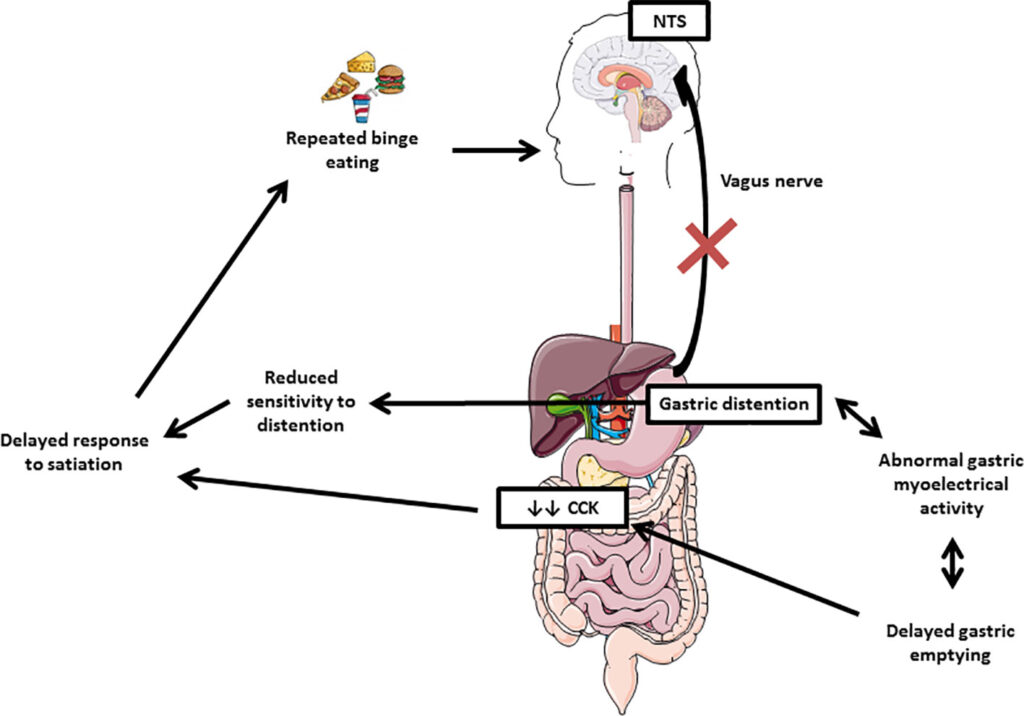
Bulimia Nervosa is a serious eating disorder marked by recurring episodes of excessive food consumption, known as binge eating, followed by actions taken to prevent weight gain. These actions often include self-induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives or diuretics, fasting, or excessive exercise. Unlike other eating disorders, individuals with this condition often maintain a relatively normal body weight, which can make it harder to detect.
