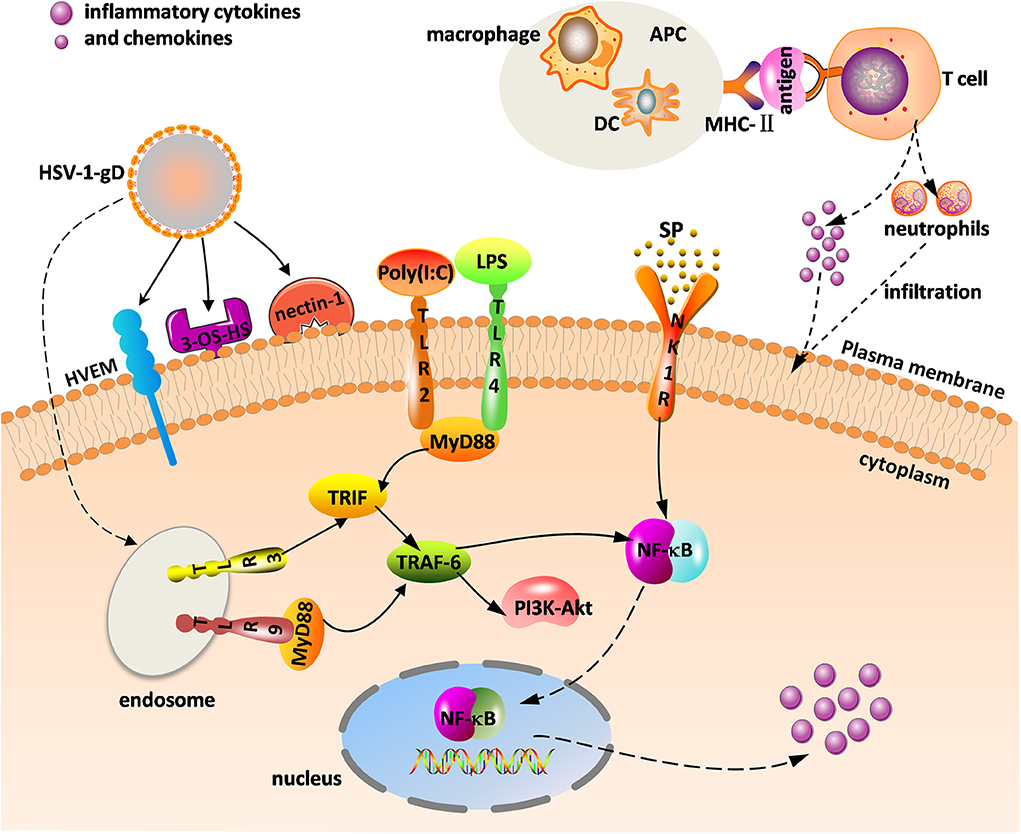
The Herpes Simplex Virus, commonly abbreviated as HSV, is a widespread viral infection that affects millions of people globally. This article delves into the two main types of the virus, their associated symptoms, methods of diagnosis, and available treatments. Understanding this condition is crucial for both prevention and effective management.
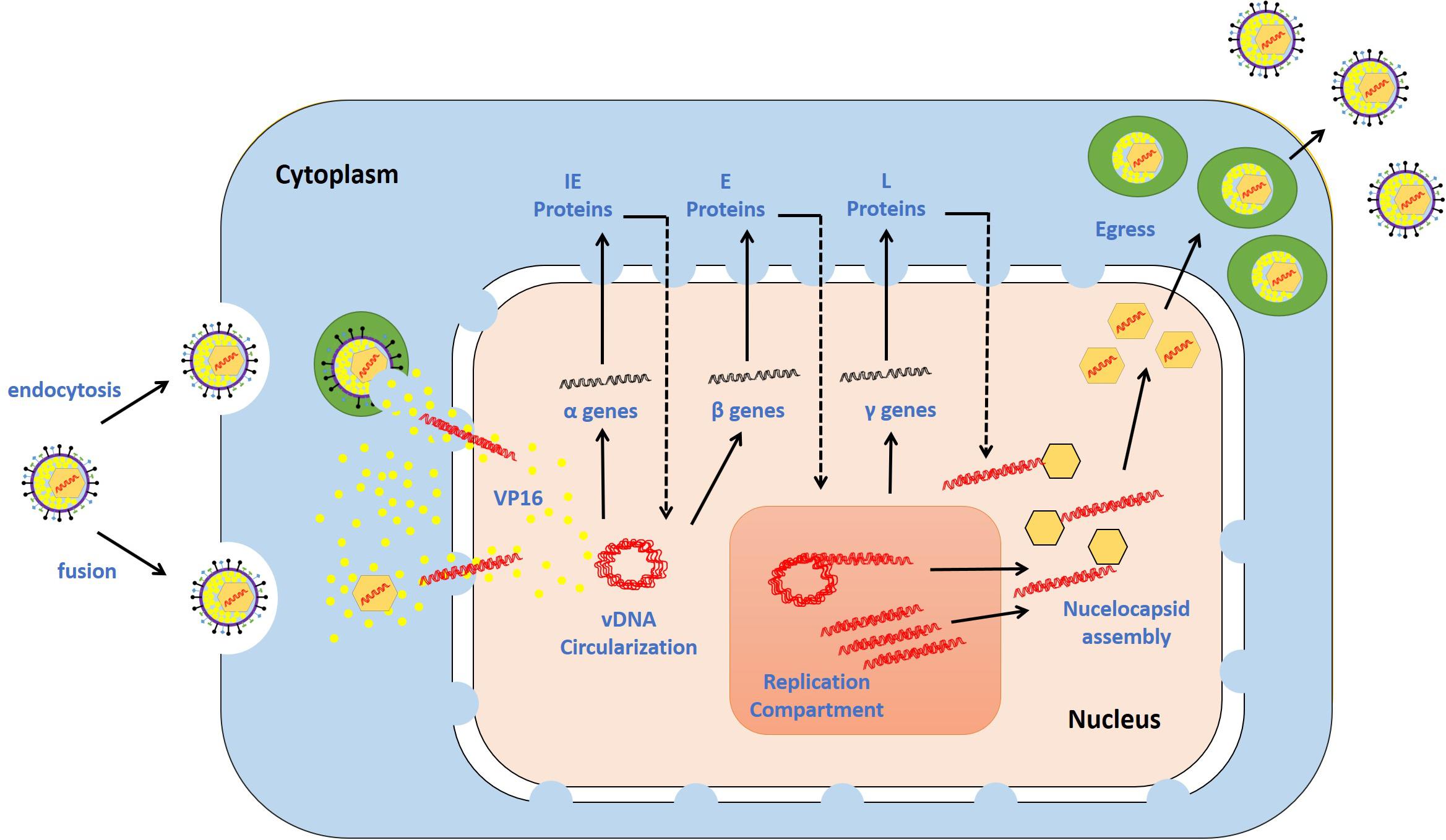
Understanding the Two Types of Herpes Simplex Virus
Type 1: Oral Herpes
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 primarily causes infections around the mouth and face. It is often referred to as oral herpes and is highly contagious. The virus spreads through direct contact with infected saliva, skin, or mucous membranes. Most people contract this type during childhood, and it can remain dormant in the body for years before manifesting symptoms.
