Dermatitis Herpetiformis, often abbreviated as DH, is a chronic skin condition that affects individuals who are sensitive to gluten. This condition is closely linked to celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by the consumption of gluten-containing foods. Dermatitis Herpetiformis is characterized by intensely itchy rashes and blistering on the skin, which can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a unique manifestation of gluten sensitivity that primarily affects the skin. Unlike other forms of dermatitis, this condition is directly tied to the immune system’s reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. People with this condition often experience skin symptoms rather than the gastrointestinal issues commonly associated with celiac disease. Despite its name, Dermatitis Herpetiformis is not related to herpes or caused by a viral infection. Instead, it is an autoimmune response that leads to inflammation and skin damage.
Symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
The symptoms of this condition can vary from person to person, but they typically include:
- Intense Itching: The most common symptom is a severe itching sensation, which often precedes the appearance of visible rashes or blisters.
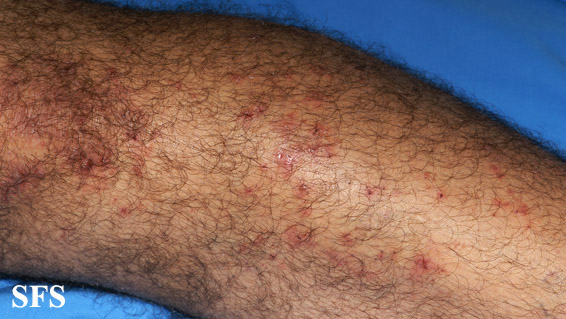
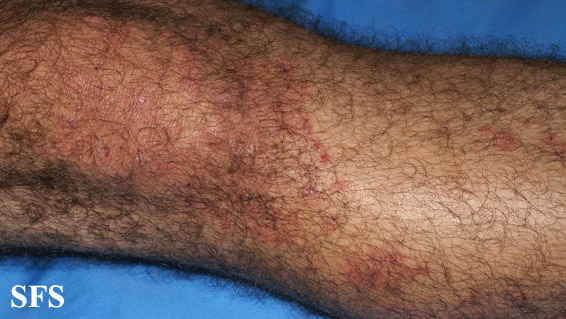
- Rashes and Blisters: Small, red bumps or blisters appear on the skin, often symmetrically distributed. These lesions are filled with fluid and can rupture, leading to crusting.
- Location of Rashes: The rashes tend to occur on specific areas of the body, such as the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and buttocks. However, they can also appear on other parts of the body.
- Burning Sensation: Some individuals report a burning feeling in the affected areas before the onset of visible symptoms.
- Chronic Nature: Without treatment, the condition tends to persist and recur over time, making it a long-term concern for those affected.
It is important to note that these symptoms can mimic other skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, which is why accurate diagnosis is essential.
Causes of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
The exact cause of this skin condition lies in the immune system’s abnormal response to gluten. When individuals with gluten sensitivity consume foods containing gluten, their immune system reacts by producing antibodies known as immunoglobulin A (IgA). These antibodies travel through the bloodstream and accumulate in the skin, triggering an inflammatory response that results in the characteristic rash and blisters.
Several factors contribute to the development of this condition:
- Genetic Predisposition: People with certain genetic markers, such as HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, are more likely to develop both celiac disease and Dermatitis Herpetiformis.
- Gluten Consumption: The ingestion of gluten-containing foods is the primary trigger for the immune response that leads to skin symptoms.
- Autoimmune Connection: This condition is considered an autoimmune disorder because the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, specifically targeting the skin in this case.
- Environmental Factors: While genetics play a significant role, environmental triggers, such as stress or infections, may exacerbate the condition in susceptible individuals.
Understanding these underlying causes is key to managing the condition effectively and preventing flare-ups.
Diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Diagnosing this condition requires a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes skin biopsies. Since the symptoms can resemble other skin disorders, healthcare providers must conduct thorough assessments to confirm the diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation
A healthcare provider will begin by examining the patient’s skin and reviewing their medical history. They will look for characteristic signs, such as symmetrical rashes and blisters, and inquire about any dietary habits or family history of gluten-related disorders.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests are often used to detect specific antibodies associated with gluten sensitivity. Elevated levels of immunoglobulin A antibodies, particularly those targeting tissue transglutaminase, are strong indicators of this condition. Additionally, testing for celiac disease may be recommended, as the two conditions frequently coexist.
Skin Biopsy
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. During this procedure, a small sample of skin is taken from an affected area and examined under a microscope. The presence of IgA deposits in the skin is a hallmark feature of Dermatitis Herpetiformis and helps differentiate it from other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Dermatitis Herpetiformis
While there is no cure for this condition, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The primary focus of treatment is eliminating gluten from the diet and using medications to control skin symptoms.
Gluten-Free Diet
The cornerstone of managing this condition is adopting a strict gluten-free diet. By avoiding foods that contain wheat, barley, and rye, individuals can reduce the immune system’s reaction and prevent flare-ups. A gluten-free diet not only alleviates skin symptoms but also addresses any underlying gastrointestinal issues associated with celiac disease.
Key considerations for a gluten-free diet include:
- Reading Labels: Many processed foods contain hidden sources of gluten, so it is essential to carefully read ingredient labels.
- Safe Alternatives: Foods such as rice, corn, quinoa, and potatoes are naturally gluten-free and can serve as substitutes for gluten-containing grains.
- Dining Out: When eating at restaurants, individuals should communicate their dietary restrictions to ensure meals are prepared safely.
It is worth noting that it may take several weeks or months for the skin to show improvement after starting a gluten-free diet, as the immune system needs time to adjust.
Medications
In addition to dietary changes, medications are often prescribed to provide relief from skin symptoms. The most commonly used medication is dapsone, an oral drug that effectively reduces itching and inflammation. Dapsone works by suppressing the immune response in the skin, providing rapid relief for many patients.
However, dapsone is not without side effects, and its use requires careful monitoring by a healthcare provider. Regular blood tests are necessary to check for potential complications, such as anemia or liver toxicity. In some cases, alternative medications, such as sulfapyridine or other antibiotics, may be prescribed if dapsone is not well-tolerated.
Topical Treatments
While systemic medications like dapsone address the root cause of the condition, topical treatments can help soothe irritated skin and promote healing. Over-the-counter corticosteroid creams or ointments may be applied to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. However, these treatments are generally less effective than systemic therapies and are best used as complementary measures.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to dietary changes and medications, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being:
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate skin conditions, so practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing may be beneficial.
- Skin Care Routine: Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products can minimize irritation and prevent further damage to the skin.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as certain fabrics or harsh detergents, can help reduce flare-ups.
Living with Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Managing this condition requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatment, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes. While living with this condition can be challenging, many individuals find that adherence to a gluten-free diet and proper medical care significantly improves their symptoms and overall quality of life.
Support groups and online communities can also provide valuable resources and emotional support for individuals navigating the challenges of this condition. Sharing experiences and tips with others who understand the daily struggles can foster a sense of community and empowerment.