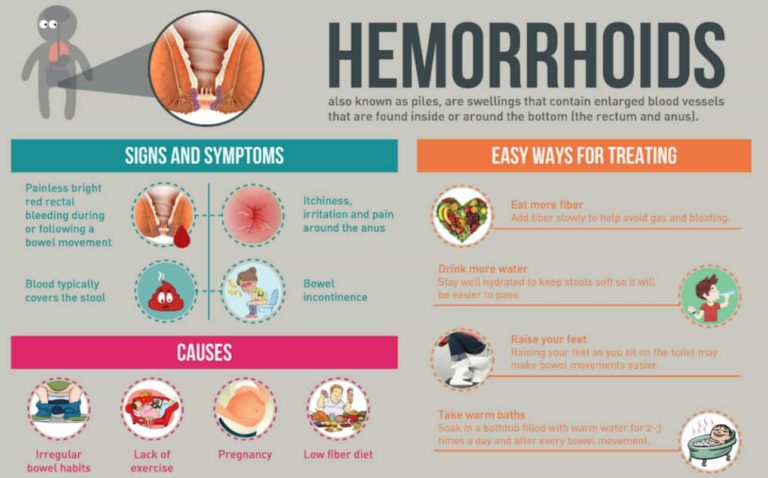
Hemorrhoids, commonly referred to as piles, are a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These swollen veins in the lower part of the rectum or anus can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily life. While they are not usually dangerous, hemorrhoids can lead to pain, itching, and bleeding, making it essential to understand their causes, recognize their symptoms, and explore treatment options.

Understanding Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids occur when the veins around the anus or lower rectum become swollen and inflamed. They can develop either internally, within the rectum, or externally, under the skin around the anus. Both types share similar causes but may present different symptoms and require distinct approaches for management.
Types of Hemorrhoids
- Internal Hemorrhoids: These develop inside the rectum and are often painless. However, they may cause bleeding during bowel movements.
- External Hemorrhoids: These form under the skin around the anus and can cause itching, pain, and swelling.
- Thrombosed Hemorrhoids: These occur when blood clots form within an external hemorrhoid, leading to severe pain and swelling.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Several factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their risk.
Increased Pressure on the Veins
The primary cause of hemorrhoids is increased pressure on the veins in the rectal area. This pressure can result from various factors, including:
- Straining During Bowel Movements: Pushing too hard while passing stools can strain the veins in the rectum and anus.
- Chronic Constipation or Diarrhea: Both conditions can irritate the rectal area and increase the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet, can put unnecessary pressure on the veins.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle habits can also increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids:
- Low-Fiber Diet: A diet lacking in fiber can lead to hard stools, which require more effort to pass and increase the risk of straining.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can add pressure to the veins in the pelvic and rectal areas.
- Pregnancy: The growing uterus can compress the veins in the lower body, increasing the risk of hemorrhoids.
Age-Related Changes
As people age, the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus may weaken, making them more prone to swelling and inflammation. This is why hemorrhoids are more common in older adults.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
The symptoms of hemorrhoids vary depending on their type and severity. Recognizing these symptoms early can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and avoid complications.
Symptoms of Internal Hemorrhoids
- Bleeding during bowel movements, often noticed as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
- Prolapse, where the internal hemorrhoid protrudes outside the anus, especially during straining.
- Mucus discharge after a bowel movement.
Symptoms of External Hemorrhoids
- Itching or irritation around the anal area.
- Pain or discomfort, particularly when sitting or during bowel movements.
- Swelling or lumps near the anus.
Symptoms of Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
- Sudden and severe pain in the anal area.
- A hard, painful lump near the anus.
- Swelling and inflammation around the affected area.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
There are several treatment options available for managing hemorrhoids, ranging from lifestyle changes and home remedies to medical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s preferences.
Lifestyle Changes
For mild cases of hemorrhoids, simple lifestyle modifications can often provide relief and prevent recurrence:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Consuming more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can soften stools and reduce straining.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain soft stools and supports healthy digestion.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: Taking breaks from sitting, especially on hard surfaces, can reduce pressure on the rectal veins.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes healthy bowel movements and reduces the risk of constipation.
Home Remedies
Several home remedies can alleviate the discomfort associated with hemorrhoids:
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the anal area in warm water for 15 to 20 minutes can reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams and ointments containing ingredients like witch hazel or hydrocortisone can soothe itching and irritation.
- Cold Compresses: Applying ice packs to the affected area can reduce swelling and numb the pain.
Medical Procedures
For more severe cases of hemorrhoids, medical interventions may be necessary. These procedures are typically performed by healthcare professionals and aim to remove or shrink the hemorrhoids.
Rubber Band Ligation
This procedure involves placing a small rubber band around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply. Over time, the hemorrhoid shrinks and falls off.
Sclerotherapy
In sclerotherapy, a chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and eventually disappear.
Hemorrhoidectomy
A hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove large or severe hemorrhoids. It is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to other treatments.
Laser or Infrared Coagulation
These minimally invasive techniques use heat or light to shrink hemorrhoids and are often used for smaller, less severe cases.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of hemorrhoids can be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant a visit to a healthcare professional:
- Persistent or heavy bleeding during bowel movements.
- Severe pain that does not improve with home remedies.
- Signs of infection, such as fever or pus drainage.
- Changes in bowel habits or unexplained weight loss, which could indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Preventing Hemorrhoids
Taking proactive steps to prevent hemorrhoids can significantly reduce the risk of developing this uncomfortable condition:
- Maintain a high-fiber diet to ensure regular bowel movements.
- Avoid straining during bowel movements and do not spend excessive time on the toilet.
- Engage in regular physical activity to promote healthy circulation and digestion.
- Monitor and manage your weight to reduce pressure on the pelvic veins.
By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the available treatment options, individuals can effectively manage hemorrhoids and improve their quality of life.