Boils, also known as furuncles, are a common skin condition that can cause discomfort and concern. These painful bumps occur when hair follicles become infected, often resulting in localized swelling and pus formation. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for boils is essential to managing this condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into all aspects of boils to provide a comprehensive guide for those seeking information on this topic.
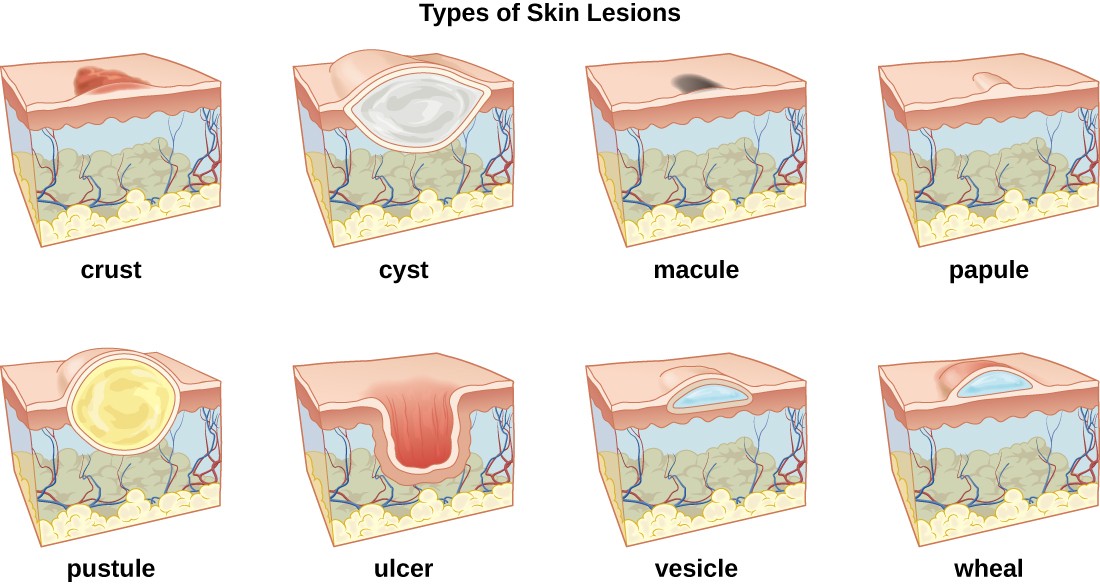
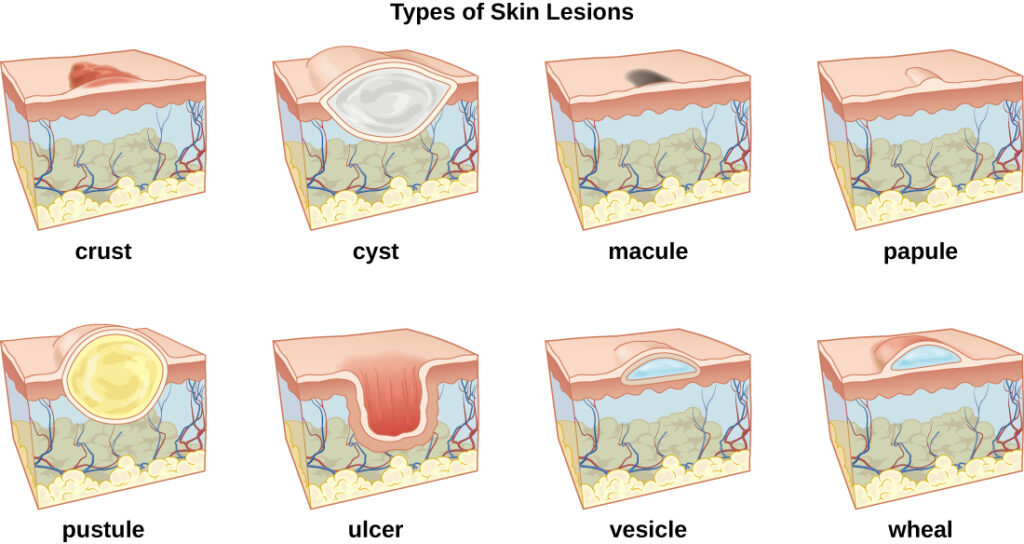
What Are Boils?
Boils are red, tender lumps that develop under the skin due to an infection in a hair follicle or oil gland. They often start as small, sore areas but can grow larger over time as they fill with pus. Boils can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, shoulders, and buttocks. The size of a boil can vary from as small as a pea to as large as a golf ball, depending on the severity of the infection.
How Do Boils Form?
