Painful intercourse, medically known as Dyspareunia, is a condition that affects many individuals across the globe. It refers to persistent or recurrent pain in the genital area before, during, or after sexual activity. This issue can lead to emotional distress, strained relationships, and a reduced quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for this condition is essential for those who experience it and for their partners. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of painful intercourse to provide clarity and guidance.

What Is Painful Intercourse?
Painful intercourse is characterized by discomfort or pain in the genital region during or after sexual activity. The pain may be sharp, burning, or throbbing and can occur in different areas, including the vagina, clitoris, or deeper within the pelvis. While it is more commonly reported by women, men can also experience painful intercourse due to certain conditions. The severity of the pain can vary, ranging from mild discomfort to intense pain that interferes with sexual intimacy.
Types of Painful Intercourse
- Superficial Pain: This type of pain occurs at the entrance of the vagina and is often felt during penetration.
- Deep Pain: This pain is felt deeper within the pelvis and may occur during thrusting or specific positions.
Causes of Painful Intercourse
The causes of painful intercourse are diverse and can stem from physical, psychological, or relational factors. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective treatment. Below are some common causes categorized by type.
Physical Causes
Several physical conditions can contribute to painful intercourse. These include:
- Vaginal Dryness: A lack of natural lubrication can lead to friction and discomfort during sexual activity. This is often caused by hormonal changes, such as those experienced during menopause or breastfeeding.
- Infections: Yeast infections, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted infections can irritate the genital area and cause pain.
- Vaginismus: This condition involves involuntary spasms of the pelvic floor muscles, making penetration difficult or painful.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing pelvic pain that can worsen during intercourse.
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries can cause pressure and pain during sex.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: An infection of the reproductive organs that can lead to chronic pelvic pain.
- Surgical Scarring: Previous surgeries, such as a hysterectomy or episiotomy, can result in scar tissue that causes discomfort.
Psychological Causes
Emotional and mental health factors can also play a significant role in painful intercourse. These include:
- Anxiety and Stress: High levels of stress or anxiety can lead to muscle tension, reducing the ability to relax during sexual activity.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness or hopelessness can decrease libido and make sexual experiences less enjoyable.
- History of Trauma: Past experiences of sexual abuse or trauma can create fear and aversion to sexual intimacy.
- Relationship Issues: Poor communication or unresolved conflicts with a partner can lead to emotional barriers that affect sexual experiences.
Hormonal Causes
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact sexual comfort. For example:
- Menopause: The decline in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to vaginal dryness and thinning of the vaginal walls.
- Postpartum Changes: Hormonal fluctuations after childbirth can affect sexual function and comfort.
- Contraceptive Use: Some birth control methods, such as hormonal contraceptives, can alter hormone levels and contribute to discomfort.
Symptoms of Painful Intercourse
The symptoms of painful intercourse can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- A sharp or burning sensation during penetration
- Throbbing or aching pain deep within the pelvis
- Tightness or spasms in the pelvic muscles
- Bleeding or spotting after sexual activity
- Feeling of soreness or tenderness in the genital area
It is important to note that these symptoms can overlap with other medical conditions. Therefore, seeking professional evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Treatments for Painful Intercourse
Treatment for painful intercourse depends on the underlying cause and may involve a combination of medical, psychological, and lifestyle interventions. Below are some common approaches to managing this condition.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments aim to address the physical causes of painful intercourse. These may include:
- Lubricants: Water-based or silicone-based lubricants can reduce friction and alleviate discomfort caused by vaginal dryness.
- Hormone Therapy: Estrogen creams, tablets, or rings can help restore vaginal moisture and elasticity, especially for individuals experiencing menopausal symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is the cause, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the underlying condition.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen, can help manage mild to moderate pain.
- Surgery: In cases where structural abnormalities, such as endometriosis or ovarian cysts, are causing pain, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Physical Therapy
Pelvic floor physical therapy is a specialized form of treatment that focuses on strengthening and relaxing the muscles of the pelvic floor. Techniques used in this therapy include:
- Manual therapy to release tension in the pelvic muscles
- Exercises to improve muscle control and flexibility
- Biofeedback to help individuals become more aware of their pelvic muscle activity
Psychological Support
Addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of painful intercourse is crucial for long-term relief. Therapeutic approaches may include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: This form of therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to sexual activity.
- Couples Counseling: Working with a therapist can improve communication and intimacy between partners, reducing emotional barriers to sexual activity.
- Trauma-Informed Therapy: For individuals with a history of sexual trauma, specialized therapy can help process past experiences and reduce fear or aversion to intimacy.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can also help alleviate symptoms of painful intercourse. These include:
- Engaging in regular exercise to improve blood flow and reduce stress
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to ease muscle tension
- Using comfortable and supportive positions during sexual activity
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco, which can negatively impact sexual health
When to Seek Medical Help
If painful intercourse persists despite trying self-care measures, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life. Additionally, seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or worsening pain
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
- Fever or other signs of infection
- Pain that interferes with daily activities or relationships
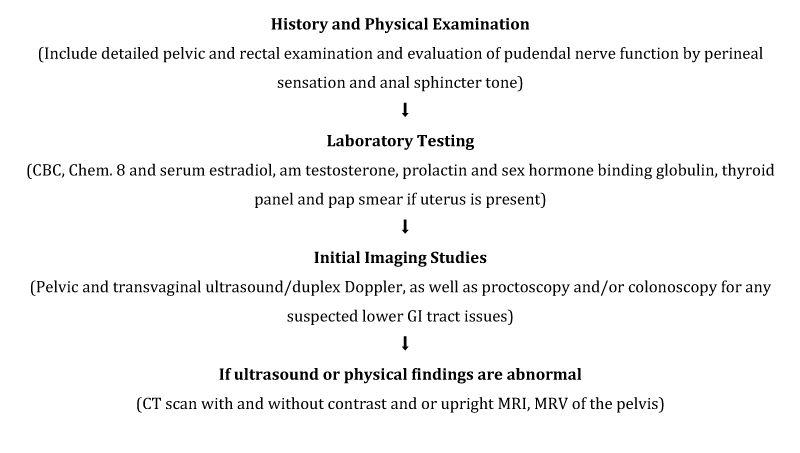
A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, which may include a physical examination, laboratory tests, or imaging studies, to determine the underlying cause of the pain.
Conclusion
Painful intercourse is a complex issue that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the potential causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving their sexual health and overall well-being.