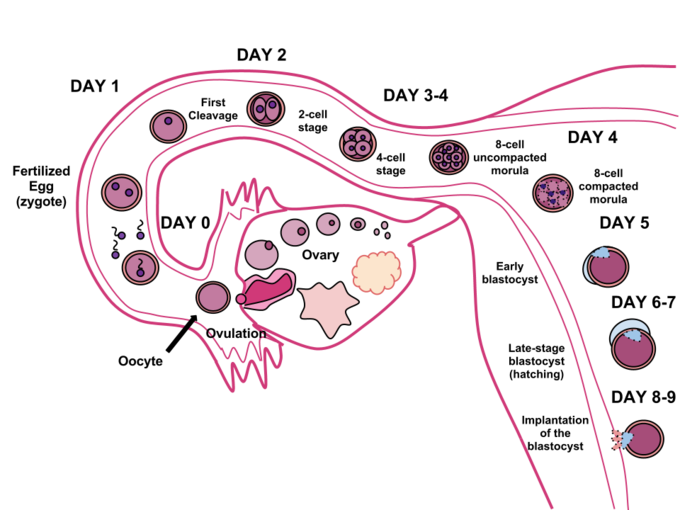
A blighted ovum, also known as an anembryonic pregnancy, is a condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the uterus but does not develop into an embryo.
This type of pregnancy loss can be emotionally challenging for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive. Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and management options can help provide clarity and support during this difficult time.
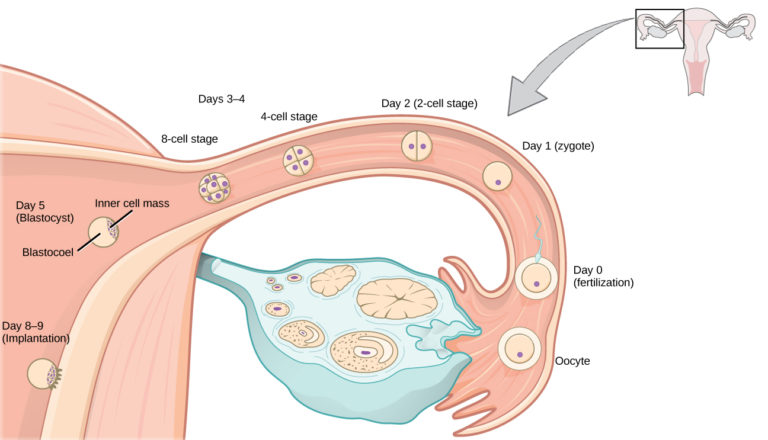
What is a Blighted Ovum?
A blighted ovum is a form of early pregnancy loss where a gestational sac forms in the uterus, but the embryo fails to develop or stops developing shortly after conception.
Despite the absence of an embryo, the body may still produce pregnancy hormones, leading to symptoms such as a missed period and positive pregnancy tests.
This can create confusion and emotional distress for those expecting a healthy pregnancy.
Why Does a Blighted Ovum Happen?
The exact cause of a blighted ovum is often unknown, but several factors may contribute to its occurrence:
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: The most common cause of a blighted ovum is abnormal chromosome division during fertilization.
These abnormalities can prevent the embryo from forming or developing properly. - Genetic Factors: In some cases, genetic issues in either parent may increase the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Insufficient levels of certain hormones, such as progesterone, may affect the development of the embryo and lead to a blighted ovum.
- Uterine Abnormalities: Structural issues within the uterus, such as fibroids or scarring, may interfere with the implantation process or the growth of the embryo.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to harmful substances, such as toxins or radiation, may increase the likelihood of pregnancy complications, including a blighted ovum.
Diagnosing a Blighted Ovum
Diagnosing a blighted ovum typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
Early detection can help individuals understand their situation and make informed decisions about their care.
Symptoms of a Blighted Ovum
In many cases, individuals with a blighted ovum may not experience any noticeable symptoms until they undergo routine prenatal testing. However, some signs may indicate the possibility of a blighted ovum:
- Positive pregnancy test followed by no visible embryo on ultrasound
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Mild cramping or pelvic pain
- Lack of typical pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea or breast tenderness
Diagnostic Procedures
To confirm a diagnosis of a blighted ovum, healthcare providers may use the following methods:
- Ultrasound Examination: An ultrasound is the primary tool used to diagnose a blighted ovum.
During the scan, the presence of a gestational sac without an embryo is a key indicator of this condition. - Blood Tests: Blood tests measuring levels of human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone produced during pregnancy, can provide additional information.
Low or declining levels of this hormone may suggest a non-viable pregnancy. - Follow-Up Appointments: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend repeat ultrasounds or blood tests to monitor changes over time before making a definitive diagnosis.
Managing a Blighted Ovum
Once diagnosed, individuals have several options for managing a blighted ovum.
The choice of treatment depends on personal preferences, medical advice, and individual health circumstances.
Expectant Management
Expectant management involves allowing the body to naturally miscarry the pregnancy without medical intervention.
This approach may take weeks or even months, and it is often recommended for individuals who prefer a non-invasive option.
During this time, healthcare providers closely monitor the individual’s condition to ensure there are no complications.
Medical Management
Medical management involves the use of medications to induce the miscarriage process.
A commonly prescribed medication for this purpose is misoprostol, which helps the uterus expel its contents.
This option allows for a more controlled and predictable timeline compared to expectant management.
Healthcare providers will provide guidance on dosage, administration, and what to expect during the process.
Surgical Management
Surgical management, also known as dilation and curettage, is a procedure performed to remove the contents of the uterus.
This option is typically recommended if there are signs of infection, heavy bleeding, or if the individual prefers a quicker resolution.
While surgery carries risks such as infection or uterine damage, it is generally considered safe when performed by experienced healthcare professionals.
Emotional Support and Counseling
Experiencing a blighted ovum can be emotionally taxing, and seeking support is an important part of the healing process.
Many individuals benefit from speaking with a counselor or joining a support group to connect with others who have gone through similar experiences.
Open communication with loved ones can also provide comfort and understanding during this challenging time.
Preventing Future Occurrences
While it is not always possible to prevent a blighted ovum, certain steps may reduce the risk of future occurrences:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and alcohol can support reproductive health.
- Monitor Hormonal Health: Addressing hormonal imbalances under the guidance of a healthcare provider may improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
- Undergo Genetic Testing: For individuals with recurrent pregnancy losses, genetic testing may help identify underlying issues that could contribute to future complications.
- Consult a Specialist: Working with a fertility specialist or obstetrician can provide personalized care and guidance for those planning future pregnancies.
When to Seek Help
If you suspect you may be experiencing a blighted ovum or are concerned about your pregnancy, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, heavy bleeding, or signs of infection require immediate evaluation to ensure your safety and well-being.
Healthcare providers are equipped to offer compassionate care and support throughout the diagnostic and management process.
Do not hesitate to ask questions or express your concerns, as open communication can help you navigate this challenging experience with confidence.