Allergic Rhinitis, commonly referred to as AR or Hay Fever, is a widespread condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the environment, leading to inflammation of the nasal passages. This article delves into the symptoms, triggers, and available treatments for this condition, providing a comprehensive understanding for those who suffer from it or wish to learn more.
Understanding Allergic Rhinitis
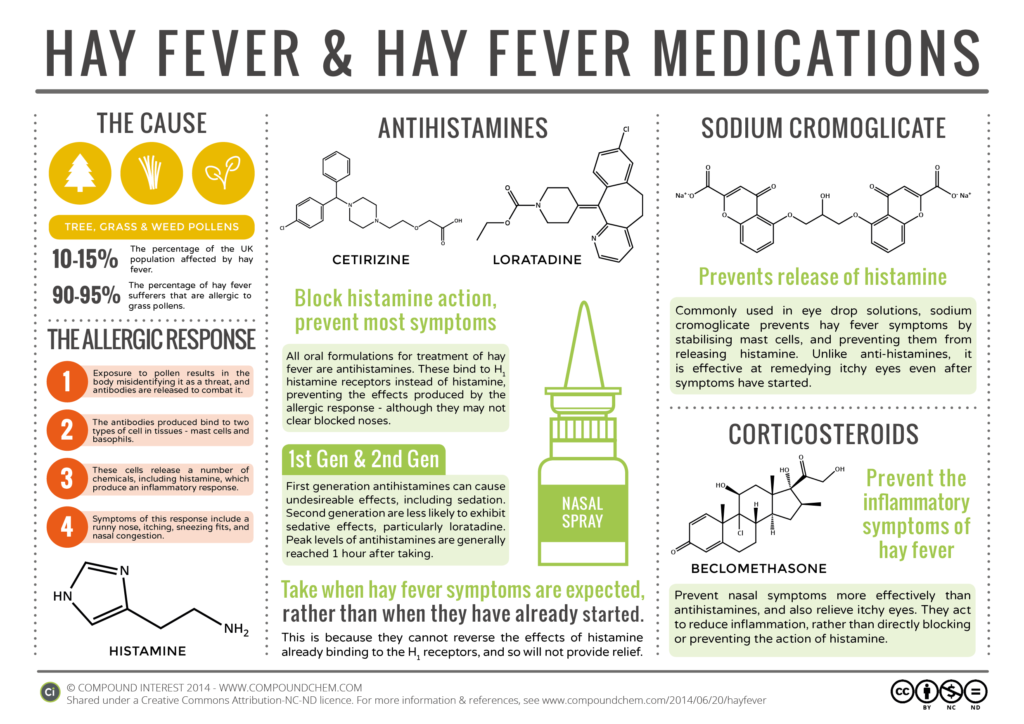
Allergic Rhinitis is an allergic reaction that primarily affects the nose. It is triggered by inhaling airborne particles such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, or pet dander. When these allergens enter the body, the immune system mistakenly identifies them as harmful invaders and releases chemicals like histamine to combat them. This response leads to the characteristic symptoms associated with the condition.
Types of Allergic Rhinitis
- Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis: This type occurs during specific times of the year, typically in spring or fall, when certain plants release pollen into the air.
- Perennial Allergic Rhinitis: Unlike seasonal rhinitis, this form persists throughout the year. It is usually caused by indoor allergens such as dust mites, mold, or pet dander.
Symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis
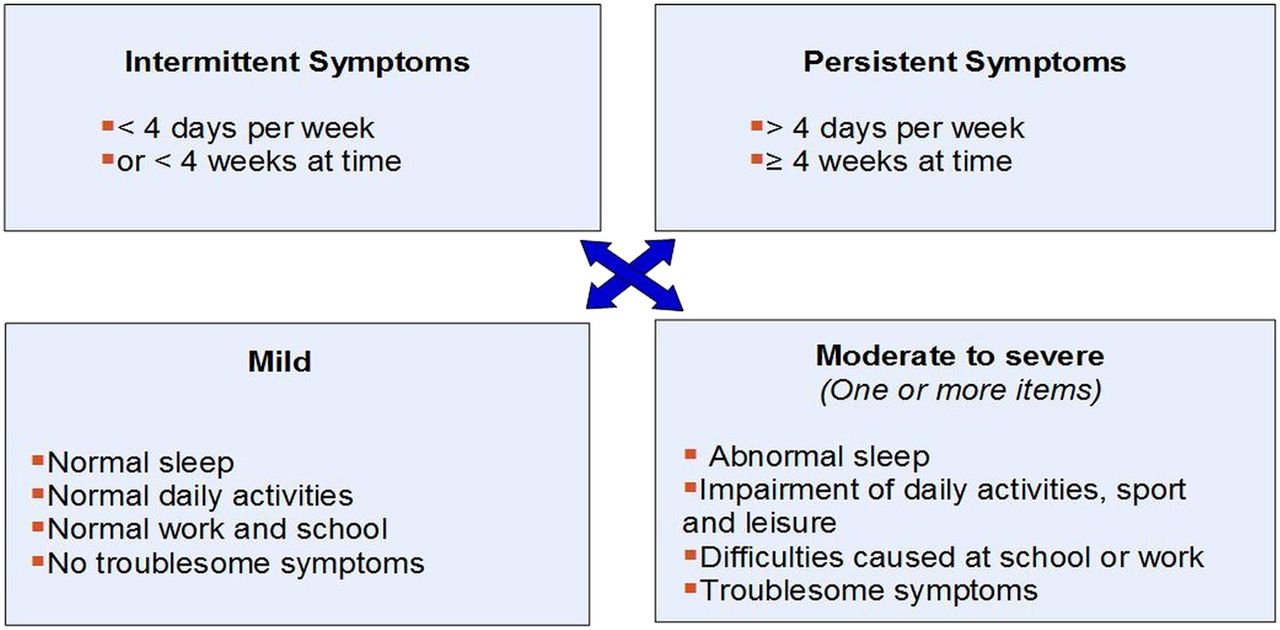
The symptoms of this condition can range from mild to severe and may significantly impact daily life. Common symptoms include:
Nasal Symptoms
- Sneezing: Frequent and uncontrollable sneezing is one of the hallmark signs of the condition.