The formation of a boil begins when bacteria enter a hair follicle or oil gland through a small cut or opening in the skin. Once inside, the bacteria multiply, leading to inflammation and the accumulation of pus. This process results in the characteristic swollen, painful lump associated with boils. Over time, the boil may rupture, releasing the pus and allowing the infection to drain.
Causes of Boils
Several factors can contribute to the development of boils. Understanding these causes can help individuals take steps to minimize their risk of experiencing this uncomfortable condition.
Bacterial Infection
The primary cause of boils is a bacterial infection. Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria commonly found on the skin and inside the nose, is the most frequent culprit. When this bacteria enters a hair follicle or oil gland, it triggers an immune response, leading to the formation of a boil.
Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene practices can increase the likelihood of developing boils. Failing to wash the skin regularly or wearing unwashed clothing can create an environment where bacteria thrive, increasing the risk of infection.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections, including boils. Conditions such as diabetes, HIV, or cancer, as well as medications that suppress the immune system, can make it harder for the body to fight off bacterial infections.
Skin Irritation
Frequent friction or irritation of the skin can damage hair follicles, making them more vulnerable to infection. Activities such as shaving, tight clothing, or repetitive rubbing can contribute to the development of boils.
Symptoms of Boils
Recognizing the symptoms of boils is crucial for early detection and treatment. While the appearance and severity of boils can vary, there are several common signs to watch for.
Redness and Swelling
A boil typically begins as a red, tender area on the skin. Over time, this area becomes increasingly swollen and painful as the infection progresses.
Pain and Tenderness
Boils are often accompanied by significant pain and tenderness. The affected area may feel warm to the touch, and the pain can worsen as the boil grows larger.
Pus Formation
As the infection develops, pus accumulates within the boil. This pus is a thick, yellowish fluid composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Eventually, the boil may rupture, releasing the pus and providing some relief from the pressure.
Fever and Fatigue
In severe cases, boils can lead to systemic symptoms such as fever and fatigue. These symptoms indicate that the infection may be spreading beyond the localized area, requiring prompt medical attention.
Treatment Options for Boils
There are several treatment options available for managing boils, ranging from home remedies to medical interventions. The appropriate treatment depends on the size, location, and severity of the boil.
Warm Compresses
One of the simplest and most effective ways to treat a boil is by applying warm compresses. Soaking a clean cloth in warm water and placing it over the boil for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day can help reduce pain and encourage the boil to drain naturally.
Antibacterial Ointments
Over-the-counter antibacterial ointments can be applied to the affected area to help combat the infection. These ointments work by killing bacteria on the surface of the skin, preventing the infection from worsening.
Incision and Drainage
For large or persistent boils, a healthcare professional may need to perform an incision and drainage procedure. During this process, the boil is carefully cut open to allow the pus to drain out. This procedure should only be performed by a qualified medical professional to avoid complications.
Oral Antibiotics
In cases where the infection has spread or is particularly severe, oral antibiotics may be prescribed. These medications work by targeting the bacteria responsible for the infection, helping to clear it from the body.
Prevention of Boils
While it may not always be possible to prevent boils entirely, there are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing this condition.
Maintain Good Hygiene
- Wash your skin regularly with soap and water, especially after sweating or exposure to dirt.
- Keep your hands clean by washing them frequently throughout the day.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or clothing with others.
Protect Your Skin
- Avoid activities that cause excessive friction or irritation to the skin, such as wearing tight clothing or using harsh skincare products.
- Shave carefully to prevent cuts or nicks that could allow bacteria to enter the skin.
- Use moisturizers to keep your skin hydrated and healthy, reducing the risk of cracks or openings that could harbor bacteria.
Boost Your Immune System
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support overall health and immune function.
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and strengthen the immune system.
- Get adequate sleep each night to ensure your body has time to repair and regenerate.
Manage Underlying Health Conditions
If you have a chronic health condition such as diabetes, it is important to manage it effectively to reduce your risk of developing boils. Work closely with your healthcare provider to maintain optimal blood sugar levels and follow any recommended treatment plans.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many boils can be treated at home, there are certain situations where medical attention is necessary. If you experience any of the following, consult a healthcare professional promptly:
- A boil that does not improve after two weeks of home treatment.
- A boil that is extremely painful or growing rapidly.
- A boil accompanied by fever, chills, or other systemic symptoms.
- Multiple boils appearing in different areas of the body.
Complications of Untreated Boils
If left untreated, boils can lead to complications such as abscess formation, cellulitis, or the spread of infection to other parts of the body. Seeking timely medical care can help prevent these complications and ensure proper healing.