The cycle of bingeing and purging is not just about food; it is deeply rooted in emotional and psychological struggles. Many individuals use these behaviors as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, or feelings of inadequacy. However, this coping mechanism can quickly spiral out of control, leading to severe consequences for both mental and physical health.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Identifying Bulimia Nervosa can be challenging, especially since those affected often go to great lengths to hide their behaviors. However, certain signs and symptoms can help in recognizing the disorder:
- Frequent episodes of consuming large amounts of food in a short period, often in secret
- Feelings of loss of control during binge episodes
- Regular use of self-induced vomiting, laxatives, or other methods to prevent weight gain
- Obsession with body weight and shape
- Withdrawal from social activities, particularly those involving food
- Dental problems, such as enamel erosion or cavities, due to frequent vomiting
- Gastrointestinal issues, including acid reflux or constipation
Causes and Risk Factors
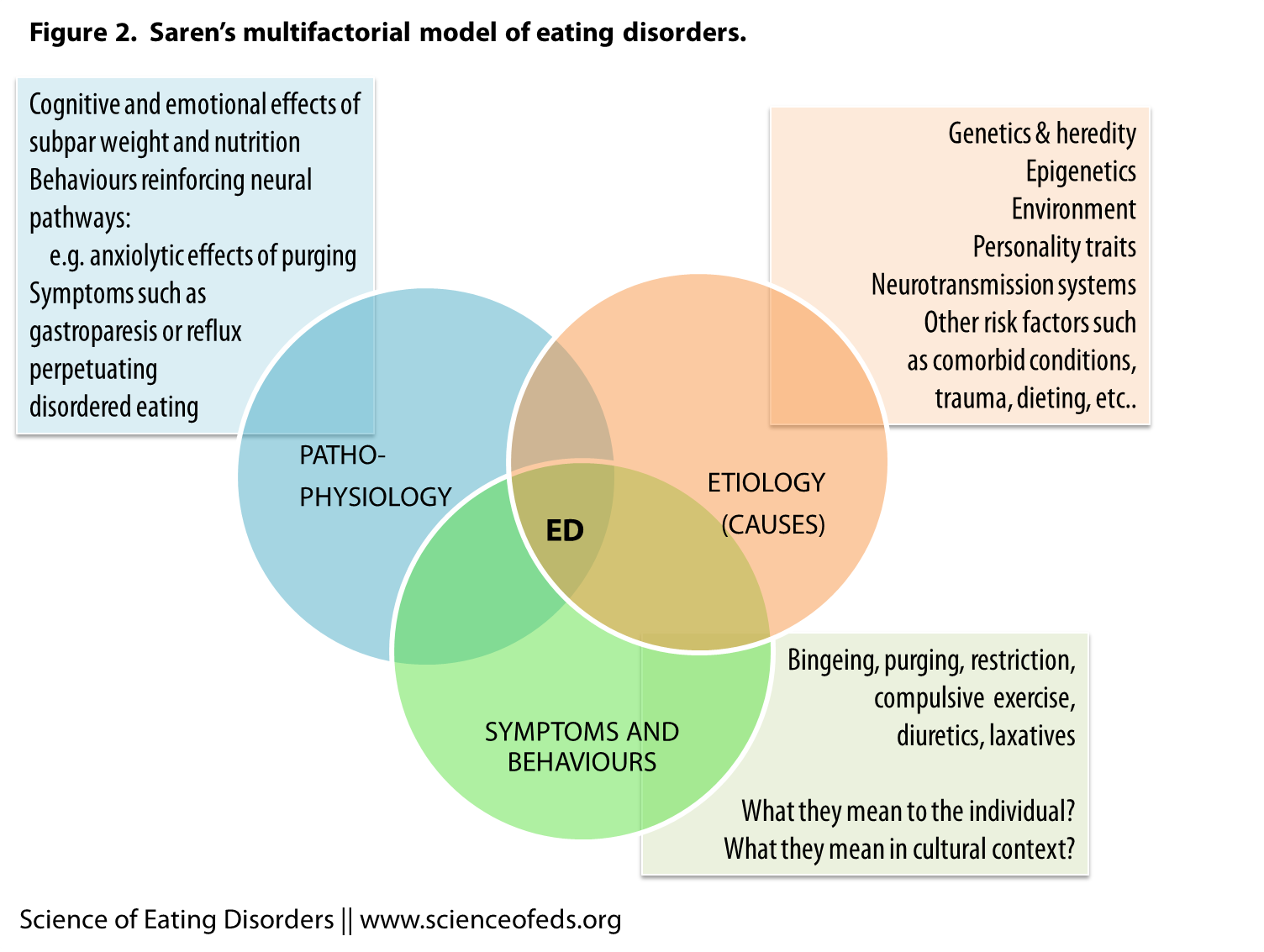
The exact cause of Bulimia Nervosa is not fully understood, but research suggests that it arises from a combination of genetic, biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Genetic Predisposition
Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of eating disorders are at a higher risk of developing Bulimia Nervosa. This suggests that genetics may play a role in predisposing someone to the condition. However, having a genetic predisposition does not guarantee that someone will develop the disorder; environmental factors also play a crucial role.
