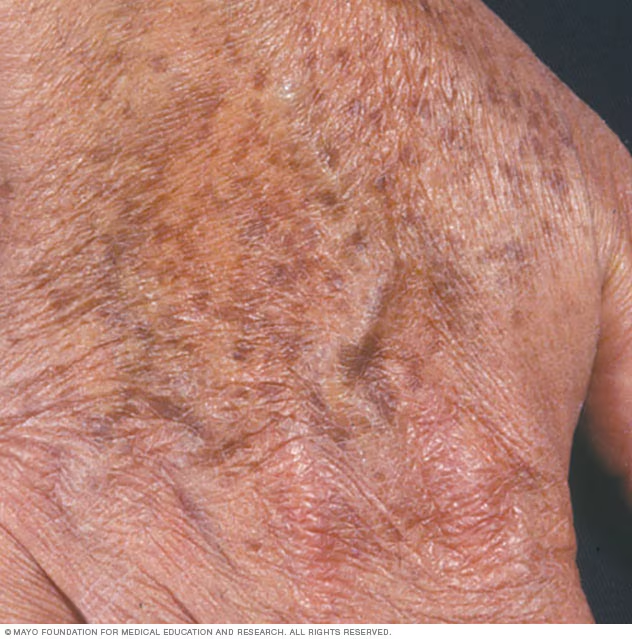
Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are a common skin condition that affects many people as they grow older. These flat, brown, black, or tan spots typically appear on areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. While age spots are harmless, they can be a cosmetic concern for some individuals. In this article, we will explore what causes age spots, how they look, and the various treatments available to manage or reduce their appearance.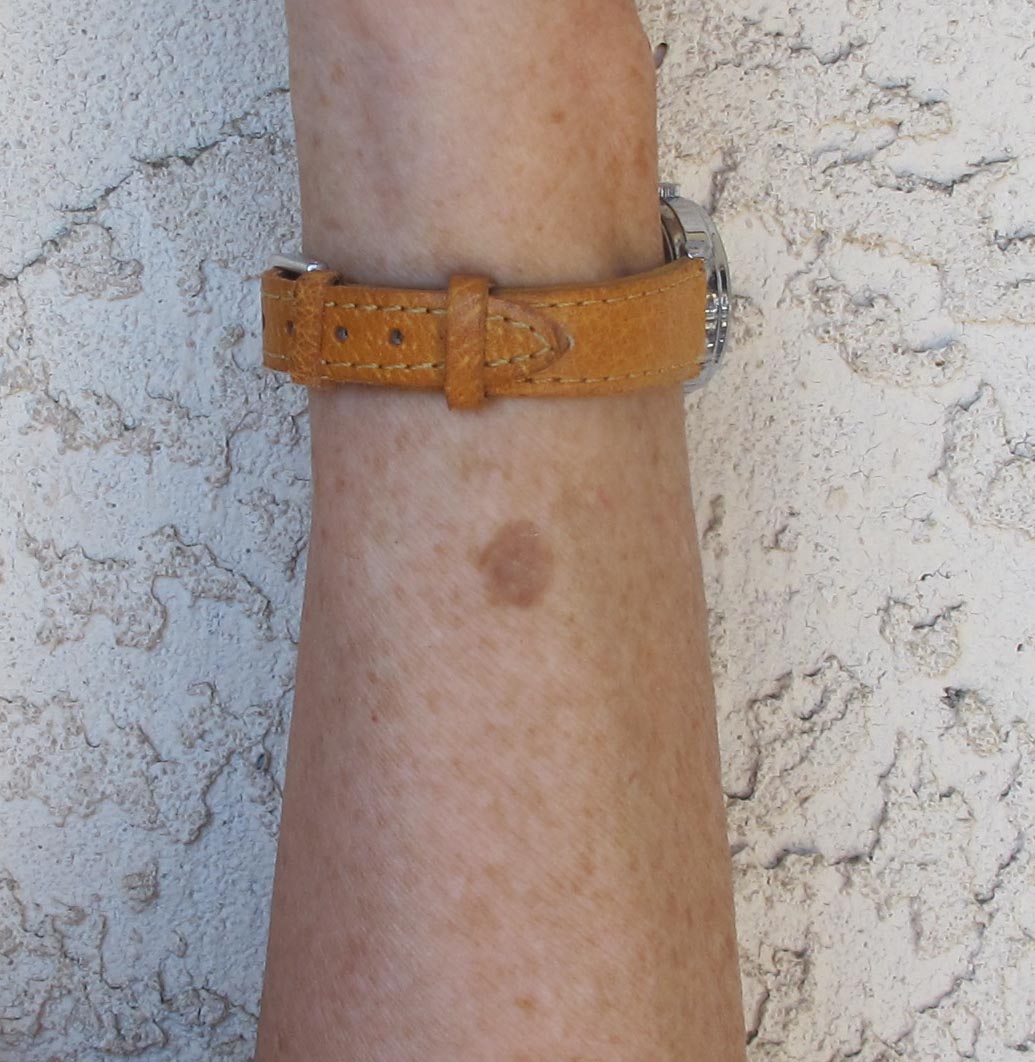
What Are Age Spots?
