Eczema, also known as Atopic Dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches on the skin, which can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Despite its prevalence, many people remain unaware of what causes eczema, how to manage its symptoms, and the various care options available. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition, its triggers, and ways to care for affected skin.
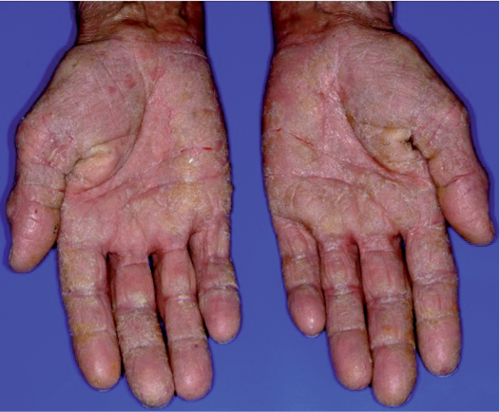
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a non-contagious inflammatory skin condition that often begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood. It is part of a group of conditions that cause the skin to become irritated or inflamed. The exact cause of eczema remains unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema often have a compromised skin barrier, making their skin more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and moisture loss.
The symptoms of eczema can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Dry, scaly skin
- Intense itching
- Red or brownish-gray patches
- Small, raised bumps that may leak fluid when scratched
- Thickened, cracked, or raw skin due to constant scratching
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, each with unique characteristics and triggers. Some of the most common types include:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form of eczema, often associated with allergies and asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: Occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp and face.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Causes small blisters on the hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema: Characterized by coin-shaped spots on the skin.
Common Triggers of Eczema
While the exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, certain triggers can exacerbate the condition or lead to flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in triggering eczema flare-ups. These include:
- Weather Changes: Cold, dry air during winter can worsen eczema symptoms, while hot and humid weather may also irritate the skin.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and mold can trigger allergic reactions that worsen eczema.
- Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, perfumes, and chemicals found in skincare products can irritate sensitive skin.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle habits and choices can also contribute to eczema flare-ups:
- Stress: Emotional stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate eczema symptoms.
- Diet: Some individuals may experience flare-ups after consuming specific foods, such as dairy, eggs, nuts, or gluten.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating can irritate the skin and lead to itching and inflammation.
Genetic Predisposition
People with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition. Genetic mutations that affect the skin’s ability to retain moisture and protect against irritants can increase susceptibility to eczema.
Managing Eczema Symptoms
While there is no cure for eczema, there are several strategies to manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups. A combination of lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and medical treatments can help individuals achieve relief and improve their quality of life.
Skincare Routine
A consistent skincare routine is essential for managing eczema. Here are some tips for maintaining healthy skin:
- Moisturize Regularly: Use fragrance-free moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
- Avoid Hot Showers: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, worsening eczema symptoms. Opt for lukewarm water instead.
- Use Gentle Cleansers: Choose mild, soap-free cleansers that do not contain harsh chemicals or fragrances.
- Pat Skin Dry: After bathing, gently pat the skin dry with a soft towel instead of rubbing it.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of eczema flare-ups:
- Wear Soft Fabrics: Choose clothing made from breathable materials like cotton to avoid irritating the skin.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to reduce stress levels.
- Identify Food Triggers: Keep a food diary to track any potential connections between diet and eczema symptoms.
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Regularly clean your living space to minimize exposure to dust mites and other allergens.
Medical Treatments
In addition to lifestyle changes, medical treatments can provide relief for eczema sufferers. These treatments may include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: Prescription creams or ointments that reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: Oral medications that help alleviate itching, especially at night.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to controlled amounts of ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation.
- Biologic Medications: Advanced treatments that target specific parts of the immune system to reduce eczema symptoms.
Natural Remedies
Some individuals prefer natural remedies to complement traditional treatments. While scientific evidence supporting these remedies varies, they may provide additional relief for some people:
- Oatmeal Baths: Soaking in a bath with colloidal oatmeal can soothe irritated skin.
- Coconut Oil: Applying virgin coconut oil may help moisturize and protect the skin.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, aloe vera gel can calm irritated skin.
When to Seek Medical Help
While many cases of eczema can be managed at home, there are instances when seeking medical help is necessary. Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Severe itching that disrupts sleep or daily activities
- Signs of infection, such as pus-filled blisters, increased redness, or warmth around affected areas
- No improvement despite following a skincare routine and using over-the-counter treatments
- Frequent flare-ups that interfere with your quality of life
Working with a Dermatologist
A dermatologist can provide specialized care for individuals with eczema. They can perform tests to identify potential triggers, recommend personalized treatment plans, and monitor progress over time. Building a strong relationship with a dermatologist can empower individuals to take control of their condition and achieve better outcomes.
Support and Resources
Living with eczema can be challenging, but support is available. Joining support groups, either in person or online, can connect individuals with others who understand their experiences. Additionally, organizations dedicated to eczema research and advocacy offer valuable resources, including educational materials, treatment guides, and updates on the latest advancements in care.





