Acute sinusitis, often abbreviated as AS, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the cavities around the nasal passages become inflamed and swollen, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for acute sinusitis in detail, helping you better understand this condition and how it can be managed effectively.
Understanding Acute Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis refers to the sudden onset of inflammation in the sinuses, which are air-filled spaces located within the bones of the face. These spaces are connected to the nasal passages and play a crucial role in filtering, warming, and humidifying the air we breathe. When these cavities become inflamed, they can trap mucus, leading to infection and discomfort.
What Are the Sinuses?
- The sinuses are hollow spaces found in the bones of the skull, primarily around the nose and eyes.
- There are four pairs of sinuses: the maxillary sinuses (located in the cheekbones), the frontal sinuses (above the eyes), the ethmoid sinuses (between the eyes), and the sphenoid sinuses (behind the nose).
- These cavities are lined with a thin layer of tissue that produces mucus, which helps keep the nasal passages clear of debris and allergens.
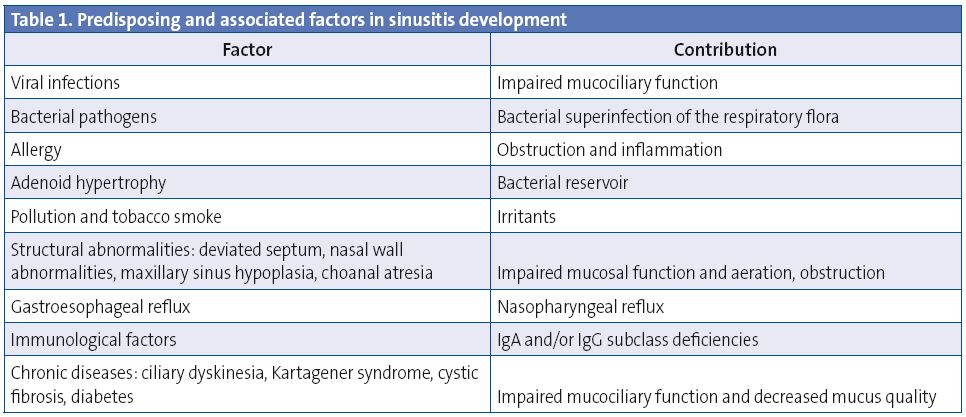
Causes of Acute Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis can develop due to various factors, with infections being the most common cause. Understanding the underlying triggers can help in preventing and managing the condition effectively.
Infections
Infections are the primary cause of acute sinusitis. These infections can be either viral or bacterial in nature:
- Viral Infections: The majority of cases of acute sinusitis are caused by viruses, such as those responsible for the common cold. Viral infections typically resolve on their own within a week or two.
- Bacterial Infections: In some cases, a viral infection can progress to a bacterial infection, leading to more severe symptoms. Bacterial sinusitis often requires medical intervention, such as antibiotics.
Allergies
Allergic reactions can also trigger acute sinusitis. Allergens like pollen, dust, mold, and pet dander can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses, leading to blockages and trapped mucus.
Nasal Polyps
Nasal polyps are soft, noncancerous growths that develop in the lining of the nasal passages or sinuses. These growths can obstruct the flow of mucus, increasing the risk of infection and inflammation.
Deviated Septum
A deviated septum occurs when the wall separating the two nostrils is displaced to one side. This structural abnormality can interfere with proper drainage of the sinuses, making individuals more susceptible to sinusitis.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to pollutants, cigarette smoke, and dry air can irritate the nasal passages and sinuses, contributing to the development of acute sinusitis.
Symptoms of Acute Sinusitis
The symptoms of acute sinusitis can vary from mild to severe, depending on the underlying cause and the individual’s overall health. Common signs and symptoms include:
Nasal Congestion
One of the hallmark symptoms of acute sinusitis is nasal congestion. Individuals may experience difficulty breathing through the nose due to swelling and excess mucus production.
Facial Pain and Pressure
Acute sinusitis often causes pain and pressure in the face, particularly around the eyes, cheeks, and forehead. This discomfort is due to the buildup of mucus and inflammation in the sinuses.
Thick Nasal Discharge
Individuals with acute sinusitis may notice thick, discolored nasal discharge. This discharge can be yellow or green and may drain down the back of the throat, causing postnasal drip.
Reduced Sense of Smell
Inflammation in the nasal passages can impair the sense of smell, making it difficult for individuals to detect odors.
Cough
A persistent cough, especially at night, is a common symptom of acute sinusitis. This cough is often caused by postnasal drip irritating the throat.
Fever
In cases where a bacterial infection is present, individuals may develop a fever along with other symptoms.
Fatigue
Acute sinusitis can cause fatigue and a general feeling of being unwell, as the body works to fight off the infection.
Diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis
Diagnosing acute sinusitis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic tests. A healthcare provider will assess the symptoms and determine the underlying cause to recommend appropriate treatment.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will check for signs of inflammation, such as swelling and tenderness in the facial area. They may also use a lighted instrument to examine the nasal passages for signs of mucus buildup or polyps.
Medical History
A detailed medical history is essential for diagnosing acute sinusitis. The healthcare provider will ask about the duration and severity of symptoms, any recent illnesses, and potential exposure to allergens or irritants.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. These tests may include:
- X-rays: X-rays can provide a basic view of the sinuses and identify areas of inflammation or blockage.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans offer a more detailed view of the sinuses and are particularly useful for identifying structural abnormalities or complications.
Nasal Endoscopy
A nasal endoscopy involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the nasal passages to examine the sinuses closely. This procedure can help identify issues such as polyps or blockages.
Treatment Options for Acute Sinusitis
The treatment of acute sinusitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. In many cases, the condition resolves on its own without medical intervention. However, certain treatments can help alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery.
Home Remedies
For mild cases of acute sinusitis, home remedies may be sufficient to manage symptoms:
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water or a warm shower can help relieve nasal congestion and promote drainage.
- Saline Nasal Irrigation: Using a saline solution to rinse the nasal passages can remove excess mucus and allergens, reducing inflammation.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus, making it easier to drain from the sinuses.
- Rest: Adequate rest allows the body to focus on fighting the infection.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications can provide relief from symptoms such as pain, congestion, and fever:
- Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce pain and fever associated with acute sinusitis.
- Decongestants: Oral or nasal decongestants can alleviate nasal congestion by shrinking swollen blood vessels in the nasal passages.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines can be helpful for individuals whose symptoms are triggered by allergies.
Prescription Medications
In cases where a bacterial infection is suspected, a healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the infection from returning.
Allergy Management
For individuals with allergy-related acute sinusitis, managing allergies is crucial. This may involve avoiding known allergens, using allergy medications, or undergoing allergy testing and immunotherapy.
Surgical Interventions
In rare cases where structural abnormalities or chronic sinusitis are present, surgical interventions may be necessary. Procedures such as endoscopic sinus surgery or balloon sinuplasty can help improve sinus drainage and reduce the frequency of infections.
Preventing Acute Sinusitis
While it may not always be possible to prevent acute sinusitis, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing the condition:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections can help prevent the spread of viruses and bacteria.
- Manage Allergies: Keeping allergies under control can reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain healthy mucus production and promotes sinus drainage.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimizing exposure to pollutants, cigarette smoke, and other irritants can protect the nasal passages from inflammation.