Common Features of Oral Herpes
- Cold sores or fever blisters on or around the lips
- Painful blisters that may burst and form scabs
- Tingling or itching sensation before an outbreak
- Mild flu-like symptoms during the initial infection
Type 2: Genital Herpes
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 predominantly causes infections in the genital area. This form of the virus is sexually transmitted and is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide. While it is less prevalent than Type 1, it poses significant health risks if left untreated.
Signs of Genital Herpes
- Painful blisters or ulcers in the genital or anal region
- Burning sensation during urination
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes
- Vaginal discharge in women or discomfort in men
Symptoms of Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
Both types of the virus share some common symptoms, but the location and severity of outbreaks vary depending on the strain. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms or remain asymptomatic, making it challenging to detect the infection without proper testing.
Initial Outbreak
The first episode of a herpes simplex virus infection is typically the most severe. Symptoms may appear within two to twelve days after exposure and include:
- Painful sores or blisters at the site of infection
- Fever and fatigue
- Body aches and headaches
- Swollen lymph nodes near the affected area
Recurrent Episodes
After the initial outbreak, the virus remains in the body and can reactivate periodically. Recurrent episodes are usually less severe and shorter in duration. Triggers for reactivation may include:
- Stress or emotional upheaval
- Weakened immune system
- Hormonal changes, such as during menstruation
- Exposure to sunlight or extreme temperatures
Diagnosing Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
Accurate diagnosis is essential for managing the infection effectively. Several diagnostic methods are available, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider may diagnose herpes based on visible symptoms. The presence of characteristic sores or blisters can provide strong evidence of the infection. However, physical examination alone is not always sufficient for a definitive diagnosis.
Laboratory Tests
For confirmation, laboratory tests are often required. These tests can detect the presence of the virus or antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the infection.
- Viral Culture: A sample from a blister is collected and analyzed to identify the virus.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This test detects viral DNA and is highly sensitive and specific.
- Blood Tests: These tests look for antibodies against the virus and can differentiate between the two types.
Treatment Options for Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
While there is no cure for herpes simplex virus infections, various treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. The goal of treatment is to alleviate discomfort, speed up healing, and minimize the risk of transmission.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral drugs are the cornerstone of herpes treatment. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus, thereby reducing the severity and duration of outbreaks.
- Acyclovir: One of the earliest antiviral drugs used to treat herpes infections. It is available in oral, topical, and intravenous forms.
- Valacyclovir: An improved version of acyclovir with better absorption and longer-lasting effects.
- Famciclovir: Another antiviral medication that is effective in treating both types of herpes infections.
Topical Treatments
In addition to oral medications, topical creams and ointments can be applied directly to the affected area to relieve pain and promote healing. Common topical treatments include:
- Anesthetic creams to numb the area and reduce discomfort
- Antiviral creams that help suppress the virus locally
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage the infection and reduce the likelihood of recurrent outbreaks:
- Maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation
- Avoiding known triggers such as excessive sun exposure
- Practicing safe sex to prevent transmission to partners
Preventing the Spread of Herpes Simplex Virus
Prevention plays a critical role in controlling the spread of herpes simplex virus infections. Although the virus cannot be eradicated, taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Safe Sexual Practices
Using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual activity is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of genital herpes. Additionally, avoiding sexual contact during active outbreaks can further minimize the risk.
Personal Hygiene
Good personal hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding sharing items like towels or razors, can help prevent the transmission of oral herpes. For individuals with active cold sores, refraining from kissing or sharing utensils is advisable.
Vaccination Research
Although there is currently no vaccine available for herpes simplex virus infections, ongoing research aims to develop one. Advances in this area could potentially lead to a significant reduction in the global burden of the disease.
Living with Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
Managing a herpes simplex virus infection requires a proactive approach. By understanding the nature of the virus and adhering to recommended treatments and preventive measures, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the impact of the condition.
Emotional and Psychological Support
A herpes diagnosis can be emotionally challenging for many individuals. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, counselors, or support groups can help address feelings of anxiety, stigma, or isolation.
Regular Monitoring
Individuals with frequent outbreaks should maintain regular follow-ups with their healthcare provider to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed. Early intervention can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.