Psychological Factors
Many individuals with Bulimia Nervosa struggle with underlying mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, or low self-esteem. These conditions can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and contribute to the development of disordered eating patterns. Additionally, perfectionism and an intense fear of gaining weight are common traits among those affected by this disorder.
Societal Pressures
Cultural and societal expectations regarding body image can significantly influence the onset of Bulimia Nervosa. The media often promotes unrealistic standards of beauty, emphasizing thinness as an ideal. This can lead to body dissatisfaction and unhealthy behaviors aimed at achieving a perceived “perfect” appearance. Adolescents and young adults, who are particularly vulnerable to societal pressures, are at a higher risk of developing the disorder.
Physical and Mental Health Consequences
Bulimia Nervosa takes a toll on both the body and mind, leading to a wide range of complications that can persist if left untreated.
Physical Effects
The repeated cycle of bingeing and purging places immense strain on the body, resulting in numerous physical health issues:
- Dental Problems: Frequent vomiting exposes teeth to stomach acid, leading to enamel erosion, cavities, and gum disease.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Misuse of laxatives and diuretics can disrupt the digestive system, causing chronic constipation, diarrhea, or irritable bowel syndrome.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Purging behaviors can lead to imbalances in essential minerals like potassium, sodium, and chloride, which can result in heart problems, muscle weakness, or even cardiac arrest.
- Hormonal Disruptions: Irregular menstrual cycles and fertility issues are common among women with this disorder.
- Kidney Damage: Chronic dehydration and misuse of diuretics can impair kidney function over time.
Mental Health Impacts
The psychological effects of Bulimia Nervosa are equally concerning. Individuals often experience:
- Depression and Anxiety: Feelings of shame, guilt, and worthlessness are common, exacerbating existing mental health conditions.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Behaviors: A preoccupation with food, calories, and body image can dominate daily life.
- Social Isolation: Fear of judgment or embarrassment may lead to withdrawal from friends and family.
- Low Self-Esteem: Negative self-perception and distorted body image can further perpetuate the cycle of disordered eating.
Treatment Options and Recovery
Recovery from Bulimia Nervosa is possible with the right support and treatment plan. A multidisciplinary approach is often necessary to address the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the disorder.
Therapy
Psychotherapy is a cornerstone of treatment for Bulimia Nervosa. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, in particular, has been shown to be highly effective in helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to food and body image. Other therapeutic approaches, such as interpersonal therapy and dialectical behavior therapy, may also be beneficial.
Medical Care
Addressing the physical consequences of the disorder is critical. Medical professionals may monitor electrolyte levels, treat dental issues, and provide nutritional counseling to restore a healthy relationship with food. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to stabilize the individual’s health.
Support Systems
Family and friends play a vital role in the recovery process. Support groups, both in-person and online, can provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and connect with others who understand their struggles. Encouragement and understanding from loved ones can make a significant difference in the journey toward healing.
Breaking the Stigma
Despite growing awareness, stigma surrounding eating disorders like Bulimia Nervosa persists. Many individuals hesitate to seek help due to fear of judgment or misunderstanding. It is essential to foster open conversations about mental health and challenge misconceptions about eating disorders. Education and advocacy can help reduce stigma and encourage those affected to seek the support they need.
Raising Awareness
Public awareness campaigns, school programs, and community initiatives can play a pivotal role in educating people about the realities of Bulimia Nervosa. By promoting empathy and understanding, we can create a more supportive environment for individuals struggling with this condition.
Encouraging Early Intervention
Early detection and intervention are crucial in preventing the long-term consequences of Bulimia Nervosa. Healthcare providers, educators, and parents should be vigilant in recognizing the warning signs and providing timely support. Open communication and access to resources can make a significant difference in improving outcomes for those affected.