Age spots are flat, oval-shaped patches that develop on the skin due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun. They are most commonly found in individuals over the age of forty, although younger people who spend significant time in the sun without proper protection may also develop them. Despite their name, these spots are not directly caused by aging but rather by cumulative sun damage over time.
How Do Age Spots Appear?
Age spots have a distinct appearance that sets them apart from other types of skin discoloration. Here are some key characteristics:
- Color: They can range in color from light brown to dark brown or black.
- Shape: Age spots are usually round or oval and have well-defined edges.
- Size: They can vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to more than a centimeter in diameter.
- Location: These spots tend to appear on areas of the body that receive the most sun exposure, such as the face, neck, chest, hands, and arms.
While age spots themselves are not harmful, it is important to monitor any changes in their appearance. If a spot becomes raised, changes color, or starts to bleed, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist to rule out the possibility of skin cancer.
What Causes Age Spots?
The primary cause of age spots is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun. However, there are several factors that contribute to their development:
Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet rays from the sun penetrate the skin and stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for giving skin its color. Over time, repeated sun exposure can lead to an overproduction of melanin, which clumps together and forms age spots. This process is why age spots are most commonly found on areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to sunlight.
Aging Process
As people age, their skin undergoes natural changes that make it more susceptible to damage. The skin’s ability to repair itself diminishes with age, making it harder to recover from sun damage. Additionally, the distribution of melanin becomes less even, leading to the formation of age spots.
Genetic Factors
Some individuals are more prone to developing age spots due to their genetic makeup. If your parents or grandparents had age spots, you may be more likely to develop them as well. Genetic predisposition can influence how your skin responds to sun exposure and how quickly age spots form.
Tanning Beds
The use of tanning beds is another significant contributor to the development of age spots. Tanning beds emit ultraviolet radiation that is similar to, or even stronger than, the sun’s rays. Regular use of tanning beds can accelerate the formation of age spots and increase the risk of other skin conditions, including skin cancer.
How Can Age Spots Be Prevented?
While age spots are primarily caused by sun exposure, there are steps you can take to prevent their formation or minimize their appearance:
Use Sunscreen
One of the most effective ways to prevent age spots is to use sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least thirty and apply it generously to all exposed areas of the skin. Reapply every two hours, especially if you are spending extended periods outdoors or swimming.
Wear Protective Clothing
In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing can help shield your skin from harmful ultraviolet rays. Opt for long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses when spending time outside. Some clothing is specifically designed to provide UV protection, offering an extra layer of defense against sun damage.
Avoid Peak Sun Hours
The sun’s rays are strongest between ten in the morning and four in the afternoon. During these peak hours, try to stay indoors or seek shade whenever possible. If you must be outside, take extra precautions to protect your skin.
Regular Skin Examinations
Performing regular self-examinations of your skin can help you identify any new or changing spots early. Pay attention to the size, shape, and color of any marks on your skin and report any concerns to a dermatologist. Early detection is key to addressing potential issues before they become serious.
Treatment Options for Age Spots
If you already have age spots and wish to reduce their appearance, there are several treatment options available. It is important to note that while these treatments can improve the look of age spots, they do not completely eliminate them. Consulting with a dermatologist can help you determine the best course of action based on your skin type and the severity of the spots.
Topical Creams
Over-the-counter and prescription creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, or glycolic acid can help lighten age spots over time. These creams work by exfoliating the top layer of the skin and promoting the growth of new, evenly pigmented skin cells. Consistent use is required to see results, and it may take several weeks or months for noticeable improvement.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a popular option for treating age spots. During the procedure, a dermatologist uses a laser to target and break down the excess melanin in the skin. Over time, the treated spots fade and blend with the surrounding skin. Multiple sessions may be needed for optimal results, and there may be some downtime as the skin heals.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the age spots with liquid nitrogen to destroy the excess pigment. After the treatment, the treated area may blister and peel, revealing new, lighter skin underneath. Cryotherapy is most effective for small, isolated spots and may not be suitable for larger areas of discoloration.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the outermost layers. This process encourages the growth of new skin cells and can help fade age spots. Depending on the strength of the peel, recovery time may vary, and multiple treatments may be necessary to achieve desired results.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that uses fine crystals or a diamond-tipped wand to gently exfoliate the surface of the skin. This treatment can help improve the appearance of age spots by removing dead skin cells and stimulating collagen production. Microdermabrasion is generally considered safe and requires little to no downtime.
When to See a Dermatologist
While age spots are typically harmless, it is important to monitor them for any changes. If you notice any of the following signs, schedule an appointment with a dermatologist:
- A sudden increase in the number or size of spots
- Spots that change color or texture
- Bleeding or itching in the affected area
- Uneven borders or irregular shapes
A dermatologist can perform a thorough examination and, if necessary, conduct a biopsy to rule out skin cancer or other underlying conditions.
Conclusion
Age spots are a common and generally harmless skin condition that can be managed with proper care and treatment. By understanding their causes and taking preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing them. For those who already have age spots, a variety of treatment options are available to help improve their appearance. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific needs.