Dermatomyositis, often abbreviated as DM, is a rare inflammatory disease that affects the muscles and skin. It belongs to a group of conditions known as idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. This condition can cause significant physical discomfort and may lead to complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for Dermatomyositis in detail.
Understanding Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, particularly the muscles and skin. This leads to inflammation, weakness, and characteristic skin rashes. While the exact cause of this condition remains unknown, researchers believe it may involve genetic factors, environmental triggers, or viral infections.
The disease can occur at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in adults between 40 and 60 years old and in children between 5 and 15 years old. Women are more frequently affected than men. Understanding the nature of this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Symptoms of Dermatomyositis
The symptoms of Dermatomyositis can vary from person to person, but they generally include both muscular and skin-related manifestations. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking timely medical intervention.
Muscular Symptoms
- Muscle Weakness: One of the hallmark symptoms of Dermatomyositis is progressive muscle weakness. This typically affects the muscles closest to the trunk of the body, such as those in the hips, thighs, shoulders, and upper arms. Patients may find it difficult to climb stairs, lift objects, or even get up from a seated position.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue is another common symptom. Patients often report feeling unusually tired, even after minimal physical activity.
- Muscle Pain: Some individuals experience muscle pain or tenderness, which can further limit their mobility and daily activities.
Skin-Related Symptoms
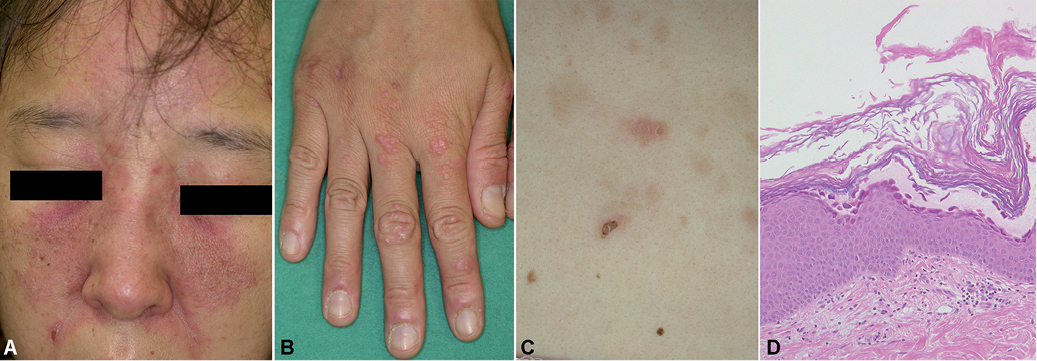
- Purple or Red Rashes: A distinctive feature of Dermatomyositis is the appearance of reddish or purplish rashes on the skin. These rashes often develop on the face, eyelids, knuckles, elbows, knees, and toes. The rash around the eyes, known as a heliotrope rash, is particularly characteristic of this condition.
- Gottron’s Papules: Raised, scaly patches may appear over the knuckles, elbows, or knees. These are referred to as Gottron’s papules and are a key diagnostic indicator.
- Photosensitivity: Many patients with Dermatomyositis experience increased sensitivity to sunlight, which can worsen their skin symptoms.
Other Symptoms
- Difficulty Swallowing: In some cases, the muscles involved in swallowing may become weak, leading to difficulty in eating and drinking.
- Lung Involvement: Certain individuals may develop lung complications, such as shortness of breath or coughing, due to inflammation in the lung tissue.
- Joint Pain: Joint pain and stiffness can also occur, adding to the overall discomfort experienced by the patient.
Diagnosing Dermatomyositis
Diagnosing Dermatomyositis can be challenging because its symptoms overlap with those of other conditions. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to confirm the diagnosis.
Clinical Examination
A doctor will begin by conducting a detailed physical examination. They will assess the patient’s muscle strength, look for characteristic rashes, and inquire about any associated symptoms like fatigue or difficulty swallowing.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are often used to detect elevated levels of certain enzymes, such as creatine kinase, which indicate muscle damage. Additionally, specific autoantibodies may be present in the blood, providing further evidence of an autoimmune process.
Electromyography
This test involves inserting small needles into the muscles to measure their electrical activity. Abnormal results can suggest muscle inflammation or damage consistent with Dermatomyositis.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, can help visualize areas of muscle inflammation. This non-invasive imaging technique provides detailed images of soft tissues and can assist in identifying affected regions.
Muscle Biopsy
In some cases, a small sample of muscle tissue may be removed and examined under a microscope. A biopsy can reveal signs of inflammation, muscle fiber damage, and other changes typical of Dermatomyositis.
Treatment Options for Dermatomyositis
While there is no cure for Dermatomyositis, several treatment strategies can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent complications. The treatment plan is usually tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and severity of the disease.
Medications
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs, such as prednisone, are often the first line of treatment. They work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation in the muscles and skin.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: If corticosteroids alone are insufficient, additional medications like methotrexate or azathioprine may be prescribed to further suppress the immune response.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin: For severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy may be recommended. This involves infusing antibodies derived from donated blood to modulate the immune system.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle strength and flexibility. A trained therapist can design a personalized exercise program to help patients regain mobility and reduce muscle stiffness.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on helping patients adapt to their daily activities despite physical limitations. Therapists may recommend assistive devices or modifications to make tasks easier and less taxing on the muscles.
Skin Care
Managing skin symptoms is an important aspect of treatment. Patients are advised to use sunscreen to protect against photosensitivity and moisturizers to soothe irritated skin. In some cases, topical corticosteroids or other dermatological treatments may be prescribed.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall health and aid in muscle recovery.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as excessive sun exposure or stress, can help minimize flare-ups.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment as needed.
Complications Associated with Dermatomyositis
If left untreated or poorly managed, Dermatomyositis can lead to several complications. These may include:
- Calcinosis: The formation of calcium deposits under the skin, which can cause pain and restrict movement.
- Respiratory Issues: Chronic inflammation may affect the lungs, leading to conditions like interstitial lung disease.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Some studies suggest a higher risk of developing certain cancers, such as ovarian or lung cancer, in individuals with Dermatomyositis.
Living with Dermatomyositis
Living with Dermatomyositis requires a proactive approach to managing symptoms and maintaining overall well-being. Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice for coping with the challenges of this chronic condition.
Education is also key. Understanding the disease, its triggers, and available treatment options empowers patients to take an active role in their care. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with Dermatomyositis can achieve better outcomes and enjoy a fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by the condition.