Bees are fascinating creatures that play a crucial role in our ecosystem. However, when they sting, it can lead to discomfort or even severe health risks for some individuals. Understanding the symptoms, allergic reactions, and first aid steps is essential for anyone who spends time outdoors. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about bee stings without abbreviations.

What Happens When a Bee Stings?
A bee sting occurs when a bee injects venom into the skin through its stinger. The stinger is a small, barbed structure located at the end of the bee’s abdomen. When a bee feels threatened, it uses its stinger as a defense mechanism. Unlike wasps and hornets, honeybees lose their stingers after stinging a human or animal, which ultimately leads to their death. This makes their sting particularly painful and concerning.
Symptoms of a Bee Sting
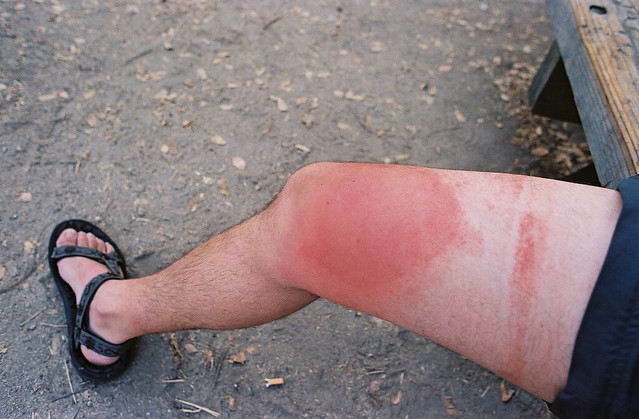
The symptoms of a bee sting can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the location of the sting. Most people experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe reactions. Below is a list of common symptoms:
- Immediate pain at the site of the sting
- Swelling around the affected area
- Redness and warmth on the skin
- A small white spot where the stinger punctured the skin
- Itching or irritation
In most cases, these symptoms subside within a few hours. However, if the sting occurs on sensitive areas such as the face, mouth, or throat, it may cause additional complications.
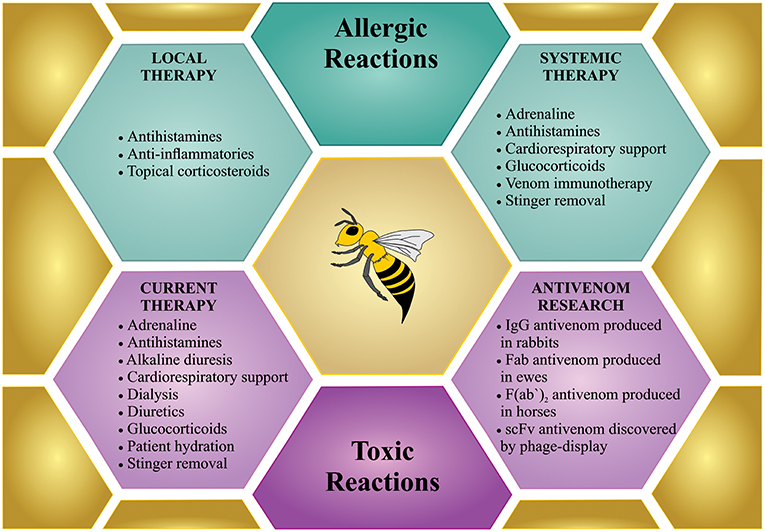
Allergic Reactions to Bee Stings
While many people experience mild discomfort from a bee sting, others may develop an allergic reaction. An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system overreacts to the venom injected by the bee. There are two types of allergic reactions: localized and systemic.
Localized Allergic Reactions
A localized allergic reaction is confined to the area of the sting. It often results in more pronounced symptoms than a typical sting. These may include:
- Extreme swelling that extends beyond the immediate sting site
- Persistent redness and warmth
- Severe itching or discomfort
Although localized reactions can be uncomfortable, they are generally not life-threatening. Over-the-counter medications and home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms.
Systemic Allergic Reactions
A systemic allergic reaction, also known as anaphylaxis, is a medical emergency. It occurs when the body’s immune system responds aggressively to the bee venom. Symptoms of anaphylaxis can appear within minutes of the sting and may include:
- Difficulty breathing due to swelling in the throat or airways
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
- Hives or widespread itching across the body
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- A drop in blood pressure leading to shock
If someone experiences any of these symptoms after a bee sting, immediate medical attention is required. Anaphylaxis can be fatal if not treated promptly.
First Aid Steps for Bee Stings
Knowing how to respond to a bee sting can make a significant difference in minimizing discomfort and preventing complications. Here are the recommended first aid steps:
Step 1: Remove the Stinger
If the stinger is still embedded in the skin, it is important to remove it as quickly as possible. Leaving the stinger in place allows more venom to enter the body. To remove the stinger:
- Use a flat object, such as a credit card or fingernail, to scrape the stinger out.
- Avoid using tweezers, as squeezing the stinger may release additional venom.
Step 2: Clean the Area
After removing the stinger, clean the affected area with soap and water. This helps reduce the risk of infection. Pat the area dry with a clean towel.
Step 3: Apply a Cold Compress
To reduce swelling and numb the pain, apply a cold compress or ice pack to the sting site. Wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin. Leave the compress on for 10 to 20 minutes at a time.
Step 4: Use Anti-Itch Creams or Antihistamines
If itching or irritation persists, consider applying an anti-itch cream or taking an oral antihistamine. These products can help relieve discomfort and reduce swelling. Follow the instructions on the packaging for proper usage.
Step 5: Monitor for Severe Symptoms
Keep a close eye on the individual for any signs of an allergic reaction. If symptoms worsen or systemic reactions occur, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Preventing Bee Stings
While it is impossible to completely avoid bees, there are several precautions you can take to minimize the risk of being stung:
- Avoid wearing bright colors or floral patterns, as these can attract bees.
- Refrain from using strong perfumes or scented lotions outdoors.
- Keep food and drinks covered when eating outside.
- Stay calm and move slowly if a bee approaches you.
- Do not swat at bees, as this may provoke them to sting.
Special Precautions for Individuals with Allergies
If you or someone you know has a known allergy to bee stings, it is crucial to take extra precautions. Always carry an epinephrine auto-injector, commonly referred to as an EpiPen, in case of an emergency. Ensure that family members or friends are aware of the allergy and know how to administer the injection if needed.
Treatment Options for Bee Stings
In addition to first aid measures, there are various treatment options available for managing bee stings. For mild cases, over-the-counter medications such as pain relievers and antihistamines are sufficient. However, individuals with severe allergies may require prescription medications or immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy for Bee Sting Allergies
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, is a long-term treatment option for individuals with severe bee sting allergies. This process involves gradually exposing the immune system to small amounts of bee venom under medical supervision. Over time, the body becomes desensitized to the venom, reducing the likelihood of severe reactions in the future.
When to See a Doctor
Most bee stings do not require medical attention. However, you should consult a healthcare professional if:
- The sting occurs on the face, mouth, or throat.
- Swelling worsens or spreads significantly.
- Symptoms persist for more than a few days.
- You suspect an infection, indicated by increased redness, warmth, or pus at the site.
Understanding the Importance of Bees
While bee stings can be painful and potentially dangerous, it is important to recognize the vital role bees play in our environment. Bees are responsible for pollinating a significant portion of the world’s crops, contributing to food production and biodiversity. By understanding their behavior and taking precautions, we can coexist safely with these essential insects.