- Runny Nose: A clear, watery discharge from the nose is common.
- Nasal Congestion: Swelling of the nasal passages can lead to difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Postnasal Drip: Excess mucus dripping down the back of the throat can cause irritation and coughing.
Ocular Symptoms
- Itchy Eyes: The eyes may feel irritated and itchy due to the allergic reaction.
- Watery Eyes: Excessive tearing is another frequent symptom.
- Redness: The whites of the eyes may appear red and inflamed.
Other Symptoms
- Fatigue: Constant discomfort and disrupted sleep can lead to tiredness.
- Headaches: Sinus pressure and congestion may result in headaches.
- Reduced Sense of Smell: Inflammation in the nasal passages can impair the ability to smell.
Common Triggers of Allergic Rhinitis
Identifying the triggers of this condition is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. Below are some of the most common culprits:
Pollen
Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds is a major trigger for seasonal allergic rhinitis. The timing and severity of symptoms depend on the type of pollen and the region you live in. For instance, tree pollen is prevalent in early spring, while grass pollen peaks in late spring and summer.
Dust Mites
Dust mites are microscopic creatures that thrive in warm, humid environments. They are commonly found in bedding, upholstered furniture, and carpets. People with perennial allergic rhinitis often experience symptoms due to exposure to dust mites.
Mold Spores
Mold grows in damp areas such as bathrooms, basements, and kitchens. Mold spores become airborne and can trigger allergic reactions when inhaled. Outdoor mold is also a concern, especially in wet or humid climates.
Pet Dander
Pet dander consists of tiny flecks of skin shed by animals such as cats, dogs, and rodents. These particles can linger in the air and settle on surfaces, making them a persistent trigger for those with allergies.
Other Triggers
- Cigarette Smoke: Even secondhand smoke can exacerbate symptoms.
- Strong Odors: Perfumes, cleaning products, and air fresheners may irritate the nasal passages.
- Air Pollution: Pollutants in the air can worsen allergic reactions.
Treatment Options for Allergic Rhinitis
While there is no cure for this condition, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, medical procedures.
Lifestyle Changes
Making adjustments to your environment and daily habits can significantly reduce exposure to allergens and alleviate symptoms.
- Keep Windows Closed: During peak pollen seasons, keep windows and doors shut to prevent allergens from entering your home.
- Use Air Purifiers: High-efficiency particulate air purifiers can remove allergens from indoor spaces.
- Wash Bedding Regularly: Hot water kills dust mites and removes allergens from bedding.
- Vacuum Frequently: Use a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter to trap allergens.
Medications
Over-the-counter and prescription medications are widely used to treat symptoms. Some of the most common options include:
- Antihistamines: These block the effects of histamine, reducing sneezing, itching, and runny nose.
- Decongestants: These relieve nasal congestion by shrinking swollen blood vessels in the nasal passages.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These sprays reduce inflammation and are highly effective for long-term symptom control.
- Eye Drops: Antihistamine or mast cell stabilizer eye drops can relieve itchy and watery eyes.
Allergy Shots
For individuals with severe or persistent symptoms, allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, may be recommended. This treatment involves receiving regular injections containing small amounts of allergens to desensitize the immune system over time. While it requires a long-term commitment, immunotherapy can provide lasting relief for many patients.
Nasal Irrigation
Nasal irrigation involves flushing out the nasal passages with a saline solution. This can help remove allergens and mucus, providing temporary relief from congestion and irritation. Devices such as neti pots or squeeze bottles are commonly used for this purpose.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals explore alternative treatments to complement traditional methods. These may include:
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, such as butterbur and stinging nettle, are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help reduce symptoms in some individuals.
- Dietary Changes: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may support overall immune health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of this condition can be managed at home, there are instances when medical attention is necessary. Consult a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms persist despite using over-the-counter medications.
- Symptoms interfere with daily activities or sleep.
- You experience severe side effects from medications.
- You suspect you may have developed additional complications, such as sinus infections or asthma.
Preventing Allergic Rhinitis
While it may not be possible to completely avoid allergens, taking preventive measures can minimize exposure and reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. Some strategies include:
- Monitoring pollen counts and staying indoors during peak times.
- Showering and changing clothes after spending time outdoors.
- Using allergen-proof covers on mattresses and pillows.
- Keeping pets out of bedrooms and